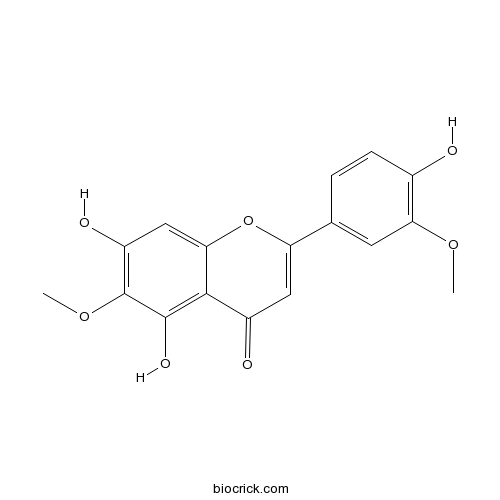
A trihydroxyflavone that is flavone with hydroxy groups at positions 5, 7 and 4' and methoxy groups at positions 3' and 6. Isolated from Salvia tomentosa and Artemisia asiatica, it exhibits anti-allergic, anti-inflammatory and apoptosis inducing activties.
InChI=1S/C17H14O7/c1-22-13-5-8(3-4-9(13)18)12-6-10(19)15-14(24-12)7-11(20)17(23-2)16(15)21/h3-7,18,20-21H,1-2H3
Jaceosidin and Eupatilin are bioactive flavones found in the medicinal herbs of the genus Artemisia, exhibit various antioxidant, antiinflammatory, antiallergic, and antitumor activities, jaceosidin is a competitive inhibitor of CYP1A2 with a K(i) value of 3.8 microM and a mixed-type inhibitor of CYP2C9 with K(i) value of 6.4 microM in human liver microsomes.[1]
Jaceosidin has anti-inflammatory effect, may reduce inflammation by inhibiting NF-kappaB activation.[2]
Jaceosidin has anticancer effect and antiproliferation effect , may be contributed by an induction of apoptosis involving cytochrome c release from mitochondria to cytosol, induces apoptosis in ras-transformed human breast epithelial cells through generation of reactive oxygen species.[3,4]
Jaceosidin exerts growth inhibitory effect by arresting the cells at G2/M phase and induction of apoptosis.[5]
English website: Jaceosidin
Japanese website: Jaceosidin
Chinese website: Jaceosidin
[1] Ji H Y, Kim S Y, Kim D K, et al. Molecules, 2010, 15(9):6466-75.
[2] Min S W, Kim NJBaek N I. J Ethnopharmacol, 2009, 125(3):497-500.
[3] Min‐Jung K, Do‐Hee K, Won L K, et al. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2007, 1095(1):483-95.
[4] Lv W, Sheng X, Chen T, et al. J Biomed Biotechnol, 2008(1):394802.
[5] Khan M, Yu B, Rasul A, et al. Evid-based Compl Al, 2011, 2012(1):72-79.
[6] Zhou Q, Sun L L, Jiang B, et al. China Pharmacy, 2013, 24(47):4464-6.