Trillium tschonoskii
Trillium tschonoskii
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Trillium tschonoskii
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN1250
Diosgenin glucoside14144-06-0
Instructions

-
BCN5549
Astragalin480-10-4
Instructions

-
BCN1053
Polyphyllin VI55916-51-3
Instructions
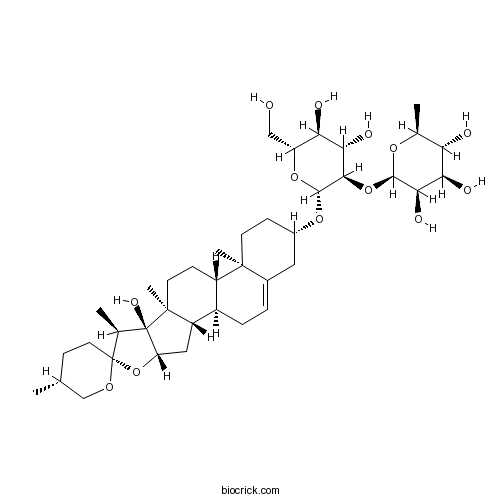
-
BCN6707
Pennogenin 3-O-beta-chacotrioside55916-52-4
Instructions
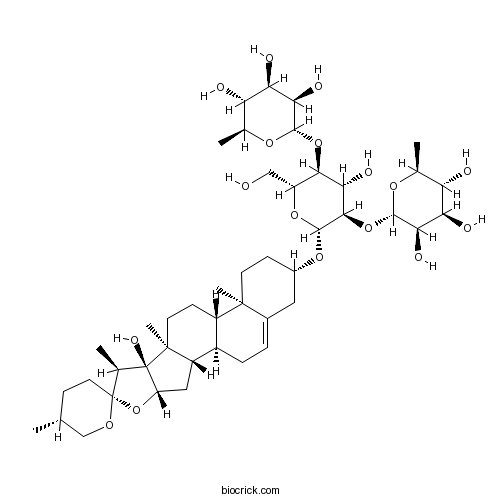
-
BCN4376
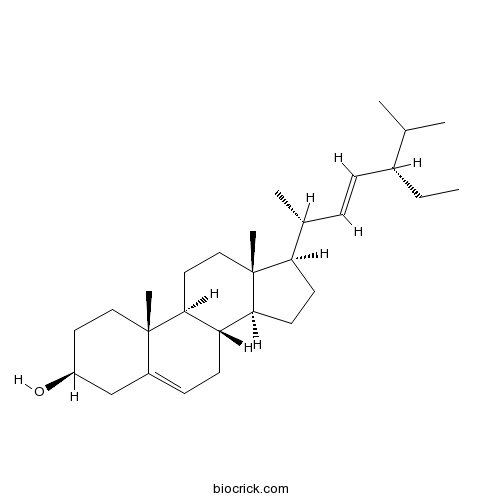
Stigmasterol83-48-7
Instructions
Paris saponin VII induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by regulating Akt/MAPK pathway and inhibition of P-glycoprotein in K562/ADR cells.[Pubmed: 29377384]
Paris saponinVII (PSVII) is a steroidal saponin isolated from the roots and rhizomes of Trillium tschonoskii Maxim. We found that PSVII could inhibit the growth of adriamycin-resistant human leukemia cells (K562/ADR) in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, the molecular mechanism underlying the cytotoxicity and downregulation of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) expression by PSVII was clarified. PSVII significantly suppressed cell proliferation by cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase, which was associated with an obvious decrease in cyclin B1/D1 and CDK2/4/6 protein expression. Moreover, PSVII could attenuate mitochondrial membrane potential, increase the expression of apoptosis-related proteins, such as Bax and cytochrome c, and decrease the protein expression levels of Bcl-2, caspase-9, caspase-3, PARP-1, and p-Akt. We also found that JNK, ERK1/2, and p38 were regulated by PSVII in K562/ADR cells. And further studies indicated that the decrease in the reactive oxygen species level inhibited intrinsic P-gp expression. Therefore, PSVII-induced apoptosis in K562/ADR cells was associated with Akt/MAPK and the inhibition of P-gp. In addition, PSVII induced a robust autophagy in K562/ADR cells as demonstrated by the degradation of LC3-I. These results provide a biochemical basis for possible clinical applications of PSVII in the treatment of leukemia.
Effects of total saponins from Trillium tschonoskii rhizome on grey and white matter injury evaluated by quantitative multiparametric MRI in a rat model of ischemic stroke.[Pubmed: 29309860]
Trillium tschonoskii rhizome (TTR), a medicinal herb, has been traditionally used to treat traumatic brain injury and headache in China. Although the potential neuroprotective efficacy of TTR has gained increasing interest, the pharmacological mechanism remains unclear. Steroid saponins are the main bioactive components of the herb.
Trillium tschonoskii maxim saponin mitigates D-galactose-induced brain aging of rats through rescuing dysfunctional autophagy mediated by Rheb-mTOR signal pathway.[Pubmed: 29287199]
During the expansion of aging population, the study correlated with brain aging is one of the important research topics. Developing novel and effective strategies for delaying brain aging is highly desired. Brain aging is characteristics of impaired cognitive capacity due to dysfunctional autophagy regulated by Rheb-mTOR signal pathway in hippocampal tissues. In the present study, we have established a rat model with brain aging through subcutaneous injection of D-galactose (D-gal). Upon the intervention of Trillium tschonoskii Maxim (TTM) saponin, one of bioactive components from local natural herbs in China, the learning and memory capacity of D-gal-induced aging rats was evaluated through Morris water maze test, and the regulation of Rheb-mTOR signal pathway and functional status of autophagy in hippocampal tissues of D-gal-induced aging rats was explored by Western blot. TTM saponin revealed an obvious function to improve learning and memory capacity of D-gal-induced aging rats through up-regulating Rheb and down-regulating mTOR, thereby rescuing dysfunctional autophagy to execute anti-aging role. Meanwhile, this study confirmed the function of TTM saponin for preventing and treating brain aging, and provided a reference for the development and utilization of natural products in health promotion and aging-associated disease treatment.
[Determination of three saponins in rhizoma and fibrous root of Trillium tschonoskii and Trillium kamtschaticum].[Pubmed: 29027431]
To compare the differences of main components between in rhizoma and fibrous root of Trillium tschonoskii and T. kamtschaticum, a simple, accurate and reliable high performance liquid chromatography coupled with the charged aerosol detector (HPLC-CAD) method was developed and then successfully applied for simultaneous quantitative analysis of three compounds, including polyphyllin Ⅶ (T1),pennogenin 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2) [α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside (T2),polyphyllin Ⅵ (T3), in 16 batches of rhizome and 14 batches of fibrous root. The analytes were well separated from other constituents on TSK gel ODS (4.6 mm×250 mm, 5 μm) with acetonitrile-water (43∶57) at a flow rate of 1.0 mL•min⁻¹. The injection volume was 20 μL. The nitrogen inlet pressure for the CAD system was 35 psi and the nebulizer chamber temperature was 35 ℃.The method was validated for linearity (r>0.999 0), intra and inter-day precision (0.29%-3.0%), repeatability (0.45%-1.4%), stability (1.9%-2.6%), recovery (100.1%-100.2%, 1.2%-1.8%), limits of detection (0.002 g•L⁻¹), and limits of quantification (0.005 g•L⁻¹).The obtained datasets were processed by principal component analysis (PCA) and it showed that there was almost no difference in rhizoma of T. tschonoskii and T. kamtschaticum from different areas of China. However, the 3 major compounds existed in rhizoma were different from those in fibrous root of T. tschonoskii and T. kamtschaticum.
Three New Sesquiterpene Glycosides from the Rhizomes of Trillium tschonoskii.[Pubmed: 28767079]
None
Enrichment of total steroidal saponins from the extracts of Trillium tschonoskii Maxim by macroporous resin and the simultaneous determination of eight steroidal saponins in the final product by HPLC.[Pubmed: 28044421]
An effective and simple method was established for the separation and enrichment of steroidal saponins from Trillium tschonoskii Maxim. The adsorption and desorption properties of seven macroporous resins were investigated. Among the tested resins, AB-8 resin showed the best adsorption and desorption capacities. The adsorption of steroidal saponins on AB-8 at 25°C was quite consistent with both the Freundlich isotherm model and the pseudo-second-order kinetics model. By optimizing the dynamic adsorption and desorption parameters, the content of steroidal saponins increased from 5.20% in the crude extracts to 51.93% in the final product, with a recovery yield of 86.67%. Furthermore, by scale-up separation, the concentration and recovery of total steroidal saponins were 43.8 and 85.5%, respectively, which suggested that AB-8 resin had great industrial and pharmaceutical potential because of its high efficiency and cost-effectiveness. In addition, a high-performance liquid chromatography method for the simultaneous determination of eight steroidal saponins was established for the first time, which was employed to qualitatively and quantitatively analyze the final product. Based on the methodological validation results, the high-performance liquid chromatography method can be widely applied to the quality control of steroidal saponins from Trillium tschonoskii Maxim due to its excellent accuracy, stability, and repeatability.
A new steroidal saponin, furotrilliumoside from Trillium tschonoskii inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in Raw264.7 cells by targeting PI3K/Akt, MARK and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways.[Pubmed: 27693742]
A new steroidal saponin, furotrilliumoside (FT) was isolated from the roots and rhizomes of Trillium tschonoskii Maxim. Its structure was elucidated on the basis of 1D- and 2D-NMR spectroscopic data as well as HR-ESI-MS analysis. FT showed superior activity of inhibiting NO production of RAW264.7 cells induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in the preliminary biological screening. In order to develop novel therapeutic drug for acute and chronic inflammatory disorders, the anti-inflammatory activity and underlying mechanism of FT were investigated in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. The results showed that FT could reduce LPS-induced expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and then resulted in the decrement of NO production. More meaningful, FT could down-regulate the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and decrease the expressions of pro-inflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β), in both gene and protein levels. In mechanism study, FT blocked the LPS-induced upregulation of phosphorylated phosphoinositide-3-kinase and Akt (PI3K/Akt). Furthermore, FT inhibited the translocation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) through the prevention of inhibitory factor kappa B alpha (IκBα) phosphorylation and degradation and also suppressed the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) signaling pathway in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. In addition, FT upregulated heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) expression via nuclear translocation of nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2). Taken together, FT might act as a natural agent to treat some inflammatory diseases by targeting PI3K/Akt, MARK and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways.


