AjacineCAS# 509-17-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 509-17-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 101667972 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C34H48N2O9 | M.Wt | 628.8 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
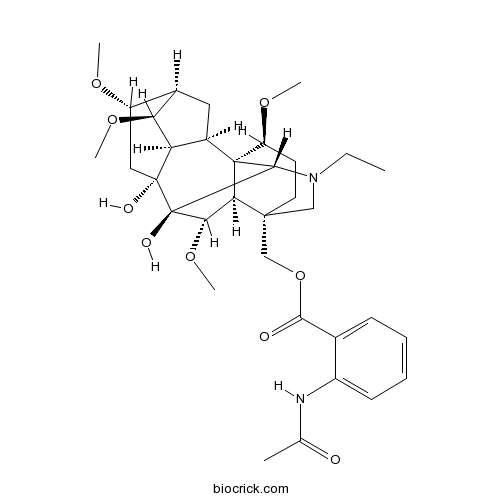
| Chemical Name | [(1S,2R,3R,4S,5R,6S,8R,9S,10S,13S,16S,17R,18S)-11-ethyl-8,9-dihydroxy-4,6,16,18-tetramethoxy-11-azahexacyclo[7.7.2.12,5.01,10.03,8.013,17]nonadecan-13-yl]methyl 2-acetamidobenzoate | ||
| SMILES | CCN1CC2(CCC(C34C2C(C(C31)(C5(CC(C6CC4C5C6OC)OC)O)O)OC)OC)COC(=O)C7=CC=CC=C7NC(=O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NUXFDCYXMLVOFU-AYBRVATOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C34H48N2O9/c1-7-36-16-31(17-45-29(38)19-10-8-9-11-22(19)35-18(2)37)13-12-24(42-4)33-21-14-20-23(41-3)15-32(39,25(21)26(20)43-5)34(40,30(33)36)28(44-6)27(31)33/h8-11,20-21,23-28,30,39-40H,7,12-17H2,1-6H3,(H,35,37)/t20-,21-,23+,24+,25-,26+,27-,28+,30+,31+,32-,33+,34-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Ajacine Dilution Calculator

Ajacine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5903 mL | 7.9517 mL | 15.9033 mL | 31.8066 mL | 39.7583 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3181 mL | 1.5903 mL | 3.1807 mL | 6.3613 mL | 7.9517 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.159 mL | 0.7952 mL | 1.5903 mL | 3.1807 mL | 3.9758 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0318 mL | 0.159 mL | 0.3181 mL | 0.6361 mL | 0.7952 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0159 mL | 0.0795 mL | 0.159 mL | 0.3181 mL | 0.3976 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Nardoeudesmol A
Catalog No.:BCN9220
CAS No.:1445952-30-6
- Ethyl 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate
Catalog No.:BCN9219
CAS No.:23795-02-0
- 3-Hydroxy-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-1-one
Catalog No.:BCN9218
CAS No.:53170-93-7
- 14β,16β-Dihydroxy-3β-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-5α-bufa-20,22-dienolide
Catalog No.:BCN9217
CAS No.:1323952-04-0
- Acutumine
Catalog No.:BCN9216
CAS No.:17088-50-5
- 3'-O-Methyltaxifolin
Catalog No.:BCN9215
CAS No.:55812-91-4
- 3α-Cinnamoyloxy-9β,17-dihydroxy-ent-kaur-15-en-19-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9214
CAS No.:2186648-60-0
- Loroglossin
Catalog No.:BCN9213
CAS No.:58139-22-3
- 3"-O-Desmethylspinorhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN9212
CAS No.:2220243-41-2
- 6-O-(p-Hydroxybenzoyl)glucose
Catalog No.:BCN9211
CAS No.:202337-44-8
- Jacaranone
Catalog No.:BCN9210
CAS No.:60263-07-2
- Ethyl chlorogenate
Catalog No.:BCN9209
CAS No.:425408-42-0
- 6,4'-Dihydroxy-7-methoxyflavan
Catalog No.:BCN9222
CAS No.:202463-50-1
- Desglucohellebrin
Catalog No.:BCN9223
CAS No.:20300-44-1
- 5,7-Dihydroxyphthalide
Catalog No.:BCN9224
CAS No.:27979-58-4
- (+)-Nyasol
Catalog No.:BCN9225
CAS No.:185020-38-6
- Sepiumol A
Catalog No.:BCN9226
CAS No.:2411999-52-3
- Delbonine
Catalog No.:BCN9227
CAS No.:95066-33-4
- Glabredelphinine
Catalog No.:BCN9228
CAS No.:132160-37-3
- (-)-Episyringaresinol
Catalog No.:BCN9229
CAS No.:6216-82-6
- N-Acetyldelectine
Catalog No.:BCN9230
CAS No.:63596-61-2
- Axinysone A
Catalog No.:BCN9231
CAS No.:1114491-57-4
- Sonnerphenolic B
Catalog No.:BCN9232
CAS No.:1627516-10-2
- Rhamnazin
Catalog No.:BCN9233
CAS No.:552-54-5
Diterpene alkaloids from the roots of Aconitum moldavicum and assessment of Nav 1.2 sodium channel activity of aconitum alkaloids.[Pubmed:24452459]
Planta Med. 2014 Feb;80(2-3):231-6.
A new aconitane alkaloid, 1-O-demethylswatinine (1), was isolated from the root of Aconitum moldavicum together with the known compounds cammaconine (2), columbianine (3), swatinine (4), gigactonine (5), delcosine (6), lycoctonine (7), and Ajacine (8). The structures were established by means of HRESIMS, 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy, including 1H-1H COSY, NOESY, HSQC, and HMBC experiments, resulting in complete 1H-NMR chemical shift assignments for 1-4. The effects of the isolated compounds 4-8, together with eighteen other Aconitum diterpene and norditerpene alkaloids with different skeletal types and substitution patterns, were studied on Nav 1.2 channels by the whole-cell patch clamp technique, using the QPatch-16 automated patch clamp system. Pyroaconitine, Ajacine, septentriodine, and delectinine demonstrated significant Nav 1.2 channel inhibition (57-42 %) at 10 microM concentration; several other compounds (acovulparine, acotoxicine, hetisinone, 14-benzoylaconine-8-O-palmitate, aconitine, and lycoctonine) exerted moderate inhibitory activity (30-22 %), while the rest of the tested alkaloids were considered to be inactive. On the basis of these results and by exhaustive comparison of data of previously published computerized QSAR studies on diterpene alkaloids, certain conclusions on the structure-activity relationships of Aconitum alkaloids concerning Nav 1.2 channel inhibitory activity are proposed.
Diterpenoid alkaloids of Aconitum vulparia Rchb.[Pubmed:22624325]
Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2012 Mar-Apr;67(3-4):103-7.
From the roots of Aconitum vulparia Rchb., collected in Prum (Germany), a new norditerpenoid alkaloid, named alexhumboldtine, has been isolated along with the known norditerpenoid alkaloids lappaconitine, anthranoyllycoctonine, lycoctonine, puberaconitine, Ajacine, and septentriodine. The structure of alexhumboldtine was established on the basis of 1H, 13C, DEPT, homonuclear 1H COSY, NOESY, HSQC, and HMBC NMR studies. From the aerial parts of the plant another norditerpenoid alkaloid, aconorine, has been isolated.
Diterpenoid alkaloids from the roots of Delphinium scabriflorum.[Pubmed:15387663]
J Nat Prod. 2004 Sep;67(9):1574-6.
Chemical investigation of the CHCl(3) extracts from the roots of Delphinium scabriflorum has resulted in the isolation of a new diterpenoid alkaloid, 13-(2-methylbutyryl)azitine (1), along with 11 known alkaloids, delbine (2), 14-deacetyl-14-isobutyrylajadine (3), methyllycaconitine (4), 14-deacetylnudicauline (5), delectinine (6), deltatsine (7), dictysine (8), geyerline (9), Ajacine (10), lycoctonine (11), and delcosine (12). The structure of 1 was determined by spectroscopic data interpretation. Complete NMR data for alkaloids 2-8 are presented. Some earlier (13)C NMR assignments made for alkaloids 4-7 were revised.
Norditerpenoid alkaloids from the roots of Delphinium stapeliosum.[Pubmed:10650068]
J Nat Prod. 2000 Jan;63(1):2-5.
From the roots of Delphinium stapeliosum three new norditerpenoid alkaloids, 14-demethyltuguaconitine (1), 14-deacetyl-14-isobutyrylnudicauline (2), and 14-deacetyl-14-isobutyrylajadine (3), and nine known norditerpenoid alkaloids, delbonine (4), methyllycaconitine (5), 14-deacetylnudicauline (6), Ajacine (7), deltatsine (8), delcosine (9), 14-deacetylajadine (10), nudicauline (11), and ajadine (12), were isolated. Structure elucidation and identification were based on NMR and mass spectra.
Interaction of the structurally related aconitum alkaloids, aconitine and 6-benzyolheteratisine, in the rat hippocampus.[Pubmed:10618469]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1999 Dec 15;386(2-3):187-94.
Aconitine is a highly toxic diterpenoid alkaloid occurring in plants of the Aconitum genus. Aconitine is known to shift the voltage-dependence of the voltage-dependent Na(+) channel towards hyperpolarized direction, thereby leading to a permanent activation of the channel. 6-benzoylheteratisine is a plant alkaloid which is structurally related with aconitine. The aim of the present study was to investigate the interaction of aconitine and 6-benzoylheteratisine in the rat hippocampus. The experiments were carried out as extracellular recordings of stimulus evoked population spikes and field excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) in rat hippocampal slices. Aconitine (10-100 nM) exerted a concentration-dependent decrease in the amplitude of the orthodromic population spike. When aconitine was applied in presence of 6-benzoylheteratisine (3 microM), the concentration-response curve was shifted to the right. Furthermore, the complete suppression of the population spike evoked by 100 nM aconitine was reversed by 10 microM 6-benzoylheteratisine. The closely related alkaloid heteratisine (3 and 30 microM), however, was not capable to antagonize the aconitine action. 6-benzoylheteratisine shifted the input-output relationship of the presynaptic fiber spike as function of the stimulation intensity and the input-output relationship of the field EPSP as function of the presynaptic fiber spike to the right. Thus, electrophysiologically this alkaloid seems to inhibit predominantly the excitability of the afferent fibres and, in consequence, neurotransmission between Schaffer collaterals and the CA1 neurons, thereby suppressing the firing of the latter. Spontaneously occurring epileptiform activity in area CA3 elicited by omission of Mg(2+) and elevation of K(+) was attenuated by 6-benzoylheteratisine (1 and 10 microM). Patch clamp studies performed on cultured rat hippocampal pyramidal cells revealed an inhibitory action of 6-benzoylheteratisine on whole cell Na(+) currents. It is concluded that the inhibitory and antiepileptiform effect of Ajacine and lappaconitine is mediated by an inhibition of the voltage-dependent Na(+) channel which might be important for filtering high frequency bursts of action potentials characteristic for epileptiform activity in the hippocampus. Thus, 6-benzoylheteratisine seems to be a naturally occurring antagonist of the Na(+) channel activator aconitine.
Antagonism of the aconitine-induced inexcitability by the structurally related Aconitum alkaloids, lappaconitine and ajacine.[Pubmed:10526129]
Brain Res. 1999 Sep 25;842(2):332-41.
Aconitine, lappaconitine and Ajacine are structurally related alkaloids occurring in several species of the Aconitum genus. While aconitine is known to activate the voltage-dependent sodium channel, lappaconitine has been reported to block this channel. To investigate a possible antagonism of the aconitine action on neuronal activity by lappaconitine and the closely related alkaloid Ajacine, we have performed extracellular recordings of stimulus evoked population spikes and field excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) in rat hippocampal slices. Aconitine (10-100 nM) diminished the amplitude of the orthodromic population spike in a concentration-dependent manner. When aconitine was applied in presence of 10 microM lappaconitine, the concentration-response curve was shifted to the right. Furthermore, the complete suppression of the population spike evoked by 100 nM aconitine was reversed by 10 microM lappaconitine. The action of lappaconitine was mimicked by Ajacine, however, the latter alkaloid was less potent. Both lappaconitine and Ajacine shifted the input-output relationship of the presynaptic fiber spike as function of the stimulation intensity and of the field EPSP as function of the presynaptic fiber spike to the right. After pharmacological isolation, the presynaptic fiber spike was decreased by both compounds in a frequency-dependent manner indicative for a use-dependent action. Thus, electrophysiologically these alkaloids seem to inhibit predominantly the excitability of the afferent fibres and, in consequence, neurotransmission between Schaffer collaterals and the CA1 neurons, thereby suppressing the firing of the latter. Ajacine and lappaconitine inhibited stimulus-triggered epileptiform population bursts in area CA1 elicited by omission of Mg(2+) as well as spontaneously occurring epileptiform discharges in area CA3 elicited by omission of Mg(2+) and elevation of K(+). It is concluded that the inhibitory and antiepileptiform effect of Ajacine and lappaconitine is mediated by a frequency-dependent inhibition of the voltage-dependent sodium channel, thereby decreasing the excitability which might be important for filtering high frequency bursts of action potentials characteristic for epileptiform activity in the hippocampus. Moreover, these alkaloids are naturally occurring antagonists of the sodium channel activator aconitine.
13-O-acetylvakhmatine, a new diterpenoid alkaloid from the seeds of Consolida ambigua.[Pubmed:8676129]
J Nat Prod. 1995 Oct;58(10):1527-32.
Vakhmatine [1] and the new diterpenoid alkaloid 13-O-acetylvakhmatine [3] have been isolated from the polar alkaloidal fractions of the seeds of Consolida ambigua, together with Ajacine, delcosine, gigactonine, and takaosomine. Structure 3 has been established on the basis of spectroscopic data and chemical correlation with 1.
N-oxides of some norditerpenoid alkaloids.[Pubmed:7673939]
J Nat Prod. 1995 Jun;58(6):929-33.
Eight new N-oxides [1-8] of the norditerpenoid alkaloids aconitine, Ajacine, delphinine, delphisine, deltaline, heteratisine, lappaconitine, and N-deacetyllappaconitine have been prepared with m-chloroperbenzoic acid. The structures of these compounds were established on the basis of their spectroscopic data (1H, 13C, DEPT, COSY, HETCOR, and selective INEPT nmr experiments). The complete nmr chemical shift assignments for all eight N-oxides are reported. Table 2 shows the differences between the 13C-nmr shifts of the N-oxides compared with those of the parent alkaloids.


