Vaccinium vitis-idaea
Vaccinium vitis-idaea
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Vaccinium vitis-idaea
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
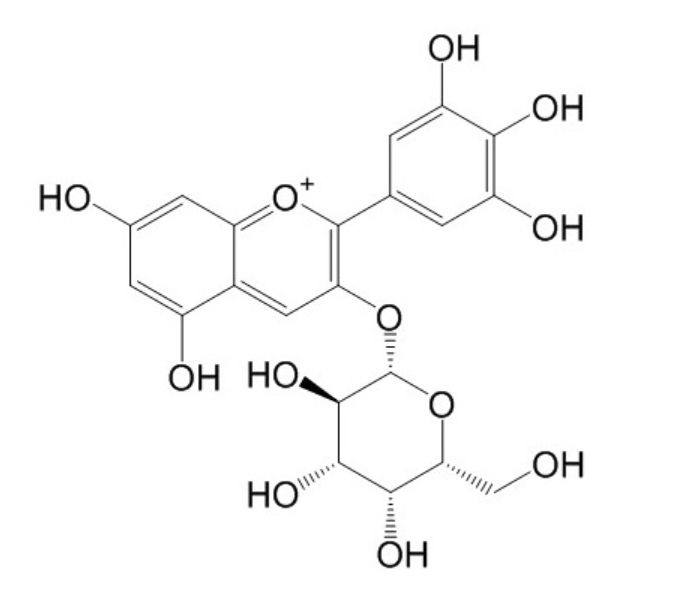
BCN9089
Delphinidin 3-O-galactoside197250-28-5
Instructions
-
BCN6307
Arbutin497-76-7
Instructions

-
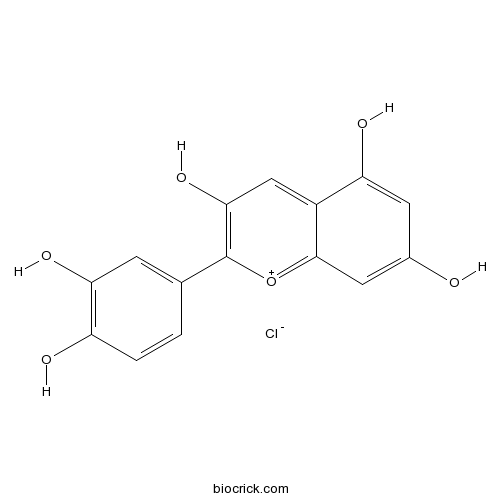
BCN1231
Cyanidin Chloride528-58-5
Instructions
-
BCN1230
Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside chloride7084-24-4
Instructions

Lowbush cranberry acts through DAF-16/FOXO signaling to promote increased lifespan and axon branching in aging posterior touch receptor neurons.[Pubmed: 29717416]
Medicinal berries are appreciated for their health benefits, in traditional ecological knowledge and nutrition science. Determining the cellular mechanisms underlying the effects of berry supplementation may contribute to our understanding of aging. Here, we report that lowbush cranberry (Vaccinium vitis-idaea) treatment causes marked nuclear localization of the central aging-related transcription factor DAF-16/FOXO in aged Caenorhabditis elegans. Further, functional DAF-16 is required for the lifespan extension, improved mechanosensation, and posterior touch receptor neuron morphological changes induced by lowbush cranberry treatments. DAF-16 is not observed in nuceli nor required for lifespan extension in lifespan-extending Alaskan blueberry treatments and, while DAF-16 is not visibly induced into the nucleus in lifespan-extending Alaskan chaga treatments, it is required for chaga-induced lifespan extension. These findings underscore the importance of DAF-16 in the aging of whole organisms and touch receptor neurons and also, importantly, indicate that this critical pathway is not always activated upon consumption of functional foods that impact aging.
Antioxidative and antibacterial activities of aqueous ethanol extracts of berries, leaves, and branches of berry plants.[Pubmed: 29579930]
Phenolic compounds were extracted with food grade solvent of acidified aqueous ethanol from leaves, berries, berry press cakes, and branches of Finnish berry plants and analyzed with HPLC-DAD, UPLC-DAD-ESI-MS and NMR. In addition, press cakes from two berry species and branches from one species were also extracted and analyzed with the same methods. The antioxidant activities of the extracts were evaluated using Folin-Ciocalteau, oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC), DPPH free radical scavenging, and total radical trapping antioxidant parameter (TRAP) assays. The antibacterial activities were investigated against various Gram-negative and Gram-positive foodborne pathogens. The leaf extracts showed higher antioxidative activities (3-20 fold in ORAC assay, 10-20 fold in TRAP) than the berry extracts, in association with the higher contents of phenolic compounds in the leaf extracts; Strongest anti-bacterial effects was observed in the leaf extracts of lingonberry (Vaccinium vitis-idaea), sea buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides ssp. rhamnoides) and saskatoon (Amelanchier alnifolia) on Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes, and Bacillus cereus. However, the antibacterial efficacy varied with bacterial species and strains. The Folin-Ciocalteu, ORAC, and TRAP values was strongly correlated with the total content of flavonoids with less association shown with the content of total phenolics and flavonol glycosides. The results suggest a major contribution of pranthocyanidins and flavan-3-ols to the antioxidative activities of the extracts. The growth inhibition on Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus was clearly associated with the content of total phenolics and ellagitannins.
Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of lingonberry (Vaccinium vitis-idaea L.) leaf, stem and fruit at different harvest periods.[Pubmed: 29478554]
Fruits and aerial parts of lingonberry could be better developed as dietary supplements if the composition in bioactive phenolic compounds and the best period for collection were known. UPLC/MS analysis revealed the predominant presence of arbutin in leaf and that of flavanols in stems harvested in May, July and September. Anthocyanins, flavanols and benzoic acid derivatives were equally present in fruits. Stem and leaf are highly homologous with (+)-catechin, A- and B-type dimers/trimers, and two quercetin glycosides as major contributors. No or only weak seasonal variations were highlighted for all phenolic classes. Additionally, flavanol oligomers showed a lower mDP for fruit (3-4) than for stem and leaf (4-6). The rate of A-type linkage was 3-5% with A-type subunits in extension mainly. Finally, the content in phenolic compounds (UPLC) correlated well with TPC and the DPPH radical scavenging activity although leaf and stem constituents reacted differently in both antioxidant tests.
Characterisation of Antimicrobial Properties of Extracts of Selected Medicinal Plants.[Pubmed: 29319517]
The scope of the experiments included analysis of the antimicrobial activity of ethanolic, methanolic and aqueous extracts against bacterial and fungal cultures and determination of the minimum inhibitory concentration of plant extracts tested microbial growth. Analysis of the antifungal and antibacterial activity was carried out by the disc diffusion method using paper discs. In the experiment 11 species of microorganisms - 8 bacterial and 3 fungal strains were used. The highest antimicrobial activity against the tested strains was demonstrated by black elder (Sambucus nigra L.), black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.) and lingonberry (Vaccinium vitis-idaea L.) extracts. The study showed the diverse morphological activity of specific parts of elderberry and quince, which is the effect of different polyphenolic profile of these plants. The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas putida and Bacillus subtilis showed the highest sensitivity to the effect of extracts of the analysed plants. As a positive control three antibiotics - amphotericin B, vancomycin and amoxicillin with clavulanic acid were used.
Genetic variation associated with healthy traits and environmental conditions in Vaccinium vitis-idaea.[Pubmed: 29291734]
Lingonberry (Vaccinium vitis-idaea L.), one of the least studied fruit crops in the Ericaceae family, has a dramatically increased worldwide demand due to its numerous health benefits. Genetic markers can facilitate the selection of berries with desirable climatic adaptations, agronomic and nutritious characteristics to improve cultivation programs. However, no genomic resources are available for this species.
Evaluation of Bioactive Compounds, Minerals and Antioxidant Activity of Lingonberry (Vaccinium vitis-idaea L.) Fruits.[Pubmed: 29278401]
None


