CMPD-1CAS# 41179-33-3 |
- PF-4708671
Catalog No.:BCC5031
CAS No.:1255517-76-0
- BIX 02565
Catalog No.:BCC4303
CAS No.:1311367-27-7
- BI-D1870
Catalog No.:BCC5030
CAS No.:501437-28-1
- FMK
Catalog No.:BCC1580
CAS No.:821794-92-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 41179-33-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11382492 | Appearance | Powder |
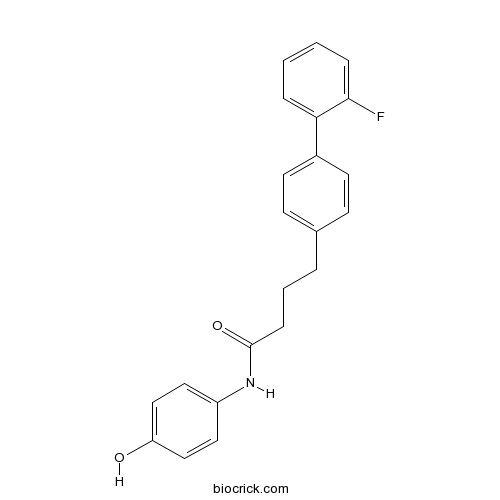
| Formula | C22H20FNO2 | M.Wt | 349.4 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO and to 100 mM in ethanol | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-[4-(2-fluorophenyl)phenyl]-N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butanamide | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C(=C1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)CCCC(=O)NC3=CC=C(C=C3)O)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ODYAQBDIXCVKAE-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H20FNO2/c23-21-6-2-1-5-20(21)17-10-8-16(9-11-17)4-3-7-22(26)24-18-12-14-19(25)15-13-18/h1-2,5-6,8-15,25H,3-4,7H2,(H,24,26) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Non-ATP-competitive, selective inhibitor of p38α-mediated MK2a (mitogen-activated protein kinase-2a) phosphorylation (apparent Ki = 330 nM). Does not inhibit p38α-mediated phosphorylation of MBP and ATF-2. Also tubulin polymerization inhibitor. Cytotoxic in glioblastoma cells at concentrations that do not affect the MK2 pathway. |

CMPD-1 Dilution Calculator

CMPD-1 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.862 mL | 14.3102 mL | 28.6205 mL | 57.241 mL | 71.5512 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5724 mL | 2.862 mL | 5.7241 mL | 11.4482 mL | 14.3102 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2862 mL | 1.431 mL | 2.862 mL | 5.7241 mL | 7.1551 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0572 mL | 0.2862 mL | 0.5724 mL | 1.1448 mL | 1.431 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0286 mL | 0.1431 mL | 0.2862 mL | 0.5724 mL | 0.7155 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Boc-Phe(4-F)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3219
CAS No.:41153-30-4
- Hirsutenone
Catalog No.:BCN5467
CAS No.:41137-87-5
- Hirsutanonol
Catalog No.:BCN5466
CAS No.:41137-86-4
- Platyphyllonol
Catalog No.:BCN5465
CAS No.:41137-85-3
- Memantine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC9018
CAS No.:41100-52-1
- Steviolbioside
Catalog No.:BCN6800
CAS No.:41093-60-1
- Skullcapflavone I
Catalog No.:BCN5464
CAS No.:41060-16-6
- Neobavaisoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN3194
CAS No.:41060-15-5
- Lipiferolide
Catalog No.:BCN5463
CAS No.:41059-80-7
- Timosaponin A3
Catalog No.:BCN4999
CAS No.:41059-79-4
- Sirtinol
Catalog No.:BCC2224
CAS No.:410536-97-9
- Palovarotene
Catalog No.:BCC4185
CAS No.:410528-02-8
- erythro-Guaiacylglycerol beta-sinapyl ether 7-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN7348
CAS No.:412029-03-9
- Pseudolarolide F
Catalog No.:BCN6428
CAS No.:412321-91-6
- H-Asp-OtBu
Catalog No.:BCC2883
CAS No.:4125-93-3
- Z-N-Me-Ile-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2617
CAS No.:4125-97-7
- 4-Methylamino-3-nitrobenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8715
CAS No.:41263-74-5
- 4-IPP
Catalog No.:BCC6023
CAS No.:41270-96-6
- TIC10
Catalog No.:BCC3906
CAS No.:41276-02-2
- Alfacalcidol
Catalog No.:BCC4962
CAS No.:41294-56-8
- BAM (8-22)
Catalog No.:BCC5806
CAS No.:412961-36-5
- Isorhamnetin 3-sophoroside-7-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN1446
CAS No.:41328-75-0
- NP118809
Catalog No.:BCC1807
CAS No.:41332-24-5
- Etodolac
Catalog No.:BCC4428
CAS No.:41340-25-4
CMPD1 inhibited human gastric cancer cell proliferation by inducing apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle arrest.[Pubmed:29661232]
Biol Res. 2018 Apr 16;51(1):11.
BACKGROUND: Gastric cancer occupies the fourth highest morbidity rate of cancers worldwide. Clinical therapies of gastric cancer remain limited because of uncertainty of mechanisms and shortness of effective medicine. Thus, new drug candidates for gastric cancer treatment is urgently needed. RESULTS: In this study, CMPD1 as a wildly used MK2 phosphorylation inhibitor was employed to find its impact on gastric cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle using colony formation assay and flow cytometry analysis. Along with its anti-proliferation effect on gastric cancer cell line MKN-45 and SGC7901, CMPD1 also induced massive apoptosis and significant G2/M phase arrest in a time-dependent and dose-dependent manner in MKN-45 cells respectively. Furthermore, Western blot confirmed that the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 was decreased while BAX, cytochrome c release and cleaved PARP were increased. In addition, oncogene c-Myc was downregulated in response to CMPD1 treatment. CONCLUSIONS: Our results demonstrated that CMPD1 has anti-tumor effect on human gastric cancer cell line MKN-45 possibly via downregulating oncogene c-Myc expression and CMPD1 could be applied as a potential candidate for treating gastric malignancy. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first report of anti-tumor effect of CMPD-1 on human gastric cancer cells.
FPHPB inhibits gastric tumor cell proliferation by inducing G2-M cell cycle arrest.[Pubmed:29304495]
Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Feb;98:694-700.
Gastric cancer is a common cancer in the world with high morbidity and mortality. Here, we report that FPHPB (4-(4-(2-fluoropyridin-3-yl)phenyl)-N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)), a derivative of CMPD-1/MK2a Inhibitor, had anti-tumor activities by inhibiting gastric tumor SNU-16 and SGC7901 cells. FPHPB dose-dependently inhibited cell proliferation, induced cell apoptosis and arrested SNU-16 and SGC7901 cells in G2-M cell cycle checkpoint. Upon treatment with FPHPB, apoptotic proteins cleaved PARP and cleaved caspase-3 were remarkably increased, and G2-M regulatory molecules, the phosphorylation of Cdc2 and Chk2, were significantly accentuated. Collectively, FPHPB has anti-tumor activities and may be a potential candidate for treating gastric cancers.
Discovery and characterization of a substrate selective p38alpha inhibitor.[Pubmed:15362850]
Biochemistry. 2004 Sep 21;43(37):11658-71.
A novel inhibitor of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38), CMPD1, identified by high-throughput screening, is characterized herein. Unlike the p38 inhibitors described previously, this inhibitor is substrate selective and noncompetitive with ATP. In steady-state kinetics experiments, CMPD1 was observed to prevent the p38alpha-dependent phosphorylation (K(i)(app) = 330 nM) of the splice variant of mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 (MK2a) that contains a docking domain for p38alpha and p38beta, but it did not prevent the phosphorylation of ATF-2 (K(i)(app) > 20 microM). In addition to kinetic studies, isothermal titration calorimetry and surface plasmon resonance experiments were performed to elucidate the mechanism of inhibition. While isothermal titration calorimetry analysis indicated that CMPD1 binds to p38alpha, CMPD1 was not observed to compete with ATP for p38alpha, nor was it able to interrupt the binding of p38alpha to MK2a observed by surface plasmon resonance. Therefore, deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (DXMS) was employed to study the p38alpha.CMPD1 inhibitory complex, to provide new insight into the mechanism of substrate selective inhibition. The DXMS data obtained for the p38alpha.CMPD1 complex were compared to the data obtained for the p38alpha.MK2a complex and a p38alpha.active site binding inhibitor complex. Alterations in the DXMS behavior of both p38alpha and MK2a were observed upon complex formation, including but not limited to the interaction between the carboxy-terminal docking domain of MK2a and its binding groove on p38alpha. Alterations in the D(2)O exchange of p38alpha produced by CMPD1 suggest that the substrate selective inhibitor binds in the vicinity of the active site of p38alpha, resulting in perturbations to regions containing nucleotide binding pocket residues, docking groove residues (E160 and D161), and a Mg(2+) ion cofactor binding residue (D168). Although the exact mechanism of substrate selective inhibition by this novel inhibitor has not yet been disclosed, the results suggest that CMPD1 binding in the active site region of p38alpha induces perturbations that may result in the suboptimal positioning of substrates and cofactors in the transition state, resulting in selective inhibition of p38alpha activity.


