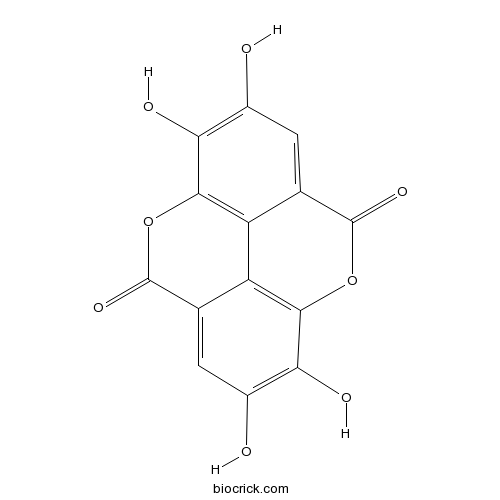
An organic heterotetracyclic compound resulting from the formal dimerisation of gallic acid by oxidative aromatic coupling with intramolecular lactonisation of both carboxylic acid groups of the resulting biaryl. It is found in many fruits and vegetables, including raspberries, strawberries, cranberries, and pomegranates.
InChI=1S/C14H6O8/c15-5-1-3-7-8-4(14(20)22-11(7)9(5)17)2-6(16)10(18)12(8)21-13(3)19/h1-2,15-18H
Ellagic acid, a naturally occurring plant phenol, inhibits the activity of the direct-acting mutagen N-methyl-N-nitrosourea (MeNU) in Salmonella typhimurium TA100, is due to specific inhibition of methylation at the O6 position of guanine through an ellagic acid-duplex DNA affinity-binding mechanism.[1]
Ellagic acid has anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, can inhibit key cell functions and activation of PSCs, including platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-BB, interleukin (IL)-1beta, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, alpha-smooth muscle actin and collagen genes. [2]
Ellagic acid has antioxidant and apoptosis-inducing activities, shows high DPPH radical scavenging and peroxidation inhibition activities, significantly reduces HOS cell proliferation, and induces apoptosis evidenced by chromosomal DNA degradation and apoptotic body appearance.[3]
English website: Ellagic acid
Japanese website: Ellagic acid
Chinese website: Ellagic acid
[1] Dixit R, Gold B. P Natl Acad Sci USA, 1986, 83(21):8039-43.
[2] Masamune A, Satoh M, Kikuta K, et al. Biochem Pharmacol, 2005, 70(6):869-78.
[3] Han D H, Lee M J, Kim J H. Anticancer Res, 2006, 26(5A):3601-6.
[4] Ou L M, Seken A, Li K A, et al. Int J Pharm Res, 2015, 42(05):637-41.