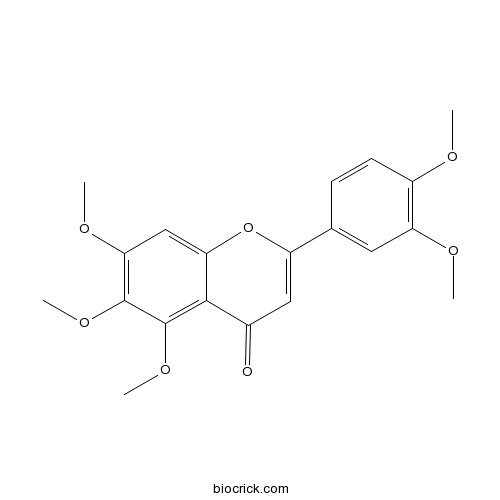
A pentamethoxyflavone that is flavone substituted by methoxy groups at positions 5, 6, 7, 3' and 4' respectively.
InChI=1S/C20H20O7/c1-22-13-7-6-11(8-15(13)23-2)14-9-12(21)18-16(27-14)10-17(24-3)19(25-4)20(18)26-5/h6-10H,1-5H3
Sinensetin is a polymethoxylated flavonoids in citrus fruit, as a novel antiangiogenesis agent, has potential for anti-carcinogenesis, antitumor, and cardiovascular protective activity.[1]
Sinensetin has antioxidative effect and has anti-inflammatory by regulating the protein level of inhibitorκB-α, which may be utilized in the development of novel anti-inflammatory treatments.[2-4]
Sinensetin enhances activation of protein kinase A and increases intracellular cAMP levels in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes, it stimulates lipolysis via a cAMP pathway in mature 3T3-L1 adipocytes, suggests that sinensetin enhances adipogenesis and lipolysis by increasing cAMP levels in adipocytes.[5]
English website: Sinensetin
Japanese website: Sinensetin
Chinese website: Sinensetin
[1] Lam I K, Alex D, You-Hua Wang †, et al. Mol Nut Food Res, 2012, 56(6):945–56.
[2] M. Amzad Hossain, S.M. Salehuddin, M.J. Kabir, et al. Food Chem 2009, 113(1):185-90.
[3] Laavola M, Nieminen R, Yam M F, et al. Planta Med, 2012, 78(8):779-86.
[4] Shin H S, Kang S I, Yoon S A, et al. Biosci Biotech Biochem, 2012, 76(4):847-9.
[5] Kang S I, Shin H S, Kim S J. Biol Pharm Bull, 2015, 38(4):552-8.
[6] Mun F Y, Elsnoussi Ali Hussin Mohamed, Lee Fung Ang,et al. J Acupuncture & Meridian Studies, 2012, 5(4):176-82.