Co 102862State-dependent of voltage-gated sodium channels CAS# 181144-66-1 |
- PF-4708671
Catalog No.:BCC5031
CAS No.:1255517-76-0
- BIX 02565
Catalog No.:BCC4303
CAS No.:1311367-27-7
- BI-D1870
Catalog No.:BCC5030
CAS No.:501437-28-1
- FMK
Catalog No.:BCC1580
CAS No.:821794-92-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

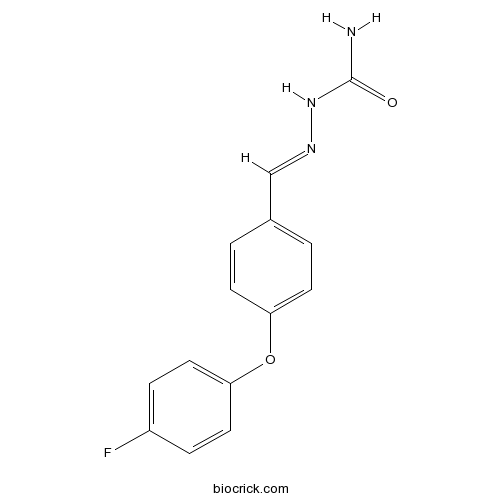
| Cas No. | 181144-66-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9816959 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H12FN3O2 | M.Wt | 273.26 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | V102862 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | [(E)-[4-(4-fluorophenoxy)phenyl]methylideneamino]urea | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1C=NNC(=O)N)OC2=CC=C(C=C2)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MHUUDVZSPFRUSK-RQZCQDPDSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H12FN3O2/c15-11-3-7-13(8-4-11)20-12-5-1-10(2-6-12)9-17-18-14(16)19/h1-9H,(H3,16,18,19)/b17-9+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Broad spectrum, state-dependent blocker of voltage-gated sodium channels. Displays ~ 80-fold higher affinity for inactivated Na+ channels compared to channels in the resting state. Anticonvulsant; displays activity in rodent models of tonic/clonic and partial-complex seizures. |

Co 102862 Dilution Calculator

Co 102862 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6595 mL | 18.2976 mL | 36.5952 mL | 73.1904 mL | 91.488 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7319 mL | 3.6595 mL | 7.319 mL | 14.6381 mL | 18.2976 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.366 mL | 1.8298 mL | 3.6595 mL | 7.319 mL | 9.1488 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0732 mL | 0.366 mL | 0.7319 mL | 1.4638 mL | 1.8298 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0366 mL | 0.183 mL | 0.366 mL | 0.7319 mL | 0.9149 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN1143
CAS No.:18110-87-7
- 5-Hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN1142
CAS No.:18110-86-6
- Proflavine Hemisulfate
Catalog No.:BCC4707
CAS No.:1811-28-5
- 5,7-Dihydroxy-3',4',5'-trimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN6807
CAS No.:18103-42-9
- Corymbosin
Catalog No.:BCN6812
CAS No.:18103-41-8
- Curcumaromin C
Catalog No.:BCN7418
CAS No.:1810034-40-2
- Curcumaromin B
Catalog No.:BCN7419
CAS No.:1810034-39-9
- Curcumaromin A
Catalog No.:BCN7417
CAS No.:1810034-38-8
- 3-O-Caffeoylshikimic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7930
CAS No.:180981-12-8
- FTI 277 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC6395
CAS No.:180977-34-8
- Neuchromenin
Catalog No.:BCN7449
CAS No.:180964-26-5
- Spiramilactone B
Catalog No.:BCN1141
CAS No.:180961-65-3
- Almotriptan Malate
Catalog No.:BCC5045
CAS No.:181183-52-8
- DEL-22379
Catalog No.:BCC6521
CAS No.:181223-80-3
- Ginsenoside F4
Catalog No.:BCN2881
CAS No.:181225-33-2
- Taxuspine W
Catalog No.:BCN6937
CAS No.:181309-92-2
- Colutehydroquinone
Catalog No.:BCN8239
CAS No.:181311-16-0
- PD 160170
Catalog No.:BCC7284
CAS No.:181468-88-2
- Isonemerosin
Catalog No.:BCN6550
CAS No.:181524-79-8
- tert-Butyldimethylsilyl Chloride
Catalog No.:BCC2796
CAS No.:18162-48-6
- SB 228357
Catalog No.:BCC7036
CAS No.:181629-93-6
- Valdecoxib
Catalog No.:BCC4441
CAS No.:181695-72-7
- Interiotherins A
Catalog No.:BCN3093
CAS No.:181701-06-4
- Cyclopiazonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6981
CAS No.:18172-33-3
V102862 (Co 102862): a potent, broad-spectrum state-dependent blocker of mammalian voltage-gated sodium channels.[Pubmed:15778702]
Br J Pharmacol. 2005 Mar;144(6):801-12.
1. 4-(4-Fluorophenoxy)benzaldehyde semicarbazone (V102862) was initially described as an orally active anticonvulsant with robust activity in a variety of rodent models of epilepsy. The mechanism of action was not known. We used whole-cell patch-clamp techniques to study the effects of V102862 on native and recombinant mammalian voltage-gated Na+ channels. 2. V102862 blocked Na+ currents (I(Na)) in acutely dissociated cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Potency increased with membrane depolarization, suggesting a state-dependent mechanism of inhibition. There was no significant effect on the voltage dependence of activation of I(Na). 3. The dissociation constant for the inactivated state (K(I)) was approximately 0.6 microM, whereas the dissociation constant for the resting state (K(R)) was >15 microM. 4. The binding to inactivated channels was slow, requiring a few seconds to reach steady state at -80 mV. 5. The mechanism of inhibition was characterized in more detail using human embryonic kidney-293 cells stably expressing rat brain type IIA Na+ (rNa(v)1.2) channels, a major Na+ channel alpha subunit in rat hippocampal neurons. Similar to hippocampal neurons, V102862 was a potent state-dependent blocker of rNa(v)1.2 channels with a K(I) of approximately 0.4 microM and K(R) approximately 30 microM. V102862 binding to inactivated channels was relatively slow (k(+) approximately = 1.7 microM(-1) s(-1)). V102862 shifted the steady-state availability curve in the hyperpolarizing direction and significantly retarded recovery of Na+ channels from inactivation. 6. These results suggest that inhibition of voltage-gated Na+ channels is a major mechanism underlying the anticonvulsant properties of V102862. Moreover, understanding the biophysics of the interaction may prove to be useful in designing a new generation of potent Na+ channel blocker therapeutics.
Development of a high-performance liquid chromatographic-tandem mass spectrometric method for the determination of pharmacokinetics of Co 102862 in mouse, rat, monkey and dog plasma.[Pubmed:11129068]
J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 2000 Nov 10;749(1):1-15.
A method for determining concentration levels of Co 102862 in mouse, rat, monkey and dog plasma was validated in the range of 5 to 2000 ng/ml using 200 microl plasma sample volume. This validation report describes the linearity, specificity, sensitivity, reproducibility, accuracy, recovery and stability of the analytical method. The inter-day RSD ranged from 3.5 to 10.1%, intra-day RSD from 0.6 to 5.7% and intra-day accuracy (mean absolute percent difference) ranged from 2.2 to 14.9% for rat, monkey and dog plasma. A mini-validation (5-2000 ng/ml) of Co 102862 was performed in mouse plasma using the same methods. Additionally, the assay range at the low end was successfully extended to 0.5 ng/ml for monkey plasma. The method was used for the routine analysis of Co 102862 in mouse, rat, monkey and dog plasma and summary of the pharmacokinetic data are presented.
Pharmacology of 2-[4-(4-chloro-2-fluorophenoxy)phenyl]-pyrimidine-4-carboxamide: a potent, broad-spectrum state-dependent sodium channel blocker for treating pain states.[Pubmed:16728593]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Sep;318(3):1083-93.
Voltage-gated Na(+) channels may play important roles in establishing pathological neuronal hyperexcitability associated with chronic pain in humans. Na(+) channel blockers, such as carbamazepine (CBZ) and lamotrigine (LTG), are efficacious in treating neuropathic pain; however, their therapeutic utility is compromised by central nervous system side effects. We reasoned that it may be possible to gain superior control over pain states and, in particular, a better therapeutic index, by designing broad-spectrum Na(+) channel blockers with higher potency, faster onset kinetics, and greater levels of state dependence than existing drugs. 2-[4-(4-Chloro-2-fluorophenoxy)phenyl]-pyrimidine-4-carboxamide (PPPA) is a novel structural analog of the state-dependent Na(+) channel blocker V102862 [4-(4-fluorophenoxy)benzaldehyde semicarbazone]. Tested on recombinant rat Na(v)1.2 channels and native Na(+) currents in cultured rat dorsal root ganglion neurons, PPPA was approximately 1000 times more potent, had 2000-fold faster binding kinetics, and > or =10-fold higher levels of state dependence than CBZ and LTG. Tested in rat pain models against mechanical endpoints, PPPA had minimal effective doses of 1 to 3 mg/kg p.o. in partial sciatic nerve ligation, Freund's complete adjuvant, and postincisional pain. In all cases, efficacy was similar to clinically relevant comparators. Importantly, PPPA did not produce motor deficits in the accelerating Rotarod assay of ataxia at doses up to 30 mg/kg p.o., indicating a therapeutic index >10, which was superior to CBZ and LTG. Our experiments suggest that high-potency, broad-spectrum, state-dependent Na(+) channel blockers will have clinical utility for treating neuropathic, inflammatory, and postsurgical pain. Optimizing the biophysical parameters of broad-spectrum voltage-gated Na(+) channel blockers may lead to improved pain therapeutics.


