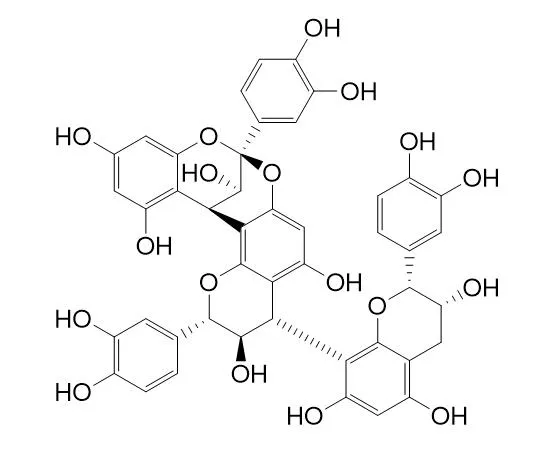
Aesculitannin BCAS# 114612-77-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 114612-77-0 | SDF | File under preparation. |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C45H36O18 | M.Wt | 864.8 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Aesculitannin B Dilution Calculator

Aesculitannin B Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.1563 mL | 5.7817 mL | 11.5634 mL | 23.1267 mL | 28.9084 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2313 mL | 1.1563 mL | 2.3127 mL | 4.6253 mL | 5.7817 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1156 mL | 0.5782 mL | 1.1563 mL | 2.3127 mL | 2.8908 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0231 mL | 0.1156 mL | 0.2313 mL | 0.4625 mL | 0.5782 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0116 mL | 0.0578 mL | 0.1156 mL | 0.2313 mL | 0.2891 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- MTCA(1-Methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-beta-carboline-3-carboxylic acid)
Catalog No.:BCX2074
CAS No.:5470-37-1
- Strychnistenolide 6-O-acetate
Catalog No.:BCX2073
CAS No.:325969-56-0
- 4'''-O-beta-D-Glucopyranosyltrifloroside
Catalog No.:BCX2072
CAS No.:188350-29-0
- Azalein
Catalog No.:BCX2071
CAS No.:29028-02-2
- Epicatechin 3-O-(4-O-methylgallate)
Catalog No.:BCX2070
CAS No.:108907-44-4
- 15-Hydroxy-7-oxo-abieta-8,11,13-triene
Catalog No.:BCX2069
CAS No.:105037-83-0
- cis-N-Feruloyloctopamine
Catalog No.:BCX2068
CAS No.:180050-83-3
- Safrole
Catalog No.:BCX2067
CAS No.:94-59-7
- Forsythoside F
Catalog No.:BCX2066
CAS No.:94130-58-2
- 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxystyrene
Catalog No.:BCX2065
CAS No.:7786-61-0
- Glycochenodeoxycholic Acid
Catalog No.:BCX2064
CAS No.:640-79-9
- Hyocholic acid
Catalog No.:BCX2063
CAS No.:547-75-1
- 16-Acetoxylsugiol
Catalog No.:BCX2076
CAS No.:1413941-65-7
- Gerardianin B
Catalog No.:BCX2077
CAS No.:2070919-73-0
- 6,12,15-Trihydroxy-5,8,11,13-abietetra-7-one
Catalog No.:BCX2078
CAS No.:371155-09-8
- Graciliflorin E
Catalog No.:BCX2079
CAS No.:1413941-66-8
- Bracteanolide A
Catalog No.:BCX2080
CAS No.:1021432-39-2
- Isobiflorin
Catalog No.:BCX2081
CAS No.:152041-16-2
- 2-Hydroxy-6-methoxy-4-O-(6''-O-alpha-L-arabinofuranosyl-beta-D-glucopyranosyl)acetophenone
Catalog No.:BCX2082
CAS No.:1452160-87-0
- Fischeroside A
Catalog No.:BCX2083
CAS No.:1307257-07-3
- 16-Acetoxy-7alpha-methoxyroyleanone
Catalog No.:BCX2084
CAS No.:109974-33-6
- Methyl-6-gingerol
Catalog No.:BCX2085
CAS No.:23513-10-2
- Rhamnetin 3-O-gentiobioside
Catalog No.:BCX2086
CAS No.:1786990-15-8
- Rhamnetin 3-sophoroside
Catalog No.:BCX2087
CAS No.:259234-17-8
Studies on the Catechin Constituents of Bark of Cinnamomum sieboldii.[Pubmed:37121688]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2023;71(5):374-379.
Screening for bioactivity related to anti-infective, anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and anti-viral activity, led us to identify active compounds from a methanol extract of Litsea japonica (Thub.) Juss. and the hot water extract of bark of Cinnamomum sieboldii Meisn (also known as Karaki or Okinawa cinnamon). The two main components in these extracts were identified as the catechin trimers (+)-cinnamtannin B(1) and pavetannin B5. Moreover, these extracts exhibited anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) activity. The structures of these catechin trimers were previously determined by chemical and spectroscopic methods. Pavetanin B5 has never been reported to be isolated as a pure form and has been obtained as a mixture with another component. Although other groups have reported the putative structure of pavetannin B5, preparation of the methylated derivative of pavetannin B5 in this study allowed us to obtain the pure form for the first time as the undecamethyl derivative and confirm its exact structure. Commercially available (+)-cinnamtannin B(1) and Aesculitannin B (C2'-epimer of cinnamtannin B(1)) both of which contained pavetannin B5 as a minor component, and C. sieboldii bark extract (approx. 5/2 mixture of (+)-cinnamtannin B(1)/pavetannin B5) were assessed for anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity. Both C. sieboldii bark extract and commercially available Aesculitannin B showed viral growth inhibitory activity.
[Condensed tannins from roots of Indigofera stachyodes].[Pubmed:34467724]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Aug;46(16):4131-4138.
Eleven condensed tannins were isolated from the roots of Indigofera stachyodes by various column chromatography techniques including silica gel, octadecyl silica(ODS), Sephadex LH-20, and semi-preparative high performance liquid chromatography(HPLC). These compounds were identified on the basis of physicochemical properties, nuclear magnetic resonance(NMR) and mass spectrometry(MS) data as stachyotannin A(1), epicatechin-(2beta-->O-->7,4beta-->8)-epiafzelechin-(4beta-->8)-catechin(2), cinnamtannin D1(3), cinnamtannin B1(4), epicatechin-(2beta-->O-->7,4beta-->8)-epiafzelechin-(4alpha-->8)-epicatechin(5), gambiriin C(6), proanthocyanidin A1(7), proanthocyanidin A2(8), Aesculitannin B(9), proanthocyanidin A4(10), and procyanidin B5(11). Compound 1 is a new compound. Compounds 2-11 were isolated from Indigofera for the first time. Furthermore, compounds 1, 2, and 4-11 showed inhibitory effects on thrombin-induced ATP release in platelets.
Conformational equilibria in selected A-type trimeric procyanidins.[Pubmed:25355183]
Org Biomol Chem. 2014 Dec 28;12(48):9837-44.
A-type procyanidin trimers cinnamtannin B-1, cinnamtannin D-1, lindetannin, and Aesculitannin B were studied in terms of their conformation and interaction with four solvents: methanol, acetone, DMSO and pyridine. The experiments demonstrated that for each trimer there are two principal conformers observable in the NMR. The ratio of the conformers (rotamers) depends on the structure of a given trimer as well as on the solvent used for NMR measurements. The DFT calculations (B3LYP/6-31G(d,p)) proved the presence of two main conformers to be the result of a steric hindrance that prevents free rotation along the B-type interflavan bond. An analysis of the solvent-procyanidin interactions showed that the strong electron donating solvents, pyridine and DMSO, favor different conformers from methanol and acetone, which prefer the lowest-energy gas phase conformer. These findings are in line with predictions of DFT/M06-2X calculations with the inclusion of the thermal corrections. The variations in the rotamer ratios in the studied solvents correlate with the solvent's capacity to induce local changes in the electron density of the particular procyanidin trimer.
Procyanidins from the stem wood of Machilus japonica and their inhibitory effect on LDL oxidation.[Pubmed:24297667]
Arch Pharm Res. 2014 Nov;37(11):1403-10.
The stem wood of Machilus japonica Siebold & Zucc were extracted with 80 % aqueous MeOH, and the concentrated extract was successively partitioned with ethyl acetate (EtOAc), normal butanol, and water. From the EtOAc fraction, five procyanidins, procyanidin A1 (1), procyanidin A2 (2), procyanidin B7 (3), cinnamtannin B1 (4), and Aesculitannin B (5), were isolated. Their chemical structures were identified through spectroscopic data analyses including NMR, MS, and IR. This is the first time any of these compounds have been isolated from this plant. The compounds were evaluated for inhibition activity on LDL oxidation. All of these compounds and the positive control, BHT, showed a very high inhibition effect with IC50 values of 0.94, 2.1, 1.8, 1.1, 1.0, and 1.9 muM, respectively.
Proanthocyanidins from the leaves of Machilus philippinensis.[Pubmed:20568785]
J Nat Prod. 2010 Aug 27;73(8):1375-80.
Seven proanthocyanidins (2-8) together with epicatechin (1) were isolated from the EtOH extract of the leaves of Machilus philippinensis. Of these, machiphilitannins A (7) and B (8) are new natural products, with respective IC(50) values of 31.3 (7) and 18.4 microM (8) against alpha-glucosidase type IV from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Their structures were elucidated mainly on the basis of CD and 2D NMR analyses. In addition, Aesculitannin B (2) showed inhibitory activity against alpha-glucosidase with an IC(50) value of 3.5 microM. This work demonstrates for the first time that the purified proanthocyanidins possess inhibitory activity against alpha-glucosidase type IV.
Chemical and pharmacological investigations of Metaxya rostrata.[Pubmed:18810987]
Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2008 Jul-Aug;63(7-8):469-75.
In a bioassay-guided approach the chemical composition of rhizomes of Metaxya rostrata (Kunth C. Presl) was studied for the first time. Investigations of the cytotoxicity of extracts and fractions on SW480 colorectal carcinoma cells resulted in the isolation of two polyphenols--cinnamtannin B-1 and Aesculitannin B. The structures of the compounds were elucidated by different NMR experiments. Additionally, sugars, common sterols, such as sitosterol, stigmasterol and campesterol, as well as chlorogenic acid and caffeic acid were identified in Metaxya rostrata.
Prolyl endopeptidase inhibitors from the roots of Lindera strychnifolia F. Vill.[Pubmed:12186408]
Biol Pharm Bull. 2002 Aug;25(8):1049-52.
Prolyl endopeptidase (PEP, EC 3.4.21.26) has been proposed to play a role in degradation of proline-containing neuropeptides involved in the processes of learning and memory, e.g., vasopressin, substance P, and thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). In the course of our search for bioactive constituents in medicinal plants, we studied the PEP inhibitory constituents of the roots of Lindera strychnifolia F. VILL and isolated two known tannins, epicatechin (1) and Aesculitannin B (2), and four known sesquiterpenes, linderene (3), linderene acetate (4), linderalactone (5) and isolinderalactone (6) as inhibitors. On the inhibitory activities of six compounds against PEP from Flavobacterium meningosepticum and that from rat brain supernatant, compounds 1, 2 and 4 inhibited the enzyme from Flavobacterium more strongly than that from rat brain supernatant. However, compounds 3, 5 and 6 inhibited the enzymes from both origins to the same extent and furthermore, compound 6 was the strongest natural inhibitor against PEP from rat brain supernatant. The kinetic study of these inhibitors indicated that compounds 1, 2 are noncompetitive inhibitors and compounds 3-6 are competitive inhibitors. This is the first example of non-phenolic constituents showing significant competitive inhibitory activity being isolated from natural medicines.
Studies on the constituents of bark of Parameria laevigata Moldenke.[Pubmed:11383605]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2001 May;49(5):551-7.
One new trimeric proanthocyanidin, epicatechin-(2beta-->O-->7, 4beta-->6)-epicatechin-(2beta-->O--->7, 4beta-->8)-epicatechin (5) and two new tetrameric proanthocyanidins, epicatechin-(2beta-->O-->7, 4beta-->8)-[epicatechin-(4beta-->6)]-epicatechin-(4beta-->8)-epicatechin, named as parameritannin A-1 (6), and epicatechin-(2beta-->O-->5, 4beta-->6)-[epicatechin-(2beta-->O-->7, 4beta-->8)]-epicatechin-(4beta-->8)-epicatechin, named as parameritannin A-2 (7), have been isolated from the bark of Parameria laevigata Moldenke (Apocynaceae) along with the two known dimers, proanthocyanidin A-2 (1) and proanthocyanidin A-6 (2), and two trimers, cinnamtannin B-1 (3) and Aesculitannin B (4). These structures were elucidated by spectral and chemical evidence.


