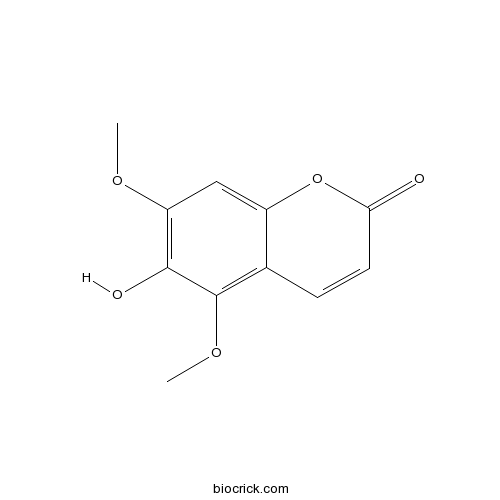
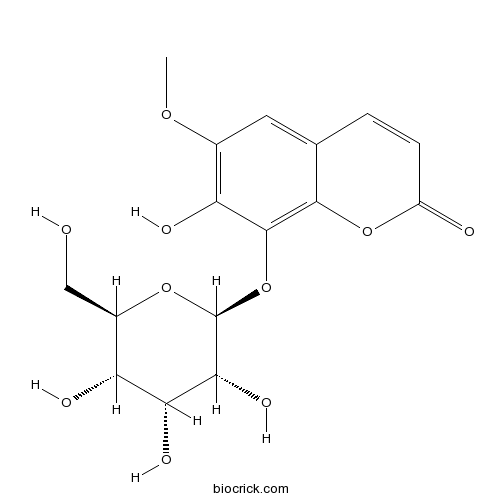
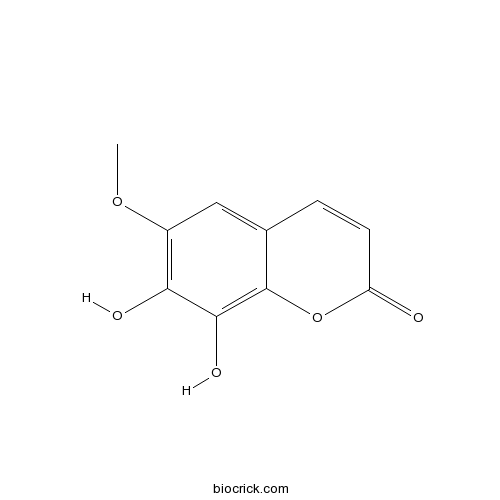
Fraxinus chinensis Roxb
Fraxinus chinensis Roxb
Trees 3-20 m. Branchlets glabrous, sparsely villous puberulent or tomentose; buds broadly ovoid or conical, brown tomentose, pubescent or glandular hairy. Leaves 12-35 cm; petiole 3-9 cm; axis puberulent or pilose at first, leaflet joint glabrous or densely tomentose; leaflets 3-7(-9). The bark is analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antitussive, astringent, diuretic, expectorant and stomachic. It controls bacterial infections and coughs. It is used in the treatment of apoplexy, liver diseases, diarrhoea, dysentery, eye diseases such as cataracts, cough and asthma. The bark contains aesculin, this has anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant and analgesic actions. The bark also contains fraxetin. This has an inhibitory effect on the central nervous system, is a stronger and safer anodyne than aspirin and has some antibacterial activity. The seeds, popularly known as keys or helicopter seeds, are a type of fruit known as a samara.