3'-O-MethyltaxifolinCAS# 55812-91-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 55812-91-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 26194552 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H14O7 | M.Wt | 318.28 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
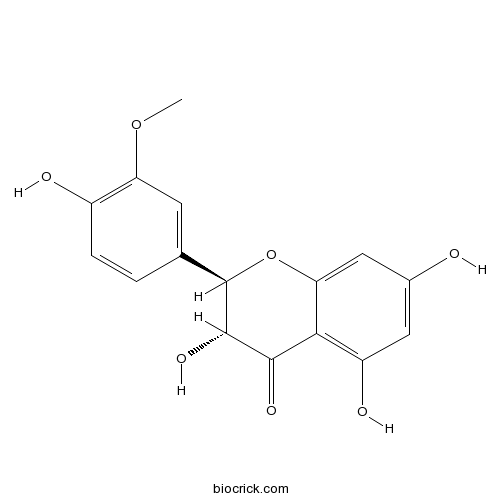
| Chemical Name | (2R,3R)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydrochromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=CC(=C1)C2C(C(=O)C3=C(C=C(C=C3O2)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JWYULKXTGMJKKM-JKSUJKDBSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H14O7/c1-22-11-4-7(2-3-9(11)18)16-15(21)14(20)13-10(19)5-8(17)6-12(13)23-16/h2-6,15-19,21H,1H3/t15-,16+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

3'-O-Methyltaxifolin Dilution Calculator

3'-O-Methyltaxifolin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1419 mL | 15.7094 mL | 31.4189 mL | 62.8378 mL | 78.5472 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6284 mL | 3.1419 mL | 6.2838 mL | 12.5676 mL | 15.7094 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3142 mL | 1.5709 mL | 3.1419 mL | 6.2838 mL | 7.8547 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0628 mL | 0.3142 mL | 0.6284 mL | 1.2568 mL | 1.5709 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0314 mL | 0.1571 mL | 0.3142 mL | 0.6284 mL | 0.7855 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 3α-Cinnamoyloxy-9β,17-dihydroxy-ent-kaur-15-en-19-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9214
CAS No.:2186648-60-0
- Loroglossin
Catalog No.:BCN9213
CAS No.:58139-22-3
- 3"-O-Desmethylspinorhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN9212
CAS No.:2220243-41-2
- 6-O-(p-Hydroxybenzoyl)glucose
Catalog No.:BCN9211
CAS No.:202337-44-8
- Jacaranone
Catalog No.:BCN9210
CAS No.:60263-07-2
- Ethyl chlorogenate
Catalog No.:BCN9209
CAS No.:425408-42-0
- Chimaphilin
Catalog No.:BCN9208
CAS No.:482-70-2
- Qingyangshengenin 3-O-α-L-cymaropyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-oleandropyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-cymaropyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-cymaropyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN9207
CAS No.:1808159-02-5
- O-Demethylstachartin C
Catalog No.:BCN9206
CAS No.:1219361-60-0
- 3,3-Dimethylacrylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9205
CAS No.:541-47-9
- (+)-Rutamarin
Catalog No.:BCN9204
CAS No.:13164-05-1
- 7α-Galloyloxysweroside
Catalog No.:BCN9203
CAS No.:2222365-76-4
- Acutumine
Catalog No.:BCN9216
CAS No.:17088-50-5
- 14β,16β-Dihydroxy-3β-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-5α-bufa-20,22-dienolide
Catalog No.:BCN9217
CAS No.:1323952-04-0
- 3-Hydroxy-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-1-one
Catalog No.:BCN9218
CAS No.:53170-93-7
- Ethyl 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate
Catalog No.:BCN9219
CAS No.:23795-02-0
- Nardoeudesmol A
Catalog No.:BCN9220
CAS No.:1445952-30-6
- Ajacine
Catalog No.:BCN9221
CAS No.:509-17-1
- 6,4'-Dihydroxy-7-methoxyflavan
Catalog No.:BCN9222
CAS No.:202463-50-1
- Desglucohellebrin
Catalog No.:BCN9223
CAS No.:20300-44-1
- 5,7-Dihydroxyphthalide
Catalog No.:BCN9224
CAS No.:27979-58-4
- (+)-Nyasol
Catalog No.:BCN9225
CAS No.:185020-38-6
- Sepiumol A
Catalog No.:BCN9226
CAS No.:2411999-52-3
- Delbonine
Catalog No.:BCN9227
CAS No.:95066-33-4
A new monoterpene glucoside and complete assignments of dihydroflavonols of Pulicaria jaubertii: potential cytotoxic and blood pressure lowering activity.[Pubmed:26247309]
Nat Prod Res. 2016 Jun;30(11):1280-8.
One new monoterpene glucoside and five dihydroflavonols were isolated for the first time from the aerial parts of Pulicaria jaubertii and identified as p-menthane-2-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside [1], dihydroquercetin (taxifolin) [2], 7,3'-di-O-methyltaxifolin [3], 3'-O-methyltaxifolin [4], 7-O-methyltaxifolin (padmatin) [5] and 7-O-methyl-dihydrokampferol (7-O-methylaromadenderin) [6]. The structures of these compounds were unambiguously assigned on the basis of NMR spectroscopic data ((1)H, (13)C, DEPT, HSQC, HMBC) and MS analysis. 2D-NMR methods required revision of assignments of H-6 and H-8 for dihydroflavonol compounds. Possible cytotoxic activity as well as blood pressure (BP) lowering activity were tested. The alcoholic extract showed cytotoxic activity against prostate carcinoma (PC-3), breast carcinoma (MCF-7) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG-2) human cell lines with IC50 19.1, 20.0 and 24.1 mug, respectively. The higher dose levels of the alcoholic extract significantly reduced normal BP of rats in a dose-dependent manner.
Study on the correlation between constituents detected in serum from Rhizoma Smilacis Glabrae and the reduction of uric acid levels in hyperuricemia.[Pubmed:24140588]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Nov 25;150(2):747-54.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Rhizoma Smilacis Glabrae (RSG) has been used in the clinical treatment of gout and hyperuricemia in China for thousands of years. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that RSG exhibits hypouricemic effects because of its significant inhibitory effect on the activity of xanthine oxidase. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The Rhizoma Smilacis Glabrae extract (RSGE) at 1 mL/100g oral administration was demonstrated to possess in vivo potent hypouricemic effects in hyperuricemic rats pretreated with oxonic acid potassium salt (200 mg/kg, 2 mL/kg). UPLC-MS was used to identify the constituents absorbed in the serum. In addition, a bivariate correlation analysis between the changes in the relative contents of the constituents from RSGE detected by HPLC and the serum uric acid levels in hyperuricemic rats at different points in time was used to calculate their correlation coefficients. RESULTS: A total of 14 constituents were observed in the RSGE-treated rat serum, and 11 of these were inferred. An RSGE constituent was considered correlated with the hypouricemic effects if its correlation coefficient was above 0.5. The results suggested that only seven of the constituents absorbed in the serum of the hyperuricemic rats were correlated with hypouricemic effects, namely, palmitic acid, 3'-O-methyltaxifolin glucuronide, 3'-O-methyiastilbin glucuronide, astilbin glucuronide, 5-O-caffeoylshikimic acid glucuronide, resveratrol glucuronide, and dihydrokaempferol. CONCLUSION: These findings provide potent evidence for the study on RSG as a pharmacodynamic material basis and for developing RSG as a safe and promising natural drug to prevent hyperuricemia and gout instead of allopurinol.
Flavonoids from the grains of C1/R-S transgenic rice, the transgenic Oryza sativa spp. japonica, and their radical scavenging activities.[Pubmed:24070395]
J Agric Food Chem. 2013 Oct 30;61(43):10354-9.
The transgenic rice cultivar of Oryza sativa spp. japonica cv. Hwa-Young, C1/R-S transgenic rice (C1/R-S rice), is a flavonoid-rich cultivar of rice. The grains of C1/R-S rice were extracted with aqueous MeOH, and the concentrated extract was partitioned with EtOAc, n-BuOH, and H2O, successively. Repeated silica gel, octadecyl silica gel (ODS), and Sephadex LH-20 column chromatographies for the EtOAc and n-BuOH fractions afforded four new flavonoids (compounds 2, 3, 7, and 8) along with four known flavonoids: (+)-3'-O-methyltaxifolin (1), brassicin (4), isorhamnetin-4'-O-beta-D-glucosyranoside (5), and 3'-O-methyltaxifolin-5-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (6). The new flavonoids were identified as 3'-O-methyltaxifolin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (2), 3'-O-methyltaxifolin-4'-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (3), isorhamnetin-7-O-beta-D-cellobioside (brassicin-4''-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside) (7), and brassicin-4'-O-beta-D-glucosyranoside (8) from the result of spectroscopic data including nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry (NMR), mass spectrometry (MS), and infrared spectroscopy (IR). Also, quantitative analysis of major flavonoids (compounds 2, 3, and 8) in C1/R-S rice, O. sativa spp. japonica cv. Hwa-Young (HY), and a hybrid of two cultivar (C1/R-S rice/HY) extracts was performed using HPLC experiment. The isolated flavonoids were evaluated for their radical-scavenging effect on DPPH and ABTS radicals.
Identification and assay of 3'-O-methyltaxifolin by UPLC-MS in rat plasma.[Pubmed:23217303]
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2012 Dec 12;911:34-42.
A new metabolite of taxifolin: 3'-O-methyltaxifolin (3'-O-MTAX) in Caco-2 cells and in rat plasma was identified. The chemical structure of 3'-O-MTAX was determined by MS and (1)H NMR. A rapid, sensitive and specific UPLC-MS method to determine 3'-O-MTAX in rat plasma was also developed. Following ethyl acetate extraction, 3'-O-MTAX in plasma was separated on a Sunfire (2.1mmx50mm, 3.5mum) column and analyzed in the selected ion recording with a negative electrospray ionization mode using puerarin as the internal standard. The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) was 2.75ng/mL. Intra- and inter-day precisions (% RSD) were all within 7.2% and accuracy (% deviation) ranged from -5.0 to 4.7%. The overall recoveries at four concentrations were all >72.0%. This validated method was successfully applied to measure 3'-O-MTAX in rat plasma after oral administration of taxifolin.
C-geranyl compounds from Paulownia tomentosa fruits.[Pubmed:17625893]
J Nat Prod. 2007 Aug;70(8):1244-8.
Five geranylflavonoids, one prenylated flavonoid, and a simple flavanone were isolated from an ethanolic extract of Paulownia tomentosa fruit. Tomentodiplacol (1), 3'-O-methyl-5'-methoxydiplacol (2), 6-isopentenyl-3'-O-methyltaxifolin (3), and dihydrotricin (4) are reported from a natural source for the first time and 3'-O-methyldiplacone (6) for the first time from the genus Paulownia. The structures of the compounds were determined by mass spectrometry, including HRMS, and by 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy. The cytotoxicity and DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl)-quenching activity of some of these compounds were tested, with diplacone proving to be the best antioxidant, although the most cytotoxic compound.


