BurchellinCAS# 38276-59-4 |
- 3a-Epiburchellin
Catalog No.:BCN7015
CAS No.:155551-61-4
- 2-Epi-3a-epiburchellin
Catalog No.:BCN7013
CAS No.:57457-99-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 38276-59-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 100199 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H20O5 | M.Wt | 340.4 |
| Type of Compound | Lignans | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
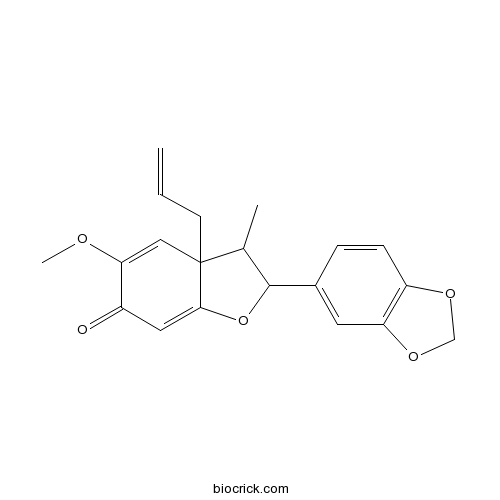
| Chemical Name | 2-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-5-methoxy-3-methyl-3a-prop-2-enyl-2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-6-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1C(OC2=CC(=O)C(=CC12CC=C)OC)C3=CC4=C(C=C3)OCO4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SOLJFAQVSWXZEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H20O5/c1-4-7-20-10-17(22-3)14(21)9-18(20)25-19(12(20)2)13-5-6-15-16(8-13)24-11-23-15/h4-6,8-10,12,19H,1,7,11H2,2-3H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Burchellin has larvicidal activity, it can interfer with the development cycle of the mosquito, where its strongest toxic effect is 100% mortality in larvae (L3) at concentrations ≥ 30 ppm. 2. Burchellin and licarin A have activity against Trypanosoma cruzi, they can induce trypomastigote death with IC(50)/24 h of 520 microM and 960 microM, respectively. |
| Targets | Antifection |

Burchellin Dilution Calculator

Burchellin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9377 mL | 14.6886 mL | 29.3772 mL | 58.7544 mL | 73.443 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5875 mL | 2.9377 mL | 5.8754 mL | 11.7509 mL | 14.6886 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2938 mL | 1.4689 mL | 2.9377 mL | 5.8754 mL | 7.3443 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0588 mL | 0.2938 mL | 0.5875 mL | 1.1751 mL | 1.4689 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0294 mL | 0.1469 mL | 0.2938 mL | 0.5875 mL | 0.7344 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Glucose-conjugated MGMT inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1597
CAS No.:382607-78-5
- Malonomicin
Catalog No.:BCN1844
CAS No.:38249-71-7
- 20(R)-Ginsenoside Rg3
Catalog No.:BCN5018
CAS No.:38243-03-7
- beta-Amyrenonol
Catalog No.:BCN5436
CAS No.:38242-02-3
- Enhydrin chlorohydrin
Catalog No.:BCN4639
CAS No.:38230-99-8
- Anhydroicaritin
Catalog No.:BCN5351
CAS No.:38226-86-7
- Filixic acid ABA
Catalog No.:BCN6330
CAS No.:38226-84-5
- Pyroxamide
Catalog No.:BCC2424
CAS No.:382180-17-8
- Coumarin VI
Catalog No.:BCN7833
CAS No.:38215-36-0
- Bacopaside II
Catalog No.:BCC8125
CAS No.:382146-66-9
- Adrenosterone
Catalog No.:BCC4061
CAS No.:382-45-6
- Sulindac
Catalog No.:BCC4861
CAS No.:38194-50-2
- Naringenin trimethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN5437
CAS No.:38302-15-7
- Minoxidil
Catalog No.:BCC4297
CAS No.:38304-91-5
- YE 120
Catalog No.:BCC6188
CAS No.:383124-82-1
- 3-O-beta-D-Glucopyranosylplatycodigenin
Catalog No.:BCN7832
CAS No.:38337-25-6
- Homovanillic Acid Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN2226
CAS No.:38339-06-9
- UC 112
Catalog No.:BCC8042
CAS No.:383392-66-3
- Neuropeptide W-23 (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5961
CAS No.:383415-79-0
- Taxinine
Catalog No.:BCN6944
CAS No.:3835-52-7
- 3',4'-Anhydrovinblastine
Catalog No.:BCN2392
CAS No.:38390-45-3
- NSC 663284
Catalog No.:BCC7199
CAS No.:383907-43-5
- Caudatin
Catalog No.:BCN5810
CAS No.:38395-02-7
- Ganaxolone
Catalog No.:BCC7397
CAS No.:38398-32-2
Burchellin: study of bioactivity against Aedes aegypti.[Pubmed:24713267]
Parasit Vectors. 2014 Apr 8;7:172.
BACKGROUND: The dengue mosquito Aedes aegypti Linnaeus, 1762 is a widespread insect pest of serious medical importance. Since no effective vaccine is available for treating dengue, the eradication or control of the main mosquito vector is regarded as essential. Since conventional insecticides have limited success, plants may be an alternative source of larvicidal agents, since they contain a rich source of bioactive chemicals. The aim of this study was to evaluate the larvicidal activity of the neolignan Burchellin isolated from Ocotea cymbarum (Lauraceae), a plant from the Amazon region, against third instar larvae of A. aegypti. METHODS: Burchellin obtained from O. cymbarum was analyzed. The inhibitory activity against A. aegypti eggs and larvae and histological changes in the digestive system of treated L3 larvae were evaluated. In addition, nitric oxide synthase activity and nitric oxide levels were determined, and cytotoxicity bioassays performed. RESULTS: The data showed that Burchellin interfered with the development cycle of the mosquito, where its strongest toxic effect was 100% mortality in larvae (L3) at concentrations >/= 30 ppm. This compound did not show target cell toxicity in peritoneal macrophages from BALB/c mice, and proved to have molecular stability when dissolved in water. The L3 and L4 larvae treated with the compound showed cellular destruction and disorganization, cell spacing, and vacuolization of epithelial cells in small regions of the midgut. CONCLUSION: The neolignan Burchellin proved to be a strong candidate for a natural, safe and stable phytolarvicidal to be used in population control of A. aegypti.
Neolignans from plants in northeastern Brazil (Lauraceae) with activity against Trypanosoma cruzi.[Pubmed:19944690]
Exp Parasitol. 2010 Mar;124(3):319-24.
Trypanosoma cruzi is the ethiological agent for Chagas disease in Latin America. This study aimed to test the trypanocidal effect of licarin A and Burchellin isolated from plants in northeastern Brazil. These neolignans were tested on T. cruzi and on peritoneal macrophages, to evaluate drug toxicity. Epimastigote growth was inhibited in 45% with licarin A and 20% with Burchellin with an IC(50)/96 h of 462.7 microM and 756 microM, respectively. Epimastigotes treated with licarin A presented swollen mitochondria and disorganized mitochondrial cristae, kDNA and Golgi complex. When treated with Burchellin, they presented enormous autophagosomes and chromatin disorganization. Licarin A and Burchellin were able to induce trypomastigote death with IC(50)/24 h of 960 microM and 520 microM, respectively. Although licarin A presented an IC(50) for trypomastigotes higher than for epimastigotes, both substances acted as therapeutic trypanocidal agents, because they were able to kill parasites without affecting macrophages. Due to our results, Burchellin and licarin A need to be further analysed to observe if they may be used as alternative blood additive prophylaxis against Chagas disease, since it has been established that blood transfusion is an important mechanism in the transmission process.


