Thymus quinquecostatus
Thymus quinquecostatus
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Thymus quinquecostatus
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN2633
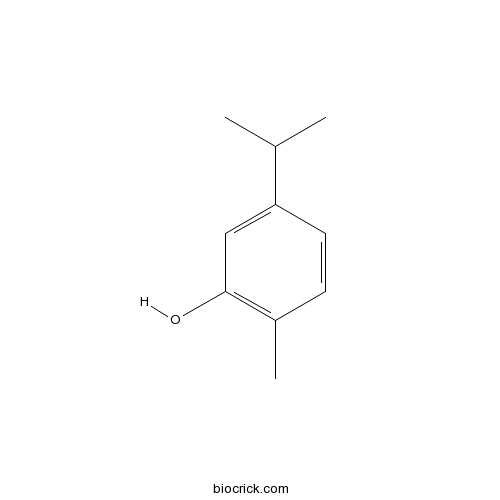
5-Isopropyl-2-methylphenol499-75-2
Instructions
-
BCN5380
Scutellarein529-53-3
Instructions

-
BCN3794
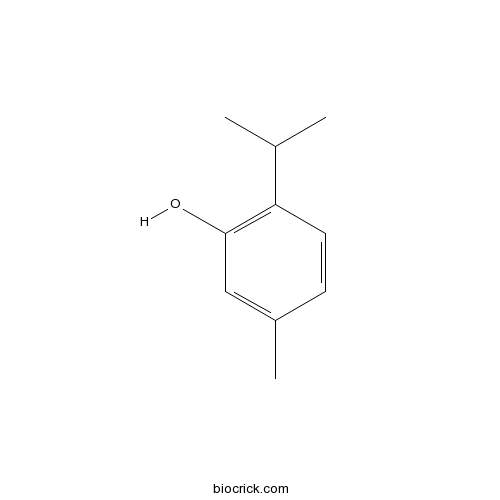
Thymol89-83-8
Instructions
Histochemical investigation and kinds of alkaloids in leaves of different developmental stages in Thymus quinquecostatus.[Pubmed: 25101324]
Thymus quinquecostatus, with more medical value, is a kind of wild plants. In order to exploit and utilize this plant, we studied the species and locations of alkaloids in its leaves. In this paper, histochemical study of leaves at different developing stages was taken to localize the alkaloids. Meanwhile, the kinds and content of alkaloids in leaves were identified using GC-MS technique. It was found that there were two kinds of glandular trichomes, namely, peltate trichomes and capitate trichomes, on the surface of leaves, and their secretory cells could secrete alkaloids. Results showed that trichomes could secrete alkaloids as soon as the first pair of leaves formed, and there were altogether 18 kinds of alkaloids identified by GC-MS. Nearly all of these alkaloids of leaves at different developing stages were distinct from each other, except one, 3-methoxy-a-methyl-benzeneethanamine, persists at different developing stages with high concentration.
Glandular trichomes and essential oil of Thymus quinquecostatus.[Pubmed: 24250266]
The distribution and types of glandular trichomes and essential oil chemistry of Thymus quinquecostatus were studied. The glandular trichomes are distributed on the surface of stem, leaf, rachis, calyx and corolla, except petiole, pistil and stamen. Three morphologically distinct types of glandular trichomes are described. Peltate trichomes, consisting of a basal cell, a stalk cell and a 12-celled head, are distributed on the stem, leaf, corolla and outer side of calyx. Capitate trichomes, consisting of a unicellular base, a 1-2-celled stalk and a unicellular head, are distributed more diffusely than peltate ones, existing on stem, leaf, rachis and calyx. Digitiform trichomes are just distributed on the outer side of corolla, consisting of 1 basal cell, 3 stalk cells and 1 head cell. All three types of glandular trichomes can secrete essential oil, and in small capitate trichomes of rachis, all peltate trichomes and digitiform trichomes, essential oil is stored in a large subcuticular space, released by cuticle rupture, whereas, in other capitate trichomes, essential oil crosses the thin cuticle. The essential oil of T. quinquecostatus is yellow, and its content is highest in the growth period. 68 constituents were identified in the essential oils. The main constituent is linalool.
Thymol from Thymus quinquecostatus Celak. protects against tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced oxidative stress in Chang cells.[Pubmed: 23771524]
The present work describes the protective effects of thymol isolated from Thymus quinquecostatus Celak. against tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP)-induced oxidative damage through various experiments with Chang liver cells. Thymol significantly protected hepatocytes against t-BHP-induced cell cytotoxicity as demonstrated by increased viability. Furthermore, observation of Hoechst staining, annexin V/PI staining, and expression of Bcl-2 and Bax indicated that thymol inhibited t-BHP-induced Chang cell damage. Further, thymol inhibited the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential in t-BHP-treated Chang cells and prevented oxidative stress-triggered reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lipid peroxidation (malondialdehyde, MDA). Thymol restored the antioxidant capability of hepatocytes including glutathione (GSH) levels which were reduced by t-BHP. These results indicated that thymol prevents oxidative stress-induced damage to liver cells through suppression of ROS and MDA levels and increase of GSH level.
In vitro protective effects of Thymus quinquecostatus Celak extracts on t-BHP-induced cell damage through antioxidant activity.[Pubmed: 22921350]
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the antioxidative activities of water and 70% ethanolic extracts from the Thymus quinquecostatus Celak (TQC) for natural antioxidant source. The antioxidant activities were compared with other natural and synthetic antioxidants. The levels of total polyphenols and flavonoids were also determined. The extracts were found to have different levels of antioxidant properties in a few kind of assay. The results showed that higher radical scavenging activity, reducing power and antioxidant capacity in FRAP than those of BHT as a positive control. In addition, the extracts from the TQC leaf and stem showed stronger antioxidant activity than that of vitamin C, α-tocopherol in ferric thiocyanate (FTC) and thiobarbituric acid (TBA) methods. Cytoprotective and anti-apoptotic effect of water extracts from TQC was also prevented t-BHP-induced toxicity in Chang liver cells. Therefore, these results indicate that TQC extracts have antioxidant properties through its ability to enhance the cell viability, reduction of production of ROS, inhibition of oxidative damage, mitochondria dysfunction and ultimately inhibition of cell apoptosis. Based on the results described above, it is suggested that TQC has the potential to protect liver on t-BHP-induced cell damage and should be considered as a prospective functional food.
Changes in structure and histochemistry of glandular trichomes of Thymus quinquecostatus Celak.[Pubmed: 22545009]
The types, morphology, distribution, structure, and development process of the glandular trichomes on the leaves of Thymus quinquecostatus Celak had been investigated in this study. Two different types of glandular trichomes were determined in detail, namely, capitate trichomes and peltate ones. Besides, there were distinct differences on morphology, distribution, structure, and development process between the two kinds of trichomes. As the peltate trichome stepping into senium stage, it caved in the epidermis integrally, which was different from the capitate one. The secretion of the capitate trichome contained essential oil, polyphenols, and flavonoids, while, in addition to these three components, the secretion of the peltate one also contained acid polysaccharides. A distinctive difference was also seen in the secretory pathway of the secretion between the two types of trichomes. The secretion of capitate one was extruded through the cuticle of the head cell, but the secretion of the peltate one kept accumulating in the subcuticular space of the head cells until it was released by cuticle rupture.
[Patch diversity and spatial structure of wild Thymus quinquecostatus].[Pubmed: 19449560]
With the combination of ISSR (inter-simple sequence repeats), SRAP (sequence-related amplified polymorphism) and spatial autocorrelation, the genetic diversity and spatial structure per unit patch of three Huaiyuan populations of Thymus quinquecostatus in southeast China were analyzed. The results showed that there existed higher levels of genetic and clonal diversity among the patches within the wild T. quinquecostatus populations, with the percentage of polymorphic loc being 75.75%, Nei's gene diversity being 0.2537, Shannon's information index being 0.3811, percent of genetype (G/N) being 0.61, Simpson index (D) being 0.96, and Fager index (E) being 0.91. Analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) showed that only 9.65% of genetic variation resided among the populations, while 90.35% of it resided among the individuals within the populations. No genotype patches in common were observed among the three populations. The spatial distribution of the same patches showed a concentrated distribution about 0-25 m, and that of different patches showed an inlaid distribution. Except for some locations that showed par correlations in the Huaiyuan populations of T. quinquecostatus, most locations lacked in spatial structure according to spatial autocorrelation analysis. The possible mechanism causing the establishment of the patches of T. quinquecostatus populations was due to seed dispersing, and the following clonal reproduction played important roles in patch development and population expanding.
[Anti-tumor effect of ethanol extracts from Thymus quinquecostatus Celak on human leukemia cell line].[Pubmed: 16159574]
To screen the anti-tumor fraction of ethanol extracts from Thymus quinquecostatus Celak and investigate its anti-tumor effect on human leukemia cell line.


