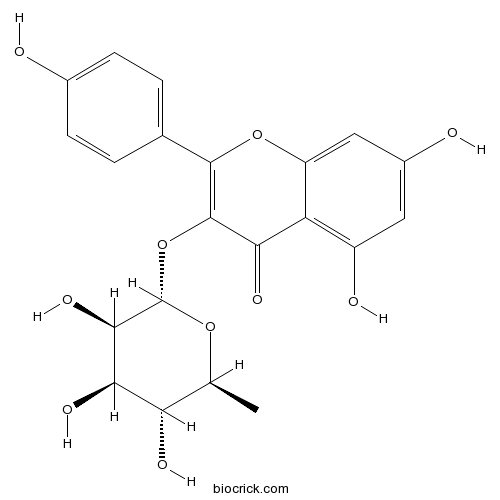
A glycosyloxyflavone that is kaempferol attached to a α-L-rhamnosyl residue at position 3 via a glycosidic linkage.
Afzelin, isolated from Cornus macrophylla, has antibacterial effects on Pseudomonas aeruginosa, its minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is 31 µg/mL.[1]
Afzelin has several cellular activities such as DNA-protective, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory as well as UV-absorbing activity and may protect human skin from UVB-induced damage by a combination of UV-absorbing and cellular activities.[2]
Afzelin has potenial anti-cancer activity against prostate cancer, the activity is due to inhibition of LIM domain kinase 021 expression, it can inhibit the proliferation of LNCaP and PC302cells, and block the cell cycle in the G002phase.[3]
Afzelin can attenuate asthma phenotypes is based on reduction of Th2 cytokine via inhibition of GATA-binding protein 3 transcription factor, which is the master regulator of Th2 cytokine differentiation and production.[4]
Afzelin promotes melanogenesis by occurs through increased MITF gene expression, which is mediated by activation of p38 MAPK, and suggest that afzelin may be useful as a protective agent against ultraviolet irradiation. [5]
[1] Lee S Y, So Y J, Shin M S, et al. Molecules, 2014, 19(3):3173-80.
[2] Shin S W, Jung E, Kim S, et al. Plos One, 2013, 8(4):e61971-e61971.
[3] Zhu K C, Sun J M, Shen J G, et al. Oncol Lett, 2015, 10(4):2359-65.
[4] Zhou W, Nie X. Mol Med Rep, 2015, 12(1):71-6.
[5] Jung E, Jin H K, Mi O K, et al. Chem-Biol Interact, 2016, 254:167-72.
[6] Huo L, Chen X H, Cao Y, et al. Chinese J Pharm Anal, 2010(05):831-3.