AristolodioneCAS# 109771-09-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 109771-09-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 184116 | Appearance | Red powder |
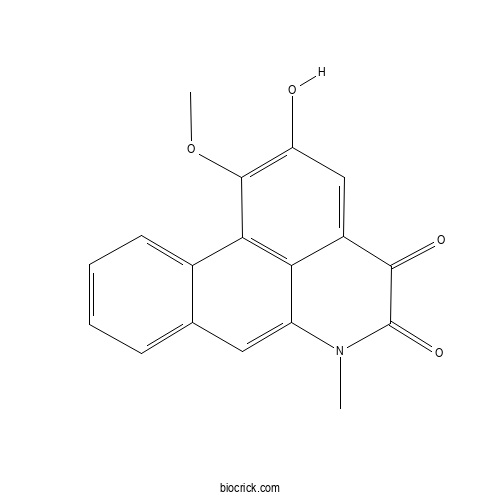
| Formula | C18H13NO4 | M.Wt | 307.3 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 15-hydroxy-16-methoxy-10-methyl-10-azatetracyclo[7.7.1.02,7.013,17]heptadeca-1(17),2,4,6,8,13,15-heptaene-11,12-dione | ||
| SMILES | CN1C2=CC3=CC=CC=C3C4=C2C(=CC(=C4OC)O)C(=O)C1=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JGDZUWXHWYXMSD-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H13NO4/c1-19-12-7-9-5-3-4-6-10(9)15-14(12)11(16(21)18(19)22)8-13(20)17(15)23-2/h3-8,20H,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Aristolodione Dilution Calculator

Aristolodione Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2541 mL | 16.2707 mL | 32.5415 mL | 65.083 mL | 81.3537 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6508 mL | 3.2541 mL | 6.5083 mL | 13.0166 mL | 16.2707 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3254 mL | 1.6271 mL | 3.2541 mL | 6.5083 mL | 8.1354 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0651 mL | 0.3254 mL | 0.6508 mL | 1.3017 mL | 1.6271 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0325 mL | 0.1627 mL | 0.3254 mL | 0.6508 mL | 0.8135 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Turmeronol B
Catalog No.:BCX0234
CAS No.:131651-38-2
- Tinospin E
Catalog No.:BCX0233
CAS No.:1582321-96-7
- N-Acetylnornuciferine
Catalog No.:BCX0232
CAS No.:1942-03-6
- Fibleucin
Catalog No.:BCX0231
CAS No.:24278-14-6
- Apigenin 6-C-(2-O-feruloyl)glucoside 8-C-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0230
CAS No.:1287786-63-3
- Makisterone A
Catalog No.:BCX0229
CAS No.:20137-14-8
- Brasilixanthone B
Catalog No.:BCX0228
CAS No.:84002-57-3
- 22-Epiinotodiol
Catalog No.:BCX0227
CAS No.:64907-49-9
- 1,3,5,7-Tetrahydroxy-8-prenylxanthone
Catalog No.:BCX0226
CAS No.:444004-76-6
- 1,6,8-Trihydroxy-2,7-dimethoxy-3-methylanthraquinone
Catalog No.:BCX0225
CAS No.:2366153-27-5
- Phenacetamide
Catalog No.:BCX0224
CAS No.:103-81-1
- 4-(1-Ethoxy-2-hydroxyethyl)benzene-1,2-diol
Catalog No.:BCX0223
CAS No.:1190632-33-7
- Ciwujianoside C2
Catalog No.:BCX0236
CAS No.:114892-56-7
- Mckeanianone B
Catalog No.:BCX0237
CAS No.:2035475-14-8
- 1-O-β-D-Glucopyranosylpaeonisuffrone
Catalog No.:BCX0238
CAS No.:1003888-20-7
- Pteroside B
Catalog No.:BCX0239
CAS No.:29774-74-1
- Kaempferol 3-O-neohesperidoside 7-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0240
CAS No.:78527-48-7
- Creticoside A
Catalog No.:BCX0241
CAS No.:34336-00-0
- (S,E)-2-Methyl-6-(p-tolyl)hept-3-en-2-ol
Catalog No.:BCX0242
CAS No.:18383-55-6
- ar-Turmerol
Catalog No.:BCX0243
CAS No.:1178899-16-5
- Bisacurone A
Catalog No.:BCX0244
CAS No.:127214-84-0
- Malaysianol D
Catalog No.:BCX0245
CAS No.:1646330-59-7
- Pyridylpaeoniflorin
Catalog No.:BCX0246
CAS No.:1427054-19-0
- Pterosin L 2'-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0247
CAS No.:61102-11-2
A three-stage-integrative approach for the identification of potential hepatotoxic compounds from botanical products.[Pubmed:21633125]
Int J Toxicol. 2011 May;30(3):287-99.
With the increasing use of herbal medicines and dietary supplements, intensive concerns about their potential toxicities have been raised. Screening and identifying the toxic compounds from these botanical products composed by hundreds of components have become a critical but challenging problem. In this study, 3 methods, including fraction separation, an in-house-developed fluorescein diacetate-based automatic microscopy screening (FAMS) platform, and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based compounds identification were integrated within the Three-Stage-Integrative (TSI) approach for the identification of potential hepatotoxicants from botanical products. The sensitivity and linear range of FAMS assay was validated and compared with 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay by previously reported hepatotoxic compounds. The success of TSI approach was further demonstrated by its application to Fructus aristolochiae. Aristolochic acid IVa and Aristolodione were tentatively identified to be potential hepatotoxicants in this plant. These applications suggested that our TSI approach provides an effective tool for identifying potential toxic compounds from botanical products.


