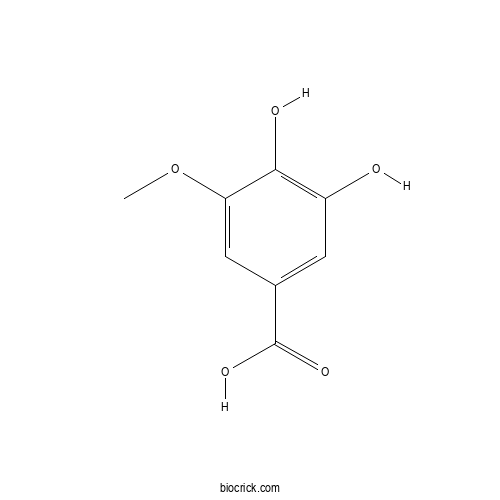
3,4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxybenzoic acidCAS# 3934-84-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 3934-84-7 | SDF | File under preparation. |
| PubChem ID | 19829 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C8H8O5 | M.Wt | 184.1 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 3,4-dihydroxy-5-methoxybenzoic acid | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=CC(=C1O)O)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KWCCUYSXAYTNKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C8H8O5/c1-13-6-3-4(8(11)12)2-5(9)7(6)10/h2-3,9-10H,1H3,(H,11,12) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

3,4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxybenzoic acid Dilution Calculator

3,4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxybenzoic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.4318 mL | 27.1592 mL | 54.3183 mL | 108.6366 mL | 135.7958 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0864 mL | 5.4318 mL | 10.8637 mL | 21.7273 mL | 27.1592 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5432 mL | 2.7159 mL | 5.4318 mL | 10.8637 mL | 13.5796 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1086 mL | 0.5432 mL | 1.0864 mL | 2.1727 mL | 2.7159 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0543 mL | 0.2716 mL | 0.5432 mL | 1.0864 mL | 1.358 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Isoarundinin II
Catalog No.:BCN0075
CAS No.:151538-56-6
- Gitoxin
Catalog No.:BCN0074
CAS No.:4562-36-1
- Procyanidin B4
Catalog No.:BCN0073
CAS No.:29106-51-2
- Undecanoic gamma-lactone
Catalog No.:BCN0072
CAS No.:104-67-6
- Homobutein
Catalog No.:BCN0071
CAS No.:34000-39-0
- Peucenidin
Catalog No.:BCN0070
CAS No.:33044-93-8
- Laricitrin
Catalog No.:BCN0069
CAS No.:53472-37-0
- Undecanolactone
Catalog No.:BCN0068
CAS No.:710-04-3
- (R)-(+)-Limonene
Catalog No.:BCN0067
CAS No.:5989-27-5
- 1,4-Cineole
Catalog No.:BCN0066
CAS No.:470-67-7
- Delta-Nonalactone
Catalog No.:BCN0065
CAS No.:3301-94-8
- Kaempferol 3,4'-diglucoside 7-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN0064
CAS No.:1131009-93-2
- Cimiaceroside A
Catalog No.:BCN0077
CAS No.:210643-83-7
- 2-Octanone
Catalog No.:BCN0078
CAS No.:111-13-7
- 3,5,7-Trihydroxy-3',4',5'-trimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN0079
CAS No.:146132-95-8
- 3,5-Dihydroxy-4-methylbenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN0080
CAS No.:28026-96-2
- Sabinyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN0081
CAS No.:53833-85-5
- Evernic acid
Catalog No.:BCN0082
CAS No.:537-09-7
- 3-Hydroxy-6-methoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN0083
CAS No.:93176-00-2
- Cascaroside A
Catalog No.:BCN0084
CAS No.:53823-08-8
- Phenethyl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCN0085
CAS No.:60-12-8
- (-)-Myrtenol
Catalog No.:BCN0086
CAS No.:19894-97-4
- Quercetin 3,5,7,3,4-pentamethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN0087
CAS No.:1247-97-8
- 2,4,6-Trihydroxybenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN0088
CAS No.:83-30-7
Antioxidant and Antiradical Properties of Selected Flavonoids and Phenolic Compounds.[Pubmed:29158919]
Biochem Res Int. 2017;2017:7616791.
Phenolic compounds and flavonoids are known by their antioxidant properties and one of the most important sources for humans is the diet. Due to the harmful effects of synthetic antioxidants such as BHA and BHT, natural novel antioxidants have become the focus of attention for protecting foods and beverages and reducing oxidative stress in vivo. In the current study, we investigated the total antioxidant, metal chelating, Fe(3+) and Cu(2+) reduction, and free radical scavenging activities of some phenolic and flavonoid compounds including malvin, oenin, ID-8, silychristin, callistephin, pelargonin, 3,4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxybenzoic acid, 2,4,6-trihydroxybenzaldehyde, and arachidonoyl dopamine. The antioxidant properties of these compounds at different concentrations (10-30 mug/mL) were compared with those of reference antioxidants such as BHA, BHT, alpha-tocopherol, and trolox. Each substance showed dose-dependent antioxidant activity. Furthermore, oenin, malvin, arachidonoyl dopamine, callistephin, silychristin, and 3,4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxybenzoic acid exhibited more effective antioxidant activity than that observed for the reference antioxidants. These results suggest that these novel compounds may function to protect foods and medicines and to reduce oxidative stress in vivo.
Inhibitory effects of some phenolic compounds on the activities of carbonic anhydrase: from in vivo to ex vivo.[Pubmed:26670706]
J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2016 Dec;31(6):1234-40.
Carbonic anhydrase (CA) inhibitors have been used for more than 60 years for therapeutic purposes in many diseases table such as in medications against antiglaucoma and as diuretics. Phenolic compounds are a new class of CA inhibitor. In our study, we tested the effects of arachidonoyl dopamine, 2,4,6-trihydroxybenzaldehyde and 3,4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxybenzoic acid on esterase and the CO2-hydratase activities of CA I and II isozymes purified from in vivo to ex vivo. The Ki values of arachidonoyl dopamine, 2,4,6-trihydroxybenzaldehyde and 3,4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxybenzoic acid were 203.80, 1170.00 and 910.00 muM, respectively for hCA I and 75.25, 354.00 and 1510.00 muM, respectively for hCA II. Additionally, IC50 values from in vivo studies were found to be in the range of 173.25-1360.0 muM for CA I and II, respectively, using CO2-hydratase activity methods. These results demonstrated that phenolic compounds used in in vivo studies could be used in different biomedical applications to inhibit approximately 30% of the CO2-hydratase activity of the total CA enzyme of rat erythrocytes.
Synthesis of 3-O-methylgallic acid a powerful antioxidant by electrochemical conversion of syringic acid.[Pubmed:23434437]
Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jun;1830(6):3643-9.
BACKGROUND: A kinetic study of the electrochemical oxidation of syringic acid (3,5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxybenzoic acid) by cyclic voltammetry at treated gold disk was combined with results of electrolyses at Ta/PbO2 anode in order to convert it into potentially high-added-value product. METHODS: The electrochemical oxidation of syringic acid was carried out in order to convert this compound to 3-O-methylgallic acid. This latter was identified by mass spectrophotometry using LC-MS/MS apparatus. The 3-O-methylgallic acid synthesis was controlled by cyclic volammetry, Ortho-diphenolicdeterminations and DPPH radical-scavenging activity. RESULTS: The proposed mechanism is based on the hypothesis of a bielectronic discharge of syringic acid molecule under free and adsorbed form involving two intermediate cation mesomers. Hydrolysis of the more stable of this last one leads to the formation of the 3,4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxybenzoic acid (3-O-methylgallic acid) as a major product. The latter aromatic compound was synthesized by anodic oxidation of syringic acid at PbO2 electrode. The cyclic voltammogram of the electrolysis bath of syringic acid shows that the anodic peak potential of 3-O-methylgallic acid was lower (Epa=128mV) than that of SA (Epa=320mV). And the strongest antiradical activity was detected when the 3-O-methylgallic acid concentration was higher". CONCLUSION: The electrochemical oxidation using PbO2 anode is a rapid, simple and efficient method tool for a conversion of SA into 3-O-methylgallic acid, a potent antioxidant derivative GENERAL SIGNIFICANCE: The electrochemical process consists in a simple transformation of the syringic acid into 3-O-methylgallic acid having a better antioxidant capacity. This result has been justified by cyclic voltametry which shows that anodic peak of 3-O-methylgallic acid is reversible. Furthermore, its potential is lower than that of the irreversible anodic peak of syringic acid to 3-O-methylgallic acid.
High performance screening, structural and molecular dynamics analysis to identify H1 inhibitors from TCM Database@Taiwan.[Pubmed:22012120]
Mol Biosyst. 2011 Dec;7(12):3366-74.
New-type oseltamivir-resistant H1N1 influenza viruses have been a major threat to human health since the 2009 flu pandemic. To resolve the drug resistance issue, we aimed to identify a new type of inhibitors against H1 from traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) by employing the world's largest TCM database () for virtual screening and molecular dynamics (MD). From the virtual screening results, sodium (+)-isolaricireinol-2 alpha-sulfate, sodium 3,4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxybenzoic acid methyl ester-4-sulfate, sodium (E)-7-hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)hept-5-ene-3S-sulfonate, and 3-methoxytyramine-betaxanthin were identified as potential drug-like compounds. MD simulation of the binding poses with the key residues Asp103 and Glu83, as well as other binding site residues, identified higher numbers of hydrogen bonds than N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (NAG), the natural ligand of the esterase domain in H1. Ionic bonds, salt bridges, and electrostatic energy also contribute to binding stability. Key binding residues include Lys71, Glu83, Asp103, and Arg238. Structural moieties promoting H-bond or salt bridge formations at these locations greatly contribute to a stable ligand-protein complex. An available sodium atom for ionic interactions with Asp103 can further stabilize the ligands. Based on virtual screening, MD simulation, and interaction energy evaluation, TCM candidates demonstrate good potential as novel H1 inhibitors. In addition, the identified stabilizing features can provide insights for designing highly stable H1 inhibitors.
A norsesquiterpene lactone and a benzoic acid derivative from the leaves of Cyclocarya paliurus and their glucosidase and glycogen phosphorylase inhibiting activities.[Pubmed:18300194]
Planta Med. 2008 Feb;74(3):287-9.
Two novel compounds, 3-methoxypterolactone ( 1) and 2-amino-3,4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxybenzoic acid ( 2), were isolated from leaves of Cyclocarya paliurus (Batal.) Iljinsk, together with nine known compounds: pterolactone ( 3), gallic acid ( 4), 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid ( 5), oleanolic acid ( 6), beta-boswellic acid ( 7), alpha-boswellic acid ( 8), beta-amyrin ( 9), beta-amyrone ( 10) and 3beta-O-trans-caffeoyl-morolic acid ( 11). The structure elucidation was based on spectroscopic methods, including two-dimensional NMR experiments ( (1)H- (1)H COSY, HMQC and HMBC). All isolated compounds were evaluated for their glycosidase and glycogen phosphorylase inhibitory activities. 2-Amino-3,4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxybenzoic acid and gallic acid showed significant alpha-glucosidase and glycogen phosphorylase inhibitory activities.


