Ginsenoside F4CAS# 181225-33-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 181225-33-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 102004835 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C42H70O12 | M.Wt | 767.0 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
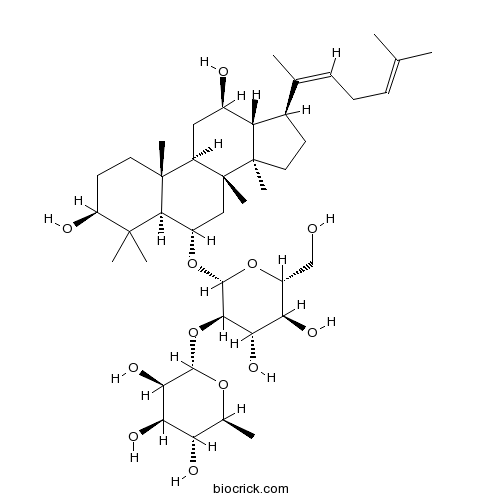
| Chemical Name | (2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-2-[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-[[(3S,5R,6S,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R,17S)-3,12-dihydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-[(2Z)-6-methylhepta-2,5-dien-2-yl]-2,3,5,6,7,9,11,12,13,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-6-yl]oxy]-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]oxy-6-methyloxane-3,4,5-triol | ||
| SMILES | CC1C(C(C(C(O1)OC2C(C(C(OC2OC3CC4(C(CC(C5C4(CCC5C(=CCC=C(C)C)C)C)O)C6(C3C(C(CC6)O)(C)C)C)C)CO)O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QOMBXPYXWGTFNR-KRPFXEAISA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C42H70O12/c1-20(2)11-10-12-21(3)23-13-16-41(8)29(23)24(44)17-27-40(7)15-14-28(45)39(5,6)36(40)25(18-42(27,41)9)52-38-35(33(49)31(47)26(19-43)53-38)54-37-34(50)32(48)30(46)22(4)51-37/h11-12,22-38,43-50H,10,13-19H2,1-9H3/b21-12-/t22-,23+,24+,25-,26+,27+,28-,29-,30-,31+,32+,33-,34+,35+,36-,37-,38+,40+,41+,42+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Ginsenoside F4 has inhibitory effect on human lymphocytoma JK cell by inducing its apoptosis, the mechanism is related to the mitochondrial dysfunction and the increase of Bax expression and decrease of Bcl-2 expression. Ginsenoside F4 also has strongly inhibit activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in signal transduction pathways. |
| Targets | Bcl-2/Bax | MMP(e.g.TIMP) | IL Receptor | p38MAPK |
| In vitro | The apoptosis-inducing effect of ginsenoside F4 from steamed notoginseng on human lymphocytoma JK cells.[Pubmed: 23962295]Nat Prod Res. 2013;27(24):2351-4.
Ginsenosides from Korean red ginseng inhibit matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in articular chondrocytes and prevent cartilage degradation.[Pubmed: 24384406]Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 Feb 5;724:145-51.Among the mammalian matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), MMP-1, -3 and -13 are collagenases. Particularly, MMP-13 is important for the degradation of major collagens in cartilage under certain pathological conditions such as osteoarthritis. |

Ginsenoside F4 Dilution Calculator

Ginsenoside F4 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.3038 mL | 6.5189 mL | 13.0378 mL | 26.0756 mL | 32.5945 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2608 mL | 1.3038 mL | 2.6076 mL | 5.2151 mL | 6.5189 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1304 mL | 0.6519 mL | 1.3038 mL | 2.6076 mL | 3.2595 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0261 mL | 0.1304 mL | 0.2608 mL | 0.5215 mL | 0.6519 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.013 mL | 0.0652 mL | 0.1304 mL | 0.2608 mL | 0.3259 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- DEL-22379
Catalog No.:BCC6521
CAS No.:181223-80-3
- Almotriptan Malate
Catalog No.:BCC5045
CAS No.:181183-52-8
- Co 102862
Catalog No.:BCC7439
CAS No.:181144-66-1
- 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN1143
CAS No.:18110-87-7
- 5-Hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN1142
CAS No.:18110-86-6
- Proflavine Hemisulfate
Catalog No.:BCC4707
CAS No.:1811-28-5
- 5,7-Dihydroxy-3',4',5'-trimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN6807
CAS No.:18103-42-9
- Corymbosin
Catalog No.:BCN6812
CAS No.:18103-41-8
- Curcumaromin C
Catalog No.:BCN7418
CAS No.:1810034-40-2
- Curcumaromin B
Catalog No.:BCN7419
CAS No.:1810034-39-9
- Curcumaromin A
Catalog No.:BCN7417
CAS No.:1810034-38-8
- 3-O-Caffeoylshikimic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7930
CAS No.:180981-12-8
- Taxuspine W
Catalog No.:BCN6937
CAS No.:181309-92-2
- Colutehydroquinone
Catalog No.:BCN8239
CAS No.:181311-16-0
- PD 160170
Catalog No.:BCC7284
CAS No.:181468-88-2
- Isonemerosin
Catalog No.:BCN6550
CAS No.:181524-79-8
- tert-Butyldimethylsilyl Chloride
Catalog No.:BCC2796
CAS No.:18162-48-6
- SB 228357
Catalog No.:BCC7036
CAS No.:181629-93-6
- Valdecoxib
Catalog No.:BCC4441
CAS No.:181695-72-7
- Interiotherins A
Catalog No.:BCN3093
CAS No.:181701-06-4
- Cyclopiazonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6981
CAS No.:18172-33-3
- (-)-beta-Pinene
Catalog No.:BCN3857
CAS No.:18172-67-3
- 25-Anhydrocimigenol 3-O-beta-D-xyloside
Catalog No.:BCN3436
CAS No.:181765-11-7
- Crotonoside
Catalog No.:BCN6281
CAS No.:1818-71-9
Ginsenosides from Korean red ginseng inhibit matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in articular chondrocytes and prevent cartilage degradation.[Pubmed:24384406]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 Feb 5;724:145-51.
Among the mammalian matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), MMP-1, -3 and -13 are collagenases. Particularly, MMP-13 is important for the degradation of major collagens in cartilage under certain pathological conditions such as osteoarthritis. To establish a potential therapeutic strategy for cartilage degradation disorders, the effects of 11 ginseng saponins (ginsenosides Rb1, Rb2, Rc, Rd, Re, Rf, Rg1, Rg3, Rg5, Rk1 and F4) on MMP-13 induction were examined in a human chondrocyte cell line, SW1353. Among these, several saponins including ginsenoside Rc, Rd, Rf, Rg3 and F4 were found to inhibit MMP-13 expression in IL-1beta-treated SW1353 cells at non-cytotoxic concentrations (1-50 muM). The most prominent inhibitors were ginsenosides F4 and Rg3. Ginsenoside F4 inhibited MMP-13 expression 33.5% (P<0.05), 57.9% (P<0.01) and 90.0% (P<0.01) at 10, 30 and 50 muM, respectively. Significantly, Ginsenoside F4 was found to strongly inhibit activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in signal transduction pathways (86.6 and 100.0% inhibition at 30 and 50 muM, P<0.01). The MMP-13 inhibitory effect was also supported by the finding that ginsenosides F4 and Rg3 reduced glycosaminoglycan release from IL-1alpha-treated rabbit joint cartilage culture to some degree. Taken together, these results indicate that several ginsenosides inhibit MMP-13 expression in IL-1beta-treated chondrocytes. Ginsenoside F4 and Rg3 blocked cartilage breakdown in rabbit cartilage tissue culture. Thus, it is suggested that certain ginsenosides have therapeutic potential for preventing cartilage collagen matrix breakdown in diseased tissues such as those found in patients with arthritic disorders.
The apoptosis-inducing effect of ginsenoside F4 from steamed notoginseng on human lymphocytoma JK cells.[Pubmed:23962295]
Nat Prod Res. 2013;27(24):2351-4.
In this study, the inhibitory and apoptosis-inducing effect of Ginsenoside F4 (GF4) from steamed notoginseng was investigated by using human lymphocytoma Jurkat (JK) cell. Cell Counting Kit-8 method was then used to assess the anti-proliferative effect of GF4, and Western blotting was run to detect the expression level of two apoptosis-related proteins including Bax and the Bcl-2. The results suggested that GF4 can effectively inhibit the proliferation of the cells, and Bax expression increased gradually, but Bcl-2 expression reduced with the increase of GF4 concentration. In conclusion, GF4 has inhibitory effect on human lymphocytoma JK cell by inducing its apoptosis. The mechanism of action could be related to the mitochondrial dysfunction and the increase of Bax expression and decrease of Bcl-2 expression by GF4.


