HirsutanonolCAS# 41137-86-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 41137-86-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9928190 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H22O6 | M.Wt | 346.4 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
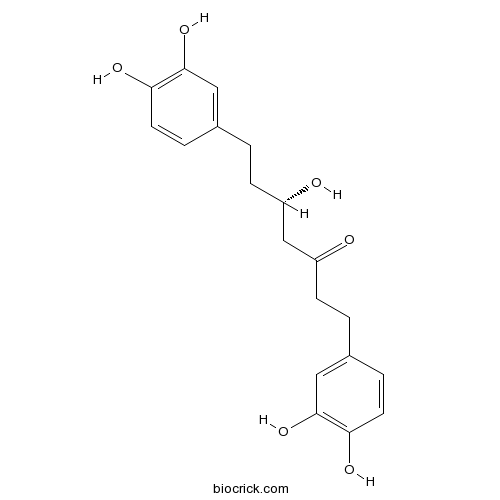
| Chemical Name | (5S)-1,7-bis(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxyheptan-3-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(C=C1CCC(CC(=O)CCC2=CC(=C(C=C2)O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MVIYWFBLVAFZID-AWEZNQCLSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H22O6/c20-14(5-1-12-3-7-16(22)18(24)9-12)11-15(21)6-2-13-4-8-17(23)19(25)10-13/h3-4,7-10,14,20,22-25H,1-2,5-6,11H2/t14-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Hirsutanonol or oregonin as an active ingredient composition for treating atopic dermatitis. 2. Hirsutanonol shows significant inhibitory effects on 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-induced cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression in immortalized human breast epithelial MCF10A cells. 3. Hirsutanonol has potent antioxidant activity, it shows significant free radical scavenging activity and exhibits inhibition effect on the mitochondrial lipid peroxidation. 4. Hirsutanonol shows potent cytotoxic activities against murine B16 melanoma cells and human SNU-C1 gastric cancer cells. 5. Hirsutanonol has chemoprotective effect on human lymphocytes DNA. 6. Hirustenone and hirsutanonol show promising anti-filarial activity both in vitro and in vivo studies. |
| Targets | COX | Antifection |

Hirsutanonol Dilution Calculator

Hirsutanonol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8868 mL | 14.4342 mL | 28.8684 mL | 57.7367 mL | 72.1709 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5774 mL | 2.8868 mL | 5.7737 mL | 11.5473 mL | 14.4342 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2887 mL | 1.4434 mL | 2.8868 mL | 5.7737 mL | 7.2171 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0577 mL | 0.2887 mL | 0.5774 mL | 1.1547 mL | 1.4434 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0289 mL | 0.1443 mL | 0.2887 mL | 0.5774 mL | 0.7217 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Platyphyllonol
Catalog No.:BCN5465
CAS No.:41137-85-3
- Memantine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC9018
CAS No.:41100-52-1
- Steviolbioside
Catalog No.:BCN6800
CAS No.:41093-60-1
- Skullcapflavone I
Catalog No.:BCN5464
CAS No.:41060-16-6
- Neobavaisoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN3194
CAS No.:41060-15-5
- Lipiferolide
Catalog No.:BCN5463
CAS No.:41059-80-7
- Timosaponin A3
Catalog No.:BCN4999
CAS No.:41059-79-4
- Sirtinol
Catalog No.:BCC2224
CAS No.:410536-97-9
- Palovarotene
Catalog No.:BCC4185
CAS No.:410528-02-8
- H-D-Ala-OBzl.TosOH
Catalog No.:BCC2850
CAS No.:41036-32-2
- Desacetylcinobufotalin
Catalog No.:BCC8166
CAS No.:4099-30-3
- Medioresinol
Catalog No.:BCN5462
CAS No.:40957-99-1
- Hirsutenone
Catalog No.:BCN5467
CAS No.:41137-87-5
- Boc-Phe(4-F)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3219
CAS No.:41153-30-4
- CMPD-1
Catalog No.:BCC7274
CAS No.:41179-33-3
- erythro-Guaiacylglycerol beta-sinapyl ether 7-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN7348
CAS No.:412029-03-9
- Pseudolarolide F
Catalog No.:BCN6428
CAS No.:412321-91-6
- H-Asp-OtBu
Catalog No.:BCC2883
CAS No.:4125-93-3
- Z-N-Me-Ile-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2617
CAS No.:4125-97-7
- 4-Methylamino-3-nitrobenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8715
CAS No.:41263-74-5
- 4-IPP
Catalog No.:BCC6023
CAS No.:41270-96-6
- TIC10
Catalog No.:BCC3906
CAS No.:41276-02-2
- Alfacalcidol
Catalog No.:BCC4962
CAS No.:41294-56-8
- BAM (8-22)
Catalog No.:BCC5806
CAS No.:412961-36-5
Antifilarial diarylheptanoids from Alnus nepalensis leaves growing in high altitude areas of Uttarakhand, India.[Pubmed:23219341]
Phytomedicine. 2013 Jan 15;20(2):124-32.
Lymphatic filariasis continues to be a major health problem in tropical and subtropical countries. A macrofilaricidal agent capable of eliminating adult filarial parasites is urgently needed. Platyphyllenone (A), alusenone (B), hirustenone (C) and Hirsutanonol (D) are important biologically active diarylheptanoids present in Alnus nepalensis. In the present study, we report the antifilarial activity in diarylheptanoids isolated from the leaves of A. nepalensis. Out of four compounds (A-D) tested in vitro one has shown promising anti-filarial activity both in vitro and in vivo studies. This is the first ever report on antifilarial efficacy of a compound of the plant and warrants further studies around this scaffold. In addition, a sensitive, selective and robust densitometric high-performance thin-layer chromatographic method was developed and validated for the above four biomarker compounds. The separation was performed on silica gel 60F(254) high-performance thin layer chromatography plates using chloroform:methanol (9:1, v/v) as mobile phase. The quantitation of marker compounds was carried out using densitometric reflection/absorption mode at 600 nm after post-chromatographic derivatization using vanillin-sulfuric acid reagent. The method was validated for peak purity, precision, robustness, limit of detection (LOD) and quantitation (LOQ) etc., as per the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) guidelines.
Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 expression by diarylheptanoids from the bark of Alnus hirsuta var. sibirica.[Pubmed:10784440]
Biol Pharm Bull. 2000 Apr;23(4):517-8.
Two known diarylheptanoids, oregonin (1), (5S)-1,7-bis-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-heptane-3-one-5-O-beta-D-xylopyranosi de and Hirsutanonol (2), (5S)-1,7-bis-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxyheptane-3-one isolated from the bark of Alnus hirsuta var. sibirica, showed significant inhibitory effects on 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-induced cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression in immortalized human breast epithelial MCF10A cells.
[Chemical constituents from roots of Chirita longgangensis var. hongyao].[Pubmed:24956847]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2014 Mar;39(6):1040-2.
To study the chemical constituents from the roots of Chirita longgangensis var. hongyao. The methanol extract was isolated and purified by silica gel, Sephadex LH-20 and preparative HPLC. Their structures were elucidated by MS and spectral data (1H, 13C-NMR). Seven compounds were isolated and identified as plantainoside A (1), plantainoside B (2), calcedarioside C (3), calcedarioside D (4), platyphylloside (5), Hirsutanonol (6), and Hirsutanonol-5-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (7). Compounds 5-7 were isolated for the first time from the family Gesneriaceae.
Diarylheptanoids from Alnus glutinosa bark and their chemoprotective effect on human lymphocytes DNA.[Pubmed:23512500]
Planta Med. 2013 Apr;79(6):499-505.
A study of secondary metabolites from the bark of Alnus glutinosa led to the isolation of fourteen diarylheptanoids: oregonin (1), platyphylloside (2), rubranoside A (3), rubranoside B (4), Hirsutanonol (5), hirsutenone (6), Hirsutanonol-5-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (7), platyphyllonol-5-O-beta-D-xylopyranoside (8), aceroside VII (9), alnuside A (10), alnuside B (11), 1,7-bis-(3,4-dihydoxyphenyl)-5-hydroxy-heptane-3-O-beta-D-xylopyranoside (12), (5S)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-heptan -3-one (13), and (5S)-1,7-bis-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-O-beta-D-[6-(3,4-dimethoxycinnamoylglucopyra nosyl)]-heptan-3-one (14). All of the diarylheptanoids, except 1 and 5, were found in A. glutinosa for the first time, while 13 and 14 were new compounds. The structures were determined by spectroscopic techniques: 1D and 2D NMR, HR-ESI-MS, FTIR, UV, and CD. All isolated compounds were analyzed for an in vitro protective effect on chromosome aberrations in peripheral human lymphocytes using the cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay. The majority of them, including the new compounds 13 and 14, exerted a pronounced effect in decreasing DNA damage in human lymphocytes. Diarylheptanoids 1, 2, 5, 13, and 14 at a concentration of 1 microg/mL decreased the frequency of micronuclei by 52.8 %, 43.8 %, 63.6 %, 44.4 %, and 56.0 %, respectively, exerting a much stronger effect than the synthetic protector amifostine (17.2 %, c = 1 microg/mL).
Cytotoxic activities of diarylheptanoids from Alnus japonica.[Pubmed:18958419]
Arch Pharm Res. 2008 Oct;31(10):1287-9.
The diarylheptanoids (1-10) 1,7-bis-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-heptane-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl(1-->3)-beta-D-xyl opyranoside (1), 1,7-bis-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-heptane-3-O-beta-D-apiofuranosyl(1-->6)-beta-D-gluc opyranoside (2), 1,7-bis-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-heptane-5-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (3), 1,7-bis-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxyheptane (4), 1,7-bis-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-heptane-3-one-5-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (5), oregonin (6), Hirsutanonol (7), hirsutenone (8), 1,7-bis-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxyheptane-3-O-beta-D-xylopyranoside (9), and platyphylloside (10), isolated from the bark of Alnus japonica, were analyzed for their cytotoxic activities on various human and mouse cancer cell lines. The cytotoxic activities of these ten compounds were evaluated against murine B16 melanoma, human SNU-1 gastric cancer, human SNU-354 hepatoma cancer and human SNU-C4 colorectal cell lines. The diarylheptanoids showed potent cytotoxic activities against murine B16 melanoma cells and human SNU-C1 gastric cancer cell when the cell viability was analyzed by MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazoliumbromide) assay.


