Viola philippica
Viola philippica
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Viola philippica
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN1673
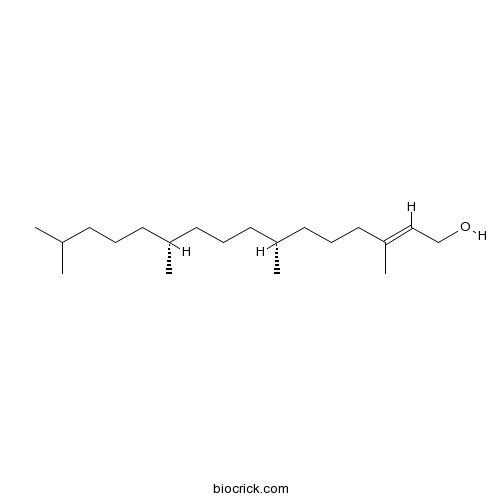
Phytol150-86-7
Instructions
-
BCN5905
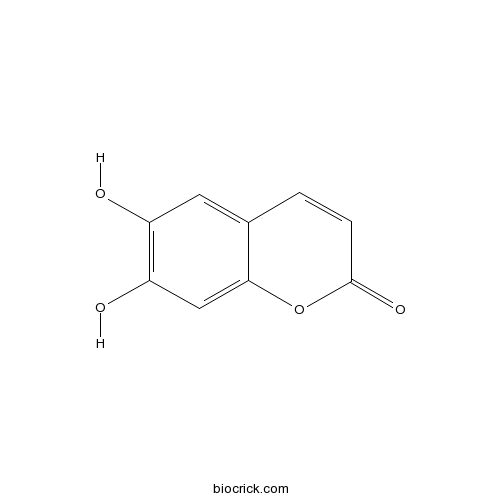
6,7-Dihydroxycoumarin305-01-1
Instructions
-
BCN5573
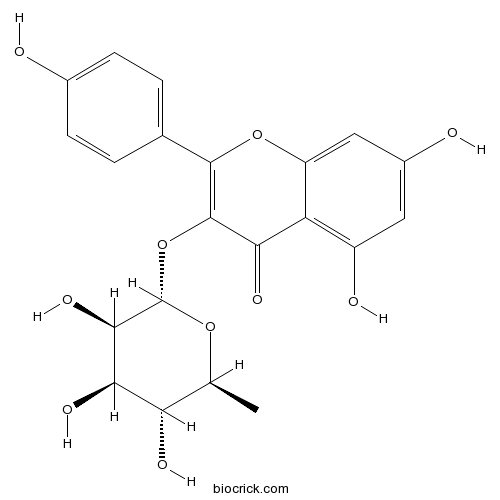
Afzelin482-39-3
Instructions
-
BCN5904
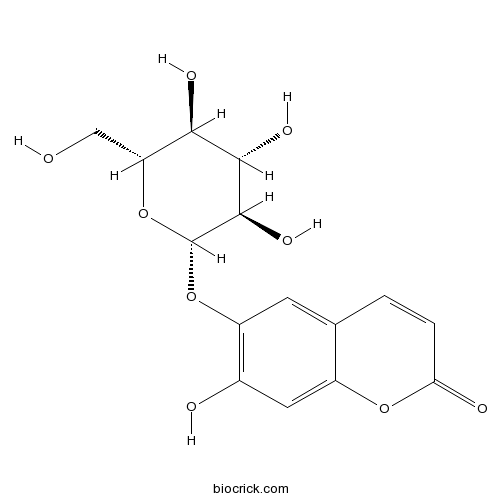
Esculin531-75-9
Instructions
-
BCN9061
(±)-Naringenin67604-48-2
Instructions
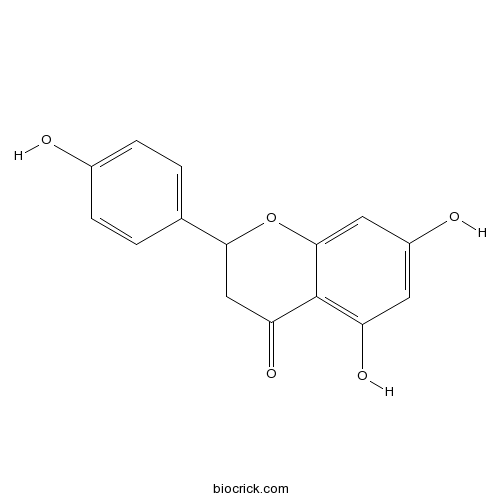
-
BCN7820
Apigenin 6-C-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl-8-C-beta-D-xylopyranoside677021-30-6
Instructions

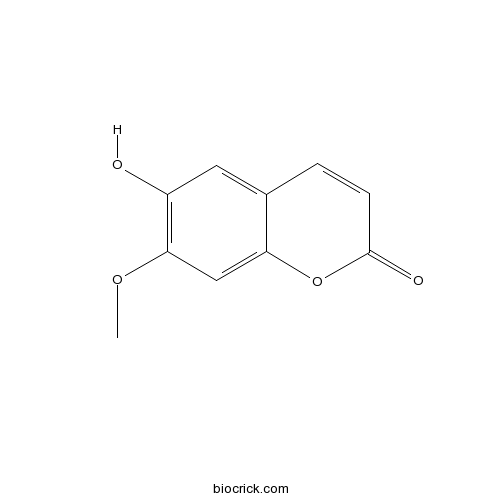
-
BCN4582
Isoscopoletin776-86-3
Instructions
Lignans, flavonoids and coumarins from Viola philippica and their α-glucosidase and HCV protease inhibitory activities.[Pubmed: 29334261]
Two lignans including a new one, five flavonoids and five coumarins were isolated from the whole plant of Viola philippica (synonymised as Viola yedoensis Makino). The new compound was structurally determined as (7R,8S,8'S) -3,3'-dimethoxy- 4,4',9-trihydroxy- 7,9'-epoxy-8,8'-lignan 9-O-rutinoside by analysis of its NMR, MS and CD spectroscopic data. The known compounds were characterised by comparing their NMR and MS data with those reported. Among the known compounds, 5-hydroxy-4'-methoxyflavone-7-O- rutinoside, 6,7-di-O-β-D- glucopyranosylesculetin, and 7R,8S-dihydrodehydrodiconiferyl alcohol 4-O-β-D- glucopyranoside were isolated and identified from this genus for the first time. Of these compounds, 5-hydroxy-4'-methoxyflavone-7-O-rutinoside and (7R,8S,8'S) -3,3'-dimethoxy- 4,4',9-trihydroxy- 7,9'-epoxy-8,8'-lignan 9-O-rutinoside were potently active against α-glucosidase, while the two dimeric coumarins, 5, 5'-bi (6, 7-dihydroxycoumarin) and 6,6',7,7'-tetrahydroxy-5,8'-bicoumarin potently inhibited HCV protease.
Expression of B-class MADS-box genes in response to variations in photoperiod is associated with chasmogamous and cleistogamous flower development in Viola philippica.[Pubmed: 27388887]
Some plants develop a breeding system that produces both chasmogamous (CH) and cleistogamous (CL) flowers. However, the underlying molecular mechanism remains elusive.
Micromonospora violae sp. nov., isolated from a root of Viola philippica Car.[Pubmed: 24803239]
A novel actinomycete, designated strain NEAU-zh8(T), was isolated from a root of Viola philippica Car collected in China and characterized using a polyphasic approach. 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity studies showed that strain NEAU-zh8(T) belongs to the genus Micromonospora, being most closely related to Micromonospora chokoriensis 2-9(6)(T) (99.9 %), Micromonospora saelicesensis Lupac 09(T) (99.3 %) and Micromonospora lupini Lupac 14N(T) (99.0 %). gyrB gene analysis also indicated that strain NEAU-zh8(T) should be assigned to the genus Micromonospora. The cell-wall peptidoglycan consisted of meso-diaminopimelic acid and glycine. The major menaquinones were MK-10(H4), MK-10(H2) and MK-10(H6). The phospholipid profile contained diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylinositol. The major fatty acids were iso-C15:0, C16:0 and C17:0 10-methyl. A combination of DNA-DNA hybridization results and some physiological and biochemical properties indicated that strain NEAU-zh8(T) could be readily distinguished from the closest phylogenetic relatives. Therefore, it is proposed that strain NEAU-zh8(T) represents a novel Micromonospora species, for which the name Micromonospora violae sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is NEAU-zh8(T) (=CGMCC 4.7102(T)=DSM 45888(T)).
Isolation and characterization of cytotoxic cyclotides from Viola philippica.[Pubmed: 21723349]
Cyclotides are a large family of plant peptides characterized by a macrocyclic backbone and knotted arrangement of three disulfide bonds. This unique structure renders cyclotides exceptionally stable to thermal, chemical and enzymatic treatments. They exhibit a variety of bioactivities, including uterotonic, anti-HIV, cytotoxic and hemolytic activity and it is these properties that make cyclotides an interesting peptide scaffold for drug design. In this study, eight new cyclotides (Viphi A-H), along with eight known cyclotides, were isolated from Viola philippica, a plant from the Violaceae family. In addition, Viba 17 and Mram 8 were isolated for the first time as peptides. The sequences of these cyclotides were elucidated primarily by using a strategy involving reduction, enzymatic digestion and tandem mass spectroscopy sequencing. Several of the cyclotides showed cytotoxic activities against the cancer cell lines MM96L, HeLa and BGC-823. The novel cyclotides reported here: (1) enhance the known sequence variation observed for cyclotides; (2) extend the number of species known to contain cyclotides; (3) provide interesting structure-activity relationships that delineate residues important for cytotoxic activity. In addition, this study provides insights into the potential active ingredients of traditional Chinese medicines.


