Solanum nigrum
Solanum nigrum
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Solanum nigrum
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCC8957
Episyringaresinol 4'-O-β-D-glncopyranoside137038-13-2
Instructions

-
BCN2302
Solasonine19121-58-5
Instructions
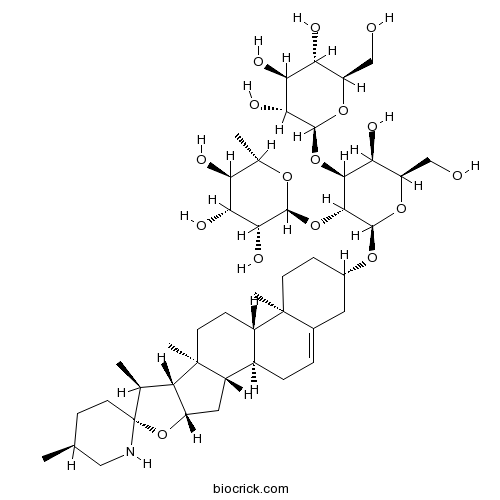
-
BCC8311
D-(+)-Mannose3458-28-4
Instructions

-
BCN1010
D-(+)-Xylose58-86-6
Instructions

-
BCN8528
D-Galactose59-23-4
Instructions

-
BCN1376
Pinoresinol 4-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside69251-96-3
Instructions

-
BCN4546
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid99-96-7
Instructions

Emerging themes of regulation of oncogenic proteins by Solanum nigrum and its bioactive molecules in different cancers.[Pubmed: 30076759]
Research over the decades has sequentially and systematically provided a near-complete resolution of multifaceted and therapeutically challenging nature of cancer. Drug discovery from plants has enjoyed a renaissance in the past few years. Natural products have provided many of the lead structures, which are currently being used as templates for the design and synthesis of novel compounds with biologically enhanced properties. With the maturity and diversification of technologies, there is a growing need to design high-throughput functional assays for the evaluation of the myriad of compounds being catalogued. This review sheds light on the tumor suppressive properties of Solanum nigrum and its bioactive ingredients. Several worthy of mention include uttroside B, solanine, solamargine, and physalins, which have been tested for efficacy in cancer cell lines and xenografted mice. We have summarized the most recent findings related to S. nigrum-mediated regulation of intracellular protein network in different cancers. α-Solanine, an active component of S. nigrum, is involved in the regulation of microRNA-21 (miRNA-21) (oncogenic) and miRNA-138 (tumor suppressor) in prostate cancer. However, this is the only available evidence that gives us a clue related to the tumor suppressive effects exerted by components of S. nigrum at a posttranscriptional level. More interestingly, S. nigrum and its components exerted inhibitory effects on different pathways including PI3K/AKT, JAK-STAT, VEGF/VEGFR, and matrix metalloproteinases in different cancers. We also provide an overview of new tools, methodologies, and approaches, which will allow researchers to extract as much information as possible out of the tremendous data sets currently being generated. The use of computational tools will be helpful in processing structurally complex natural products and also in prediction of their macromolecular targets.
Differential effects of acetophenone on shoots' and roots' metabolism of Solanum nigrum L. plants and implications in its phytoremediation.[Pubmed: 30064095]
The wide ranges of uses for acetophenone make it more available and expected to accumulate in the biosphere, where consequently it can threat ecosystems. To remediate this problem, the use of Solanum nigrum L. plants for the clean-up of acetophenone-contaminated sites was explored. Also, plant root and shoot biometry and metabolism where assayed to better understand the effects of this organic compound and to pinpoint possible metabolic pathways to be targeted for future manipulations for increasing this plant species' remediation efficiency. Although undergoing through some stress, detected by increases in ROS and lipid peroxidation in both organs, plants were able to rapidly eliminate all acetophenone from the nutrient solution after 7 days of exposure, being this compound mainly detoxified at the root level. Additionally, acetophenone lead to a differential metabolic response in roots and shoots, where antioxidant mechanisms where differentially activated, while nitrogen assimilation was repressed in shoots and activated in roots. These results confirm that S. nigrum is a good phytoremediation tool for acetophenone and suggest that enhancing shoot GS activity may provide more nitrogen precursors for the synthesis of thiolated proteins and glutathione to increase tolerance to acetophenone in roots and shoots, respectively.
Insecticidal properties of Solanum nigrum and Armoracia rusticana extracts on reproduction and development of Drosophila melanogaster.[Pubmed: 30015192]
Plant-derived substances, because of high biological activity, arouse interest of many scientists. Thus, plant extracts and pure substances are intensively studied on various insects as potential insecticides. In such studies, D. melanogaster is one of the most important model organisms. In our studies, we analysed the contents of two plant extracts and tested the activity of their main components against fruit flies and compared observed effects to effects caused by crude extracts. Then, we assessed the development of the next, unexposed generation. The chemical analysis of extracts revealed the presence of numerous glycoalkaloids and glucosinolates in Solanum nigrum and Armoracia rusticana extracts. These extracts, as well as their main components, revealed lethal and sublethal effects, such as the altered developmental time of various life stages and malformations of imagoes. Interestingly, the results for the extracts and pure main compounds often varied. Some of the results were also observed in the unexposed generation. These results confirm that the tested plants produce a range of substances with potential insecticidal effects. The different effects of extracts and pure main components suggest the presence of minor compounds, which should be tested as insecticides.


