JaceosidinCAS# 18085-97-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 18085-97-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5379096 | Appearance | Yellowish powder |
| Formula | C17H14O7 | M.Wt | 330.29 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 4'-Demethyleupatilin; 6-Hydroxyluteolin 3',6-dimethyl ether; 6-Methoxyluteolin 3'-methyl ether; 4',5,7-Trihydroxy 3',6-dimethoxyflavone | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 125 mg/mL (378.46 mM; Need ultrasonic) Ethanol : 7.14 mg/mL (21.62 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
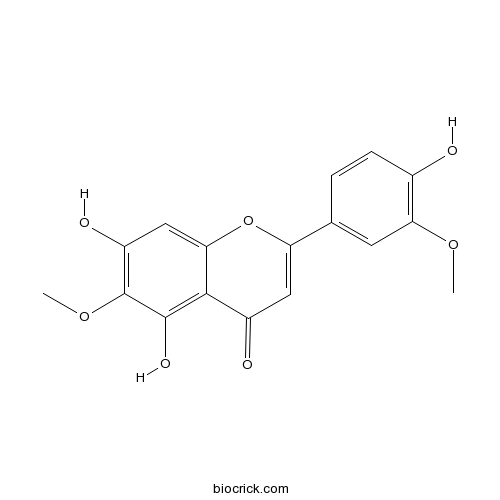
| Chemical Name | 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-6-methoxychromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=CC(=C1)C2=CC(=O)C3=C(C(=C(C=C3O2)O)OC)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GLAAQZFBFGEBPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H14O7/c1-22-13-5-8(3-4-9(13)18)12-6-10(19)15-14(24-12)7-11(20)17(23-2)16(15)21/h3-7,18,20-21H,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Jaceosidin has immunosuppressive, anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer activities, it is also a microglial inhibitor with anti-neuroinflammation activity. Jaceosidin modulates the ERK/ATM/Chk1/2 pathway, leading to inactivation of the Cdc2-cyclin B1 complex, followed by G2/M cell cycle arrest in endometrial cancer cells. Jaceosidin inhibits T cell proliferation and activation, which is closely associated with its potent down-regulation of the IFN-γ/STAT1/T-bet signaling pathway. |
| Targets | VEGFR | FAK | PI3K | Akt | NF-kB | p21 | Chk | ATM/ATR | NO | P450 (e.g. CYP17) | IFN-γ | IL Receptor | STAT | TNF-α |
| In vitro | Jaceosidin, isolated from dietary mugwort (Artemisia princeps), induces G2/M cell cycle arrest by inactivating cdc25C-cdc2 via ATM-Chk1/2 activation.[Pubmed: 23274058]Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 May;55:214-21.Jaceosidin, a flavonoid derived from Artemisia princeps (Japanese mugwort), has been shown to inhibit the growth of several human cancer cells, However, the exact mechanism for the cytotoxic effect of Jaceosidin is not completely understood. |
| In vivo | Natural flavone jaceosidin is a neuroinflammation inhibitor.[Pubmed: 22619052]Phytother Res. 2013 Mar;27(3):404-11.Jaceosidin is a naturally occurring flavone with pharmacological activity. Jaceosidin, as one of the major constituents of the medicinal herbs of the genus Artemisia, has been shown to exert anticancer, anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, and immunosuppressive effects. This study was undertaken to determine the effect of Jaceosidin on microglia and neuroinflammation. Jaceosidin inhibits contact hypersensitivity in mice via down-regulating IFN-γ/STAT1/T-bet signaling in T cells.[Pubmed: 21093428]Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Jan 25;651(1-3):205-11.In the present study, we aimed to investigate the immunosuppressive activity of Jaceosidin, a flavone isolated from Artemisia vestita, on T lymphocytes both in vitro and in vivo, and further explore its potential molecular mechanism. |
| Kinase Assay | In vitro metabolism of jaceosidin and characterization of cytochrome P450 and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzymes in human liver microsomes.[Pubmed: 21191764]Jaceosidin, a natural flavone, promotes angiogenesis via activation of VEGFR2/FAK/PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathways in endothelial cells.[Pubmed: 24939823 ]Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2014 Oct;239(10):1325-34.Angiogenesis, the growth of new blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature, plays an important role in physiological and pathological processes such as embryonic development wound healing and revascularization of tissues after exposure to ischemia. Arch Pharm Res. 2010 Dec;33(12):1985-96.Jaceosidin is an active component in Artemisia species as well as Eupatorium species and it exhibits antiallergic, anticancer, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimutagenic activities. Jaceosidin was metabolized to Jaceosidin glucuronide, 6-O-desmethylJaceosidin, hydroxyJaceosidin, 6-O-desmethylJaceosidin glucuronide, and hydroxyJaceosidin glucuronide in human liver microsomes. |

Jaceosidin Dilution Calculator

Jaceosidin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0276 mL | 15.1382 mL | 30.2764 mL | 60.5528 mL | 75.6911 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6055 mL | 3.0276 mL | 6.0553 mL | 12.1106 mL | 15.1382 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3028 mL | 1.5138 mL | 3.0276 mL | 6.0553 mL | 7.5691 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0606 mL | 0.3028 mL | 0.6055 mL | 1.2111 mL | 1.5138 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0303 mL | 0.1514 mL | 0.3028 mL | 0.6055 mL | 0.7569 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 4-O-Caffeoylshikimic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7931
CAS No.:180842-65-3
- CHMFL-ABL-053
Catalog No.:BCC3988
CAS No.:1808287-83-3
- LG 100754
Catalog No.:BCC7786
CAS No.:180713-37-5
- Polypodine B
Catalog No.:BCN8117
CAS No.:18069-14-2
- 1,4-Bis(5-phenyl-2-oxazolyl)benzene
Catalog No.:BCC8424
CAS No.:1806-34-4
- 2,2'-Biphenol
Catalog No.:BCC8488
CAS No.:1806-29-7
- Peiminine
Catalog No.:BCN1095
CAS No.:18059-10-4
- Gentioflavin
Catalog No.:BCN3619
CAS No.:18058-50-9
- Fmoc-D-Asn(Trt)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3084
CAS No.:180570-71-2
- Solifenacin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5193
CAS No.:180468-39-7
- Perillaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN8294
CAS No.:18031-40-8
- Cyclo(Leu-Ala)
Catalog No.:BCN2428
CAS No.:1803-60-7
- Spiramilactone B
Catalog No.:BCN1141
CAS No.:180961-65-3
- Neuchromenin
Catalog No.:BCN7449
CAS No.:180964-26-5
- FTI 277 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC6395
CAS No.:180977-34-8
- 3-O-Caffeoylshikimic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7930
CAS No.:180981-12-8
- Curcumaromin A
Catalog No.:BCN7417
CAS No.:1810034-38-8
- Curcumaromin B
Catalog No.:BCN7419
CAS No.:1810034-39-9
- Curcumaromin C
Catalog No.:BCN7418
CAS No.:1810034-40-2
- Corymbosin
Catalog No.:BCN6812
CAS No.:18103-41-8
- 5,7-Dihydroxy-3',4',5'-trimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN6807
CAS No.:18103-42-9
- Proflavine Hemisulfate
Catalog No.:BCC4707
CAS No.:1811-28-5
- 5-Hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN1142
CAS No.:18110-86-6
- 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN1143
CAS No.:18110-87-7
Jaceosidin inhibits contact hypersensitivity in mice via down-regulating IFN-gamma/STAT1/T-bet signaling in T cells.[Pubmed:21093428]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Jan 25;651(1-3):205-11.
In the present study, we aimed to investigate the immunosuppressive activity of Jaceosidin, a flavone isolated from Artemisia vestita, on T lymphocytes both in vitro and in vivo, and further explore its potential molecular mechanism. Jaceosidin exerted a significant inhibition on the T cell proliferation and activation induced by concanavalin A (Con A) in a concentration-dependent manner and it also inhibited the secretion of the proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-2, TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma of activated T cells. Further study showed that Jaceosidin down-regulated STAT1 activation and T-bet expression in activated T cells. Moreover, in order to investigate the immunosuppressive effect of Jaceosidin in vivo, the picryl chloride (PCl)-induced ear contact dermatitis model was performed on BALB/c mice. Jaceosidin significantly ameliorated PCl-induced ear swelling in a dose-dependent manner, which was due to its inhibition of the STAT1/T-bet signaling pathway. In summary, these findings suggest that Jaceosidin exerts its immunosuppressive effect both in vitro and in vivo through inhibiting T cell proliferation and activation, which is closely associated with its potent down-regulation of the IFN-gamma/STAT1/T-bet signaling pathway.
Jaceosidin, isolated from dietary mugwort (Artemisia princeps), induces G2/M cell cycle arrest by inactivating cdc25C-cdc2 via ATM-Chk1/2 activation.[Pubmed:23274058]
Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 May;55:214-21.
Jaceosidin, a flavonoid derived from Artemisia princeps (Japanese mugwort), has been shown to inhibit the growth of several human cancer cells, However, the exact mechanism for the cytotoxic effect of Jaceosidin is not completely understood. In this study, we investigated the molecular mechanism involved in the antiproliferative effect of Jaceosidin in human endometrial cancer cells. We demonstrated that Jaceosidin is a more potent inhibitor of cell growth than cisplatin in human endometrial cancer cells. In contrast, Jaceosidin-induced cytotoxicity in normal endometrial cells was lower than that observed for cisplatin. Jaceosidin induced G2/M phase cell cycle arrest and modulated the levels of cyclin B and p-Cdc2 in Hec1A cells. Knockdown of p21 using specific siRNAs partially abrogated Jaceosidin-induced cell growth inhibition. Additional mechanistic studies revealed that Jaceosidin treatment resulted in an increase in phosphorylation of Cdc25C and ATM-Chk1/2. Ku55933, an ATM inhibitor, reversed Jaceosidin-induced cell growth inhibition, in part. Moreover, Jaceosidin treatment resulted in phosphorylation of ERK, and pretreatment with the ERK inhibitor, PD98059, attenuated cell growth inhibition by Jaceosidin. These data suggest that Jaceosidin, isolated from Japanese mugwort, modulates the ERK/ATM/Chk1/2 pathway, leading to inactivation of the Cdc2-cyclin B1 complex, followed by G2/M cell cycle arrest in endometrial cancer cells.
Jaceosidin, a natural flavone, promotes angiogenesis via activation of VEGFR2/FAK/PI3K/AKT/NF-kappaB signaling pathways in endothelial cells.[Pubmed:24939823]
Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2014 Oct;239(10):1325-34.
Angiogenesis, the growth of new blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature, plays an important role in physiological and pathological processes such as embryonic development wound healing and revascularization of tissues after exposure to ischemia. We investigated the effects of Jaceosidin, a main constituent of medicinal herbs of the genus Artemisia, on angiogenesis and signaling pathways in endothelial cells. Jaceosidin stimulated proliferation, migration and tubulogenesis of ECs as well as ex vivo sprouting from aorta rings, which are phenomena typical of angiogenesis. Jaceosidin activated vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2, FLk-1/KDR) and angiogenic signaling molecules such as focal adhesion kinase, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and its downstream target, the serine-threonine kinase AKTWe also demonstrated that Jaceosidin activated the NF-kappaB-driven expression of a luciferase reporter gene and NF-kappaB binding to DNA. Jaceosidin-induced proliferation and migration of human umbilical vascular endothelial cells were strongly inhibited by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor LY294002 and NF-kappaB inhibitor BAY11-7082, indicating that the PI3K/AKT/NF-kappaB signaling pathway is involved in Jaceosidin-induced angiogenesis. Our results suggest that Jaceosidin stimulates angiogenesis by activating the VEGFR2/FAK/PI3K/AKT/NF-kappaB signaling pathway and that it may be useful in developing angiogenic agents to promote the growth of collateral blood vessels in ischemic tissues.
In vitro metabolism of jaceosidin and characterization of cytochrome P450 and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzymes in human liver microsomes.[Pubmed:21191764]
Arch Pharm Res. 2010 Dec;33(12):1985-96.
Jaceosidin is an active component in Artemisia species as well as Eupatorium species and it exhibits antiallergic, anticancer, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimutagenic activities. Jaceosidin was metabolized to Jaceosidin glucuronide, 6-O-desmethylJaceosidin, hydroxyJaceosidin, 6-O-desmethylJaceosidin glucuronide, and hydroxyJaceosidin glucuronide in human liver microsomes. This study characterized the human liver cytochrome P450 (CYP) and UDPglucuronosyltransferase (UGT) enzymes responsible for the metabolism of Jaceosidin. CYP1A2 was identified as the major enzyme responsible for the formation of 6-O-desmethylJaceosidin and hydroxyJaceosidin from Jaceosidin on the basis of a combination of correlation analysis and experiments including immuno-inhibition, chemical inhibition in human liver microsomes, and metabolism by human cDNA-expressed CYP enzymes. Jaceosidin glucuronidation was catalyzed by UGT1A1, UGT1A3, UGT1A7, UGT1A8, UGT1A9, and UGT1A10. These results suggest that the pharmacokinetics of Jaceosidin may be dramatically affected by polymorphic CYP1A2, UGT1A1, and UGT1A7 responsible for the metabolism of Jaceosidin or by the coadministration of relevant CYP1A2 or UGT inhibitors or inducers.
Natural flavone jaceosidin is a neuroinflammation inhibitor.[Pubmed:22619052]
Phytother Res. 2013 Mar;27(3):404-11.
Jaceosidin is a naturally occurring flavone with pharmacological activity. Jaceosidin, as one of the major constituents of the medicinal herbs of the genus Artemisia, has been shown to exert anticancer, anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, and immunosuppressive effects. This study was undertaken to determine the effect of Jaceosidin on microglia and neuroinflammation. Microglia are the innate immune cells in the central nervous system, and they play a central role in the initiation and maintenance of neuroinflammation. We report that Jaceosidin inhibits inflammatory activation of microglia, reducing nitric oxide (NO) production and proinflammatory cytokine expression. IC50 for NO inhibition was 27 +/- 0.4 muM. The flavone also attenuated microglial neurotoxicity in the microglia/neuroblastoma co-culture. Systemic injection of Jaceosidin ameliorated neuroinflammation in the mouse model of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. These results indicate that plant flavone Jaceosidin is a microglial inhibitor with anti-neuroinflammation activity.


