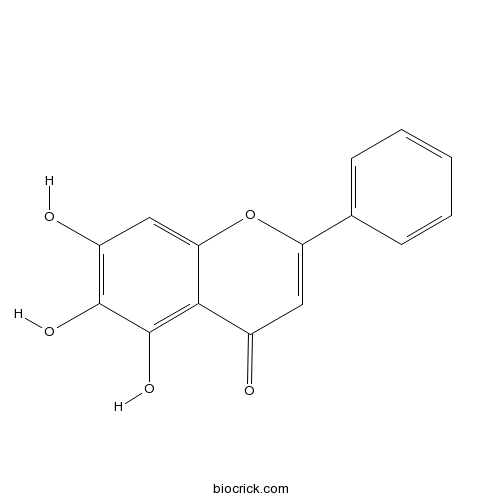
A trihydroxyflavone with the hydroxy groups at positions C-5, -6 and -7.
Baicalin, saikosaponins, and baicalein have antitumor effects on human hepatoma cell lines and bladder cancer cell lines.[1,2]
Baicalin, wogonin,and baicalein inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 gene expressions induced by nitric oxide synthase inhibitors and lipopolysaccharide .[3]
Baicalin and its aglycone baicalein have widely investigated in hematological malignancies because both of them exhibit remarkable pharmacological properties.[4]
Baicalin, baicalein, and wogonin have antioxidant and free radical scavenging effects.[5]
Baicalin exhibits the greatest inhibition activity against carrageenan-induced rat paw edema.[6]
Baicalein can induce cancer cell death and proliferation retardation by the inhibition of CDC2 kinase and survivin associated with opposite role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and AKT.[7]
[1] Motoo Y, Sawabu N. Cancer Lett, 1994, 86(1):91-5.
[2] Ikemoto S, Sugimura K, Yoshida N, et al. Urology, 2000, 55(6):951-5.
[3] Chen Y C, Shen S C, Chen L G, et al. Biochem Pharmacol, 2001, 61(11):1417-27.
[4] Chen H, Gao Y, Wu J, et al. Cancer Lett, 2014, 354(1):5-11.
[5] Shieh D E, Liu L T, Lin C C. Anticancer Res, 2000, 20(5A):2861-5.
[6] ChunChing Lin, DenEn Shieh. Am J Chinese Med, 1996, 24(1):31-6.
[7] Chao J, Su W H. Mol Cancer Ther, 2007, 6(11):3039-48.
[8] Dong W J, Liu Y L. Chinese J Pharma Anal, 2009, 29(3):2120-2.