Xylaria nigripes
Xylaria nigripes
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Xylaria nigripes
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
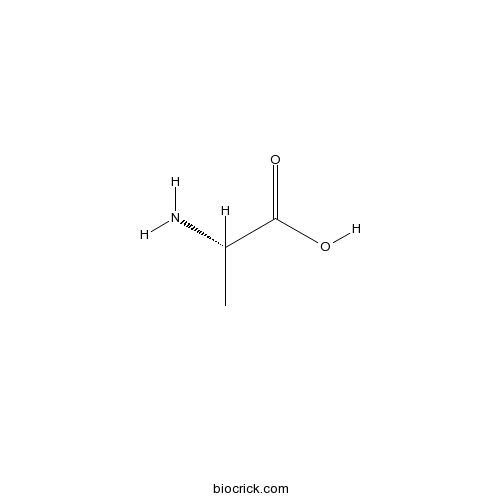
BCC3190
H-Ala-OH56-41-7
Instructions
Differences in water soluble non-digestible polysaccharides and anti-inflammatory activities of fruiting bodies from two cultivated Xylaria nigripes strains.[Pubmed: 29763701]
Polysaccharides including β-glucans are important bioactive components of mushroom. Xylaria nigripes is a popular medicinal fungus that has been used for treating trauma, insomnia and mental illness. This study examined the physicochemical characteristics and anti-inflammatory activities of water soluble non-digestible polysaccharides (TXNP and CXNP) from fruiting bodies of two cultivated X. nigripes strains (TXN and CXN). Results showed that both TXNP and CXNP possessed relatively similar FT-IR spectra. TXNP had a triple helix conformation and molecular weight of 853.8 kDa, whereas the molecular weight of CXNP was 14.7 kDa. The monosaccharide composition of TXNP was predominantly glucose, whereas CXNP contained xylose, mannose and glucose. Although both TXNP and CXNP dose-dependently suppressed the production of NO, IL-1β, TNF-α and PGE2, as well as the expression of iNOS, COX-2 and NF-κB in the lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 macrophages, the potency of TXNP was stronger. This study reveals that under similar conditions of cultivation and extraction procedures, the different physicochemical characteristics of polysaccharides from TXN and CXN may have contributed to the differences in their anti-inflammatory potency.
Synthetic approaches to access acortatarins, shensongines and pollenopyrroside; potent antioxidative spiro-alkaloids with a naturally rare morpholine moiety.[Pubmed: 29617626]
Pyrrole spiroketal alkaloids (PSAs) are a class of novel natural products that have been recently disclosed. Acortatarin A and acortatarin B, two potent antioxidative spiroalkaloids with a naturally rare morpholine moiety, are important members of this class. These spiroalkaloids are isolated from Acorus tatarinowii, Brassica campestris, Capparis spinose, bread crust, Xylaria nigripes and medicine Shensong Yangxin and could inhibit significantly the reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in high-glucose-induced mesangial cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Hence, these natural products are promising starting points for the formation of new therapeutics to medicate cardiovascular diseases, cancer, diabetic complications, and other diseases in which ROS are implicated. The impressive structure combined with an interesting pharmacological activity prompted synthetic chemists to construct an asymmetric synthetic strategy that could be used to access structural derivatives in addition to the larger quantities of natural products required for further biological investigations. This review summarizes the current state of the literature regarding with the synthesis of acortatarin A and B and its other family members viz. shensongine A, B and C, and pollenopyrroside A. The present review discusses the pros and cons of synthetic methodologies, which would be beneficial for further developments in the synthetic methodologies. Hopefully, this struggle pushes the reader's mind to consider new perspectives, think differently and forge new connections.
Anti-Inflammatory Activity and Bioactive Constituents of Cultivated Fruiting Bodies of Xylaria nigripes (Ascomycetes), a Chinese Medicinal Fungus.[Pubmed: 29256845]
Xylaria nigripes, also known as Wu Ling Shen, is popular for treating insomnia and trauma in traditional Chinese medicine. This study aimed to examine the anti-inflammatory activity and bioactive constituents of cultivated X. nigripes fruiting bodies in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Results showed that among the different extracts, the hexane fraction exhibited the best protection against cell toxicity induced by 1 μg/mL LPS and the strongest inhibitory effect on nitric oxide (NO) production. This fraction led to the isolation of 2 bioactive compounds (namely, XN-CP1 and XN-CP2), which were confirmed to be ergostarien-3β-ol and ergosterol peroxide, respectively. Although both XN-CP1 and XN-CP2 showed good inhibitory effects on NO, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and prostaglandin E2 production in LPS-stimulated macrophages, XN-CP2 was shown to have a stronger anti-inflammatory activity; this was further supported by its strong suppressive effects on inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression and nuclear factor (NF)-κB activation. These results conclude that ergosterol peroxide (XN-CP2) could be the main bioactive compound contributing to the potent anti-inflammatory activity of X. nigripes, and its mechanism of action is mediated through inhibition of iNOS and COX-2 expression via the NF-κB signaling pathway.
Protective effect of medicinal fungus Xylaria nigripes mycelia extracts against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells.[Pubmed: 28281874]
None
Bioactive Constituents from the Termite Nest-Derived Medicinal Fungus Xylaria nigripes.[Pubmed: 28055210]
None
Wuling Capsule for Major Depressive Disorder: A Meta-analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials.[Pubmed: 27703096]
In China, Wuling capsule, a traditional Chinese medicine consisting of Wuling mycelia of Xylaria nigripes (Kl.) Sacc (a rare type of fungus), is used to treat major depressive disorders. A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials was performed to compare the efficacy and safety of Wuling capsule alone with Wuling capsule-antidepressant combination in the treatment of major depressive disorders.
Three New Ergot Alkaloids from the Fruiting Bodies of Xylaria nigripes (Kl.) Sacc.[Pubmed: 27448231]
Three new ergot alkaloids, xylanigripones A - C (1 - 3) together with three known compounds, agroclavine (4), 8,9-didehydro-10-hydroxy-6,8-dimethylergolin (5), and (6S)-agroclavine N-oxide (6) were isolated from the fungus Xylaria nigripes (Kl.) Sacc. Their structures were elucidated by comprehensive spectroscopic analyses and high-resolution mass spectrometry as well as by comparison with the literature. The absolute configuration was determined by Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculation methods. In addition, all of the compounds were evaluated for bioactivity via a cytotoxicity assay, an acetylcholinesterase inhibition assay and a cholesterol ester transfer protein inhibition assay.
SCREENING FOR MOSQUITO LARVICIDAL ACTIVITY OF THAI MUSHROOM EXTRACTS WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO STECCHERINUM SP AGAINST AEDES AEGYPTI (L.) (DIPTERA: CULICIDAE).[Pubmed: 26867377]
For over 50 years, biological control of mosquito larvae has depended mainly on plant extracts, fish, bacteria, protozoa, filamentous fungi, viruses or nematodes. In this study, we screened 143 mushroom samples from 44 confirmed species in Thailand for their mosquito larvicidal activity. One g% (w/v) aqueous extracts of dried powdered mushroom samples were tested against 3rd stage Aedes aegypti larvae. Four mushroom species, namely, Thaeogyroporus porentosus, Xylaria nigripes, Chlorophyllum sp and Steccherinum sp, and two unidentified species showed larvicidal mortality ranging from 10%-70% and 18%-90% for 24- and 48-hour exposure time, respectively. Steccherinum sp aqueous crude extract, after 48-hour exposure, did not show any larvicidal activity at 1,000 ppm, whereas that from ethanol, after 24-hour exposure, had 50% and 90% lethal concentration of 203 ppm and 412 ppm, respectively, with higher levels of mortality after 48- hour exposure. This is the first report of mosquito larvicidal properties of Thai mushroom extracts.
The anti-depression effect of Xylaria nigripes in patients with epilepsy: A multicenter randomized double-blind study.[Pubmed: 26076841]
The comorbidity of depression in patients with epilepsy is common and treatment is still controversial. This pilot study was aimed at evaluating the efficacy and safety of Xylaria nigripes for treating depressive symptoms in patients with epilepsy during 12 weeks of treatment.


