4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-oneCAS# 18110-87-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 18110-87-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 638215 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Formula | C16H12N2O3 | M.Wt | 280.3 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
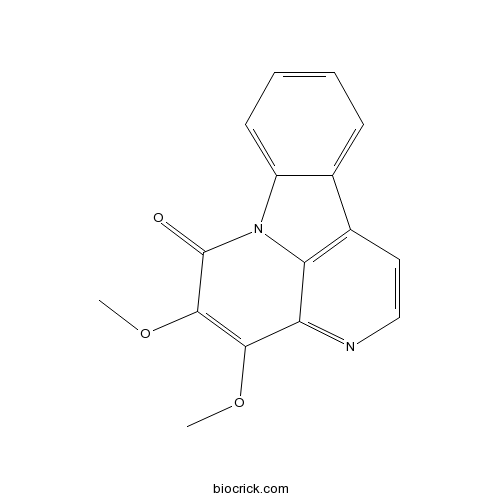
| SMILES | COC1=C(C(=O)N2C3=CC=CC=C3C4=C2C1=NC=C4)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ATONBUGCNDSBBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one has antibacterial actiyity, it exhibits inhibition against Staphylococcus aureus and its drug-resistant strains. 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one has a strong inhibitory effect on cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) phosphodiesterase. It also shows cytotoxicity against the tumor cell lines, U937 and HepG2. |
| Targets | cAMP | Antifection |
| In vitro | Cytotoxic alkaloids from the wood of Picrasma quassioides.[Reference: WebLink]J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem.,2009, 52(6):663-7.Six alkaloid compounds were isolated from the chloroform soluble fraction of the methanolic extract of the wood of Picrasma quassioides Benn (Simarobaceae) as the cytotoxic components against the tumor cell lines, U937 and HepG2. Inhibitors of cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase in Picrasma quassioides Bennet, and inhibitory activities of related .BETA.-carboline alkaloids.[Reference: WebLink]Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1984 May;32(5):1872-7.
Chemical investigation of the alkaloids of Ku-Mu [Picrasma quassioides (D. Don) Benn.[Reference: WebLink]Yao Xue Xue Bao,1979, 14(3):167-77.Some preparation of the total alkaloids of Ku-Mu (Picrasma quassioides (D. Don) Benn.) was Shown to have antibacterial actiyity in clinical trial. For the exploration of the active principles, the present paper deals with the studies of the alkaloids of this medicinal plant. |
| Structure Identification | Journal of Chromatography B,2015, 986–987,(1):100–7.Simultaneous quantification of two canthinone alkaloids of Picrasma quassioides in rat plasma by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry and its application to a rat pharmacokinetic study[Reference: WebLink]Picrasma quassioides (D. Don) Benn. is used in traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of inflammation. Characteristic components of the medicinal extract are canthinone alkaloids. |

4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one Dilution Calculator

4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5676 mL | 17.838 mL | 35.6761 mL | 71.3521 mL | 89.1902 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7135 mL | 3.5676 mL | 7.1352 mL | 14.2704 mL | 17.838 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3568 mL | 1.7838 mL | 3.5676 mL | 7.1352 mL | 8.919 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0714 mL | 0.3568 mL | 0.7135 mL | 1.427 mL | 1.7838 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0357 mL | 0.1784 mL | 0.3568 mL | 0.7135 mL | 0.8919 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 5-Hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN1142
CAS No.:18110-86-6
- Proflavine Hemisulfate
Catalog No.:BCC4707
CAS No.:1811-28-5
- 5,7-Dihydroxy-3',4',5'-trimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN6807
CAS No.:18103-42-9
- Corymbosin
Catalog No.:BCN6812
CAS No.:18103-41-8
- Curcumaromin C
Catalog No.:BCN7418
CAS No.:1810034-40-2
- Curcumaromin B
Catalog No.:BCN7419
CAS No.:1810034-39-9
- Curcumaromin A
Catalog No.:BCN7417
CAS No.:1810034-38-8
- 3-O-Caffeoylshikimic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7930
CAS No.:180981-12-8
- FTI 277 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC6395
CAS No.:180977-34-8
- Neuchromenin
Catalog No.:BCN7449
CAS No.:180964-26-5
- Spiramilactone B
Catalog No.:BCN1141
CAS No.:180961-65-3
- Jaceosidin
Catalog No.:BCN2529
CAS No.:18085-97-7
- Co 102862
Catalog No.:BCC7439
CAS No.:181144-66-1
- Almotriptan Malate
Catalog No.:BCC5045
CAS No.:181183-52-8
- DEL-22379
Catalog No.:BCC6521
CAS No.:181223-80-3
- Ginsenoside F4
Catalog No.:BCN2881
CAS No.:181225-33-2
- Taxuspine W
Catalog No.:BCN6937
CAS No.:181309-92-2
- Colutehydroquinone
Catalog No.:BCN8239
CAS No.:181311-16-0
- PD 160170
Catalog No.:BCC7284
CAS No.:181468-88-2
- Isonemerosin
Catalog No.:BCN6550
CAS No.:181524-79-8
- tert-Butyldimethylsilyl Chloride
Catalog No.:BCC2796
CAS No.:18162-48-6
- SB 228357
Catalog No.:BCC7036
CAS No.:181629-93-6
- Valdecoxib
Catalog No.:BCC4441
CAS No.:181695-72-7
- Interiotherins A
Catalog No.:BCN3093
CAS No.:181701-06-4
Quality Assessment of Kumu Injection, a Traditional Chinese Medicine Preparation, Using HPLC Combined with Chemometric Methods and Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Multiple Alkaloids by Single Marker.[Pubmed:29642544]
Molecules. 2018 Apr 9;23(4). pii: molecules23040856.
Kumu injection (KMI) is a common-used traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) preparation made from Picrasma quassioides (D. Don) Benn. rich in alkaloids. An innovative technique for quality assessment of KMI was developed using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) combined with chemometric methods and qualitative and quantitative analysis of multi-components by single marker (QAMS). Nigakinone (PQ-6, 5-hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one), one of the most abundant alkaloids responsible for the major pharmacological activities of Kumu, was used as a reference substance. Six alkaloids in KMI were quantified, including 6-hydroxy-beta-carboline-1-carboxylic acid (PQ-1), 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one (PQ-2), beta-carboline-1-carboxylic acid (PQ-3), beta-carboline-1-propanoic acid (PQ-4), 3-methylcanthin-5,6-dione (PQ-5), and PQ-6. Based on the outcomes of twenty batches of KMI samples, the contents of six alkaloids were used for further chemometric analysis. By hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA), radar plots, and principal component analysis (PCA), all the KMI samples could be categorized into three groups, which were closely related to production date and indicated the crucial influence of herbal raw material on end products of KMI. QAMS combined with chemometric analysis could accurately measure and clearly distinguish the different quality samples of KMI. Hence, QAMS is a feasible and promising method for the quality control of KMI.
Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of 4,5-dimethoxycanthin-6-one and its major metabolites in rats.[Pubmed:28258983]
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2017 May 30;139:22-29.
4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one and 5-hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one are the active ingredients of P. quassiodes. In the present work, a LC-MS/MS method was developed for the determination of 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one and its major metabolites 5-hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one (M1) and 4-hydroxy-5-methoxycanthin-6-one (M2) in rat plasma and tissues, and applied to study their pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution after intramuscular administration of 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one to rats. By protein precipitation with methanol for plasma samples and liquid-liquid extraction with ethyl acetate for tissue samples, the analytes were separated on an ODS C18 column with a mobile phase consisted of methanol and water (0.1% formic acid), and quantified by a MS detector in positive multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode. MS transitions were m/z 281.0-->167.1 for 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one, m/z 267.0-->168.1 for M1 and M2, m/z 251.0-->195.1 for 3-methylcanthin-2,6-dione (IS). The pharmacokinetic results indicate that 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one is absorbed rapidly (Tmax=5.4-6.4min), distributed rapidly and widely in the order of liver>kidney approximately lung approximately large intestine approximately small intestine, and eliminated quickly (t1/2z=64.9-77.7min) following the intramuscular administration. Furthermore, M1 and M2 were detected only in rat plasma and liver at the indicated times after the intramuscular administration.
Identification of in vivo and in vitro metabolites of 4,5-dimethoxycanthin-6-one by HPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS.[Pubmed:27030894]
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016 May 1;1020:78-84.
4,5-Dimthexycanthin-6-one and 5-hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one are the main active ingredients of Picrasma quassioides, which is a widely used herbal medicine for the treatment of gastroenteritis, snakebite, infection and hypertension in China. In the present study, the in vitro metabolites of 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one in rat, mouse, dog and human liver microsomes, as well as the in vivo metabolites in rat plasma and urine following a single oral dose of 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one, were identified by high-performance liquid chromatography combined with triple TOF mass spectrometry (HPLC-TOF/MS/MS). The metabolites were elucidated based on an accurate mass measurement, the MS/MS fragmentation patterns, the retention times of the parent drug and its metabolites, and the relevant drug biotransformation rules. After incubation in liver mcrosomes for 50 min, 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one produced 8 phase I metabolites including 2 mono-demethylated metabolites (M1, M2), 3 mono-hydroxylated metabolites (M3-M5), and 3 mono-demethylated and mono-hydroxylated metabolites (M6-M8) in rat and mouse liver microsomes, 7 phase I metabolites (without M7) in dog and human liver microsomes. After a single oral administration of 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one to rats, there were 3 phase I metabolites (M1, M2 and M5) detected in rat plasma and 5 phase I metabolites (M1-M5) in rat urine. Phase II metabolites were not detected in rat plasma and urine. Among these metabolites, mono-demethylated metabolites (M1 and M2) were the major metabolites of 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one, mono-hydroxylated metabolites (M3-M5) were the minor metabolites of 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one.
The pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of three canthinone alkaloids after administration of Kumu injection to rats.[Pubmed:26806576]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Apr 22;182:235-41.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Kumu injection (KMI) is made from the branches and stems of Picrasma quassiodes (D. Don) Benn. and has been used clinically for the treatment of upper respiratory tract infection, acute tonsillitis, enteritis and bacillary dysentery. 3-methylcanthin-2,6-dione, 5-hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one, 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one are the active ingredients of KMI because of its therapeutic effects. AIM OF THE STUDY: To develop a LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of three active canthinone alkaloids (4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one, 5-hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one and 3-methylcanthin-2,6-dione) in rat plasma and for the pharmacokinetic study of them after administered of KMI to rats. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Rats were divided into 5 groups (n=5 per group), 3 groups administered intramuscularly with a single dose of KMI at 0.30, 0.45 and 0.90mL/kg respectively, and the other 2 groups administered intragastically or intravenously a single dose of KMI at 0.9mL/kg respectively. The concentrations of 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one, 5-hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one and 3-methylcanthin-2,6-dione in plasma were determined by the established LC-MS/MS method at different time points and the pharmacokinetic parameters were estimated by non-compartmental analysis. RESULTS: Pharmacokinetic results indicated that all of the alkaloids were absorbed rapidly and 3-methylcanthin-2,6-dione was eliminated fastest in rats. After intramuscular administration of KMI to rats, the absolute bioavailability is excellent, and the pharmacokinetic profiles are characterized by the first order kinetics. CONCLUSION: The established method is suitable for the quantitation of the three alkaloids in rat plasma. And this pharmacokinetic study suggested that intramuscular injection of KMI was suitable in clinical usage.
Simultaneous quantification of two canthinone alkaloids of Picrasma quassioides in rat plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and its application to a rat pharmacokinetic study.[Pubmed:25725320]
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2015 Apr 1;986-987:100-7.
Picrasma quassioides (D. Don) Benn. is used in traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of inflammation. Characteristic components of the medicinal extract are canthinone alkaloids. In this study, a sensitive and rapid liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry method has been developed for simultaneous quantification of two major canthinone alkaloids, 5-hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one and 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one, in rat plasma after oral administration of P. quassioides extract (200 mg/kg). The chromatographic separation was performed on a C18 column using acetonitrile-aqueous 0.1% formic acid (90:10, v/v) as the mobile phase. Plasma samples were prepared for analysis using a simple liquid-liquid extraction with ethyl acetate. Analytes were detected using tandem mass spectrometry in positive multiple reaction monitoring mode. Method validation revealed excellent linearity over the range 1.25-900 ng/mL for 5-hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one and 0.5-800 ng/mL for 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one with satisfactory intra- and inter-day precision, accuracy and recovery. Samples were stable under the conditions tested. The pharmacokinetic profiles of the analytes in rats showed that both canthinones were rapidly absorbed and that 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one was eliminated faster than 5-hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one.
[Study on chemical constituents of Picrasma quassioides].[Pubmed:21761728]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2011 Apr;36(7):886-90.
To study the chemical constituents of Picrasma quassioides. The chemical constituents were isolated and purified by chromatographic methods over Sephadex LH-20 and silica gel column, and structurally elucidated by spectral analysis, including UV, IR, MS, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR. Fourteen compounds were obtained and identified as trifolirhizin(1), maackiain(2), 3', 7-dihydroxy-4'-methoxylisoflavone(3), umbelliferone(4), emodin(5), nigakilactone F(6), picrasin B(7),picraqualide B (8),4-methoxy-5-hydroxycanthin-6-one(9), 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one (10),5-methoxycanthin-6-one(11), 11-hydroxycanthin-6-one(12) , 1-methoxycarbonyl-beta-carboline(13), 1-hydroxymethyl-beta-carboline(14). Compounds 1-5 are reported from the first time for the genus Pricrasma.
Canthin-6-one alkaloids from Picrasma quassioides and their cytotoxic activity.[Pubmed:19031238]
J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2008 Nov-Dec;10(11-12):1009-12.
A new alkaloid, 4,5-dimethoxy-10-hydroxycanthin-6-one (1), was isolated from the stem of Picrasma quassioides Bennet (Simaroubaceae) together with four known canthin-6-one alkaloids, 8-hydroxycanthin-6-one (2), 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one (3), 5-hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one (4), and 3-methylcanthin-5,6-dione (5). Their structures were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic data. The cytotoxic activity of the canthin-6-one alkaloids was evaluated using human nasopharyngeal carcinoma (CNE2) and human liver cancer (Bel-7402) cell lines. Among these isolates, compounds 1-4 exhibited significant cytotoxic activity against CNE2 cell line.
Cytotoxic constituents of the twigs of Simarouba glauca collected from a plot in Southern Florida.[Pubmed:15852485]
Phytother Res. 2005 Feb;19(2):136-40.
Activity-guided fractionation of a chloroform-soluble extract of Simarouba glauca twigs collected from a plot in southern Florida, and monitored with a human epidermoid (KB) tumor cell line, afforded six canthin-6-one type alkaloid derivatives, canthin-6-one (1), 2-methoxycanthin-6-one (2), 9-methoxycanthin-6-one (3), 2-hydroxycanthin-6-one (4), 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one (5) and 4,5-dihydroxycanthin-6-one (6), a limonoid, melianodiol (7), an acyclic squalene-type triterpenoid, 14-deacetyleurylene (8), two coumarins, scopoletin (9) and fraxidin (10), and two triglycerides, triolein (11) and trilinolein (12). Among these isolates, compounds 1-4, 7 and 8 exhibited cytotoxic activity against several human cancer cell lines. 14-Deacetyleurylene (8) was selectively active against the Lu1 human lung cancer cell line, but was inactive in an in vivo hollow fiber assay using this same cell type.
[Indole alkaloids of Odyendea gabonensis].[Pubmed:17396971]
Planta Med. 1982 Nov;46(3):187-9.
From the trunk bark of Odyendea gabonensis six indole alkaloids have been isolated: Canthin-6-one (I); 5-Methoxy-canthin-6-one (II); 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one (III); 8-Hydroxy-canthin-6-one (IV); 1-Hydroxy-methyl-beta-carboline (V); and 1-Carboxamide-beta-carboline (VI). This is the first report of these products from this plant.


