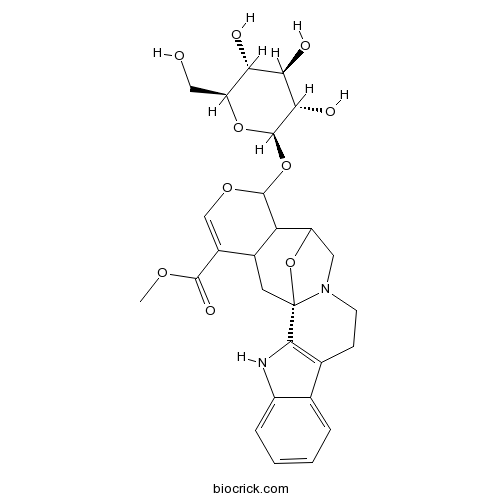
CadambineCAS# 54422-49-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 54422-49-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 25199699 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C27H32N2O10 | M.Wt | 544.5 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | methyl (1S)-17-[(2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-18,23-dioxa-3,13-diazahexacyclo[13.7.1.01,13.02,10.04,9.016,21]tricosa-2(10),4,6,8,19-pentaene-20-carboxylate | ||
| SMILES | COC(=O)C1=COC(C2C1CC34C5=C(CCN3CC2O4)C6=CC=CC=C6N5)OC7C(C(C(C(O7)CO)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OVRROYYXOBYCSR-JPXAJPAESA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C27H32N2O10/c1-35-24(34)15-11-36-25(38-26-22(33)21(32)20(31)18(10-30)37-26)19-14(15)8-27-23-13(6-7-29(27)9-17(19)39-27)12-4-2-3-5-16(12)28-23/h2-5,11,14,17-22,25-26,28,30-33H,6-10H2,1H3/t14?,17?,18-,19?,20-,21+,22-,25?,26+,27-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Cadambine Dilution Calculator

Cadambine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8365 mL | 9.1827 mL | 18.3655 mL | 36.7309 mL | 45.9137 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3673 mL | 1.8365 mL | 3.6731 mL | 7.3462 mL | 9.1827 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1837 mL | 0.9183 mL | 1.8365 mL | 3.6731 mL | 4.5914 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0367 mL | 0.1837 mL | 0.3673 mL | 0.7346 mL | 0.9183 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0184 mL | 0.0918 mL | 0.1837 mL | 0.3673 mL | 0.4591 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 8,9-Dehydro-7,9-diisobutyryloxythymol
Catalog No.:BCN9340
CAS No.:22518-03-2
- Hancolupenone
Catalog No.:BCN9339
CAS No.:132746-04-4
- Phochinenin G
Catalog No.:BCN9338
CAS No.:1070883-75-8
- Jasnervoside C
Catalog No.:BCN9337
CAS No.:1622337-36-3
- 1-Methyleffusol
Catalog No.:BCN9336
CAS No.:144106-78-5
- Thymol isobutyrate
Catalog No.:BCN9335
CAS No.:5451-67-2
- Aureusidin
Catalog No.:BCN9334
CAS No.:38216-54-5
- Sampsone B
Catalog No.:BCN9333
CAS No.:1309125-17-4
- 3α,30-Diacetoxy-12α-hydroxy-23-oxoeupha-7,24-dien-21,16β-olid-28-oic acid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN9332
CAS No.:215160-96-6
- 7β-Hydroxycucurbitacin B
Catalog No.:BCN9331
CAS No.:1135141-79-5
- Hancokinol
Catalog No.:BCN9330
CAS No.:132294-77-0
- Methyl lucidenate E2
Catalog No.:BCN9329
CAS No.:98665-12-4
- Methyl lucidenate N
Catalog No.:BCN9342
CAS No.:1276655-49-2
- Methyl ganoderenate D
Catalog No.:BCN9343
CAS No.:748136-03-0
- Thymyl 2-methylbutyrate
Catalog No.:BCN9344
CAS No.:69844-32-2
- Murrayafoline A
Catalog No.:BCN9345
CAS No.:4532-33-6
- Phochinenin I
Catalog No.:BCN9346
CAS No.:1070883-77-0
- 2α,3α,24-Trihydroxyursa-12,20(30)-dien-28-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9347
CAS No.:341503-22-8
- 8-Hydroxythymol
Catalog No.:BCN9348
CAS No.:4478-33-5
- Visartiside E
Catalog No.:BCN9349
CAS No.:1212005-08-7
- Girinimbine
Catalog No.:BCN9350
CAS No.:23095-44-5
- Benzyl [5-O-benzoyl-β-D-apiofuranosyl(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN9351
CAS No.:1097040-08-8
- Pomegralignan
Catalog No.:BCN9352
CAS No.:1562492-32-3
- Methyl lucidenate D
Catalog No.:BCN9353
CAS No.:98665-09-9
Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of Neolamarckia cadamba and its bioactive monoterpenoid indole alkaloids.[Pubmed:32569718]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Jun 20;260:113103.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Neolamarckia cadamba has been used traditionally to treat inflammation, fever, and pruritus in the Dai ethnopharmacy in Yunnan province, P.R. China. However, according to literature survey, the action basis of anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of this plant were rarely reported, which accounts for the original intentions of this investigation. AIM OF THE STUDY: The study aimed to investigate the anti-inflammatory and analgesic action of methanolic extract (ME), ethyl acetate (EA), and aqueous (AQS) fractions of N. cadamba and further explore the accurate compounds responsible for the activities of EA fraction. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The in vivo anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of ME, EA, and AQS fractions at the doses of 200 and 400 mg/kg and two major constituents (compounds 5 and 7) at 50 and 100 mg/kg via intragastrically administrated, respectively, were evaluated by carrageenan-induced paw edema and acetic acid-stimulated writhing animal models. Aspirin (ASP) was used as the positive control at the dose of 200 mg/kg. The monoterpenoid indole alkaloids (MIAs) in EA fraction were phytochemically studied utilizing chromatographic techniques, and their structures and absolute configurations were established on the basis of multiple spectroscopic analyses and quantum computational chemistry method. Moreover, the in vitro anti-inflammatory activities of all the isolates were assessed by suppressing releases of LPS-activated inflammatory mediators (TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, and COX-2) in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells at a concentration of 10 mug/mL. Dexamethasone (DXM) was used as the positive control. RESULTS: Three fractions (ME, EA, and AQS) significantly ameliorated the paw edema caused by carrageenan and reduced the number of writhing induced by acetic acid in comparison to the control group at the doses of 200 and/or 400 mg/kg (in vivo). Subsequent phytochemical investigation of EA fraction led to the structural characterization of four new monoterpenoid indole alkaloids, neoCadambines A-D (1-4), as well as eight known analogues (5-12). NeoCadambine A possesses a novel 14-nor-MIA skeleton that could be derived from the corynantheine-type MIAs via oxidative cleavage of C3-C14 bond and subsequently degradation of C14. Moreover, the structure of a bioactive known MIA, Cadambine acid (6), was reassigned by analysis of its NMR spectroscopic data. Further biological assays revealed that the major constituent 3beta-dihydroCadambine (7) significantly relieved the paw edema and decreased the number of writhing at 100 mg/kg in vivo. In addition, most of the isolates displayed remarkable in vitro anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the secretion of aforementioned inflammatory mediators (COX-2, IL-1beta, and TNF-alpha) at a concentration of 10 mug/mL, and compounds 4, 7, and 9 showed better anti-inflammatory effects than that of positive control, dexamethasone. CONCLUSIONS: This study further validated the anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of N. cadamba, and revealed that monoterpenoid indole alkaloids could partly contribute to the efficacy of this ethnodrug. The major constituent 3beta-dihydroCadambine (7) showed significant anti-inflammatory activities both in vitro and in vivo, which suggested that it could be a promising anti-inflammatory lead compound. Our findings provided scientific justification to support the traditional application of N. cadamba for treating inflammatory and nociceptive disorders.
UFLC-PDA-MS/MS Profiling of Seven Uncaria Species Integrated with Melatonin/5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptors Agonistic Assay.[Pubmed:31933166]
Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2020 Feb;10(1):23-36.
Uncariae Ramulus Cum Uncis (Gou-Teng), the dried hook-bearing stems of several Uncaria plants (Rubiaceae), is a well-known herbal medicine in China. The clinical application of Gou-Teng is bewildered for the morphological and chemical similarity between different species. In order to discern their chemical and biological difference, an ultra-fast liquid chromatography equipped with ion trap time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UFLC-IT/TOF-MS) combining with melatonin (MT1 and MT2) and 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT1A and 5-HT2C) receptors agonistic assay in vitro was conducted on seven Uncaria species. As a result, 57 compounds including 35 indole alkaloids, ten flavonoids, five triterpenoids, five chlorogenic analogues, and two other compounds were characterized based on their MS/MS patterns and UV absorptions. Specifically, Cadambine-type and corynanthein-type alkaloids were exclusively present in U.rhynchophylla and U.scandens, whereas corynoxine-type alkaloids were commonly detected in all the seven Uncaria plants. Three Uncaria species, U. rhynchophylla, U. macrophylla, and U. yunnanensis showed obviously agnostic activity on four neurotransmitter receptors (MT1, MT2, 5-HT1A, and 5-HT2C). This first-time UFLCMS-IT-TOF analyses integrated with biological assay on seven Uncaria plants will provide scientific viewpoints for the clinical application of Gou-Teng.
In silico Inhibition of BACE-1 by Selective Phytochemicals as Novel Potential Inhibitors: Molecular Docking and DFT Studies.[Pubmed:30767744]
Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2019 Feb 14. pii: CDDT-EPUB-96664.
BACKGROUND: Alzheimer's disease (AD) has become the most common age-dependent disease of dementia. The trademark pathologies of AD are the presence of amyloid aggregates in neurofibrils. Recently phytochemicals being considered as potential inhibitors against various neurodegenerative, anti-fungal, antibacterial and antiviral diseases in human beings. OBJECTIVE: This study targets the inhibition of BACE-1 by phytochemicals using in silico drug discovery analysis. METHODS: A total of 3150 phytochemicals were collected from almost 25 different plants through literature assessment. The ADMET studies, molecular docking and density functional theory (DFT) based analysis was performed to analyze the potential inhibitory properties of these phytochemicals. RESULTS: The ADMET and docking results exposed seven compounds that have high potential as an inhibitory agent against BACE-1 and show binding affinity >8.0 kcal/mol against BACE-1. They show binding affinity greater than those of various previously reported inhibitors of BACE-1. Furthermore, DFT based analysis shown high reactivity for these seven phytochemicals in the binding pocket of BACE-1, based on ELUMO, EHOMO and Kohn-Sham energy gap. Seven out of seven phytochemicals are testified (as compared to experimental ones) as novel inhibitors against BACE-1. CONCLUSION: Out of seven phytochemicals, four are from plant Glycyrrhiza glabra i.e. Shinflavanone, Glabrolide, Glabrol and PrenyllicoflavoneA, one from Huperzia serrate i.e. Macleanine, one from Uncaria rhynchophylla i.e. 3a-dihydro-Cadambine and another one is VolvalerelactoneB from plant Valeriana-officinalis. It is concluded that these phytochemicals are candidate for drug/inhibitor against BACE-1, and can be administered to humans after experimental validation through in vitro and in vivo trials.
Traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacological properties of Neolamarckia cadamba: A review.[Pubmed:26821190]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Apr 2;181:118-35.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: There are more than 3000 officially documented plants in the Indian subcontinent that hold great medicinal potential. One such under-explored plant is an evergreen tropical tree Neolamarckia cadamba (Roxb.) Bosser (Rubiaceae). It is widely distributed in tropical and subtropical regions of the world and has therapeutic potential against many diseases such as diabetes, anaemia, stomatitis, leprosy, cancer and infectious diseases. Neolamarckia cadamba has historical existence in India and it is mentioned in mythical stories. There are several reports on medicinal values of root, bark and leaves of N. cadamba; but the literature on its fruits is scanty. Therefore, the present review aims to provide updated comprehensive information on the phytochemistry and pharmacological properties of different parts of N. cadamba tree with special reference to its fruit, in order to open new perspectives for future food and pharmacological research. MATERIALS AND METHODS: A literature search was performed on N. cadamba using ethnobotanical textbooks, published articles in peer-reviewed journals, unpublished materials, government survey reports and scientific databases such as Pubmed, Scopus, Web of Science, Science Direct, Google Scholar and other web search engines (Google, Yahoo). The Plant List, International Plant Name Index and Kew Botanical Garden Plant name databases were used to validate the scientific names. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION: Neolamarckia cadamba is one of the economically important trees, which is being exploited for paper, pulp and wood industry. In folk medicine, various parts of N. cadamba are used in the treatment of various ailments such as fever, uterine complaints, blood diseases, skin diseases, tumour, anaemia, eye inflammation and diarrhoea. Other reported uses of N. cadamba include antihepatotoxic, antimalarial, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, diuretic and laxative. Various phytochemicals such as Cadambine and its derivatives (dihydroCadambine and isodihydroCadambine) and indole alkaloids (Neolamarckines) were isolated from the leaves; whereas the presence of quinovic acid derivatives have been reported in the bark of N. cadamba. CONCLUSION: The present review compiles information on an ethnopharmacologically useful plant N. cadamba. Bioactive compounds responsible for its various medicinal properties and their effects at the molecular level need to be investigated in more detail. Furthermore, the detailed study of toxicity and pharmacological properties of extracts as well as molecules in N. cadamba is required to confirm the ethnomedicinal claims of N. cadamba for food and pharmaceutical applications.
Bio-assay Guided Isolation of Anti-cancer Compounds from Anthocephalus cadamba Bark.[Pubmed:26434112]
Nat Prod Commun. 2015 Aug;10(8):1349-50.
Anthocephalus cadamba, an important plant in the traditional system of medicine in India, is reported to possess anticancer activity. Guided by bio-assay tests using human colorectal (HCT116) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cell lines, it has been shown to contain three active constituents, the triterpenoid saponins 3-O-[alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl]-quinovic acid (1) and 3-O-[alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl]-quinovic acid 28-O-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl] ester (2), and the alkaloid Cadambine (3). The structures of the isolated compounds were established using spectroscopic techniques. The isolated compounds demonstrated concentration dependent inhibition of both the cell lines, where compound 3 proved to be the most potent inhibitor of cell line HCT116 (IC50 45 +/- 4 mug/mL) and compound 2 demonstrated maximum inhibitory activity against HepG2 cell line with an IC50 value of 89 +/- 7 mug/mL.
Cadamba: A miraculous tree having enormous pharmacological implications.[Pubmed:26392707]
Pharmacogn Rev. 2015 Jul-Dec;9(18):107-13.
The Cadamba is one of the important medicinal plants belonging to the Rubiaceae family. It is crucially significant as it has the largest number of phytochemicals and secondary metabolites (viz., cadambagenic acid, cadamine, quinovic acid, beta-sitosterol, Cadambine, etc.) having pharmacological and biological properties. It can be used as an alternative to various synthetic chemical compounds in the prevention as well as the treatment of several incurable diseases. More than 100 years of research has been done to discover various phytochemicals and their implications. Very few of them, i.e.
Anthocephaline, a new indole alkaloid and cadambine, a potent inhibitor of DNA topoisomerase IB of Leishmania donovani (LdTOP1LS), isolated from Anthocephalus cadamba.[Pubmed:25920266]
Nat Prod Commun. 2015 Feb;10(2):297-9.
Chemical investigation of the stem bark of Anthocephalus cadamba has resulted in the isolation of anthocephaline (1), a new indole alkaloid, along with strictosamide (2), vincosamide (3) and Cadambine (4). The structures of the isolated alkaloids (1-4) were established by detailed 2D NMR spectral analysis. Cadambine (4) exhibited potent DNA topoisomerase IB inhibitory activity.
Alkaloids from the hook-bearing branch of Uncariarhynchophylla and their neuroprotective effects against glutamate-induced HT22 cell death.[Pubmed:24899363]
J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2014;16(8):876-83.
One new alkaloid, 4-geissoschizine N-oxide methyl ether (1), was isolated from the EtOH extract of the hook-bearing branch of Uncariarhynchophylla, together with 10 known alkaloids, 3-epi-geissoschizine methyl ether (2) isolated from U.rhynchophylla for the first time, geissoschizine methyl ether (3), 4-hirsuteine N-oxide (4), hirsuteine (5), hirsutine (6), 3alpha-dihydro-Cadambine (7), 3beta-isodihydro-Cadambine (8), Cadambine (9), strictosamide (10), and akuammigine (11). The structures were elucidated by spectroscopic methods including UV, ESI-QTOF MS, NMR, and circular dichroism experiments. Neuroprotective effects of 1-9 were investigated against 3 mM glutamate-induced HT22 cell death. The activity assay showed that 2, 3, 5, and 6 exhibited potent neuroprotective effects against glutamate-induced HT22 cell death. However, only weak neuroprotective activities were observed for 1, 4, 7, 8, and 9.
Analysis of the traditional medicine YiGan San by the fragmentation patterns of cadambine indole alkaloids using HPLC coupled with high-resolution MS.[Pubmed:24106099]
J Sep Sci. 2013 Dec;36(23):3723-32.
YiGan San (YGS) has long been used in traditional Japanese and Chinese folk medicine and serves as a potent and novel therapeutic agent to treat Alzheimer's disease. In the present study, a rapid and sensitive method based on HPLC coupled with diode-array detection and quadrupole TOF MS (Q-TOF-MS) was designed to reveal the chemical constituents of YGS. Thirty-six compounds were identified and assigned in YGS, including 14 alkaloids, nine gamma-lactones, six flavonoids, three triterpenoid saponinares, two small molecular organic acids, and two other types of compounds. In addition, the accurate fragment weight and MS/MS fragmentation reactions of a subtype indole alkaloid in Uncariae ramulus cum uncis were summarized for the first time to realize rapid identification without reference substances. For the first time, 11 major constituents were comprehensively quantified with a HPLC coupled with triple-quadrupole MS method. A three-section switch was used to realize such multicomponent identification. The contents of saikosaponin B2 and isoliquiritin, which produce anti-inflammatory and antidepressant-like effects, were extremely different, up to 700 times, in two sources of YGS. The developed qualitative and quantitative method was proved to be precise, accurate, and reproducible.
Chemical and bioactivity evaluation of the bark of Neonauclea purpurea.[Pubmed:22474944]
Nat Prod Commun. 2012 Feb;7(2):169-70.
Bioassay-guided fractionation of the MeOH extract from the stem bark of Neonauclea purpurea used in traditional medicine, resulted in the isolation of 2 indole alkaloids, Cadambine (1) and alpha-dihydroCadambine (2), as well as a quinolic compound, 2,6-dimethoxy-1,4-benzoquinone (3). Antimalarial activity evaluation showed that compounds 2 and 3 exhibited mild in vitro antimalarial activity against Plasmodium falciparum, the chloroquine-resistant strain K1 with IC50 values of 6.6 and 11.3 microM, respectively. Compounds 1 and 2 showed no cytotoxicity to monkey (Vero) cells, but compound 3 showed weak cytotoxicity with an IC50 value of 1.19 microM.
Two new triterpenoid glycosides from the leaves of Anthocephalus chinensis.[Pubmed:21985583]
J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2011 Oct;13(11):1008-13.
Nine compounds were isolated from the leaves of Anthocephalus chinensis by column chromatography on silica gel and Sephadex LH-20, and their structures were elucidated by spectroscopic techniques as clethric acid-28-O-beta-d-glucopyranosyl ester (1), mussaendoside T (2), beta-stigmasterol (3), hederagenin (4), ursolic acid (5), clethric acid (6), 3beta,6beta,19alpha,24-tetrahydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid (7), mussaendoside I (8), and Cadambine (9). Compounds 1 and 2, and 7 and 8 were isolated from the plants of this genus for the first time, and compounds 1 and 2 were new triterpenoid glycosides.
Antileishmanial activity of quinovic acid glycosides and cadambine acid isolated from Nauclea diderrichii.[Pubmed:17089325]
Planta Med. 2006 Dec;72(15):1396-402.
Nine quinovic acid glycosides and the alkaloid Cadambine acid isolated from N. diderrichii, an evergreen endemic plant of West and Central Africa, were assessed for their in vitro antileishmanial activity against Leishmania infantum. Four quinovic acid glycosides and Cadambine acid revealed a strong antileishmanial activity (IC (50) = 1 microM) highly specific for the intracellular amastigote form of the parasite. Quinovic acid glycosides were shown to inhibit parasite internalisation by interfering with promastigotes while Cadambine acid exerted immunomodulatory activity by inducing NO production in human macrophages. The association of Cadambine acid with amphotericin B demonstrated an interesting synergism, suggesting that Cadambine acid could be used as a complement of such conventional therapy.
Gluco-indole alkaloids from the bark of Nauclea diderrichii. 1H and 13C NMR assignments of 3alpha-5alpha-tetrahydrodeoxycordifoline lactam and cadambine acid.[Pubmed:15674811]
Magn Reson Chem. 2005 May;43(5):427-9.
Detailed (1)H and (13)C NMR assignments of 3alpha-5alpha-tetrahydrodeoxycordifoline lactam and Cadambine acid, isolated from the bark of the Nauclea diderrichii (de Wild.) Merr. (Rubiaceae) were achieved by 1D and 2D techniques such as DEPT, HMBC, HMQC, COSY and NOESY.
Gluco-indole alkaloids from Nauclea cadamba in Thailand and transformation of 3 alpha-dihydrocadambine into the indolopyridine alkaloid, 16-carbomethoxynaufoline.[Pubmed:12576667]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2003 Feb;51(2):232-3.
Three monoterpenoid gluco-indole alkaloids, 3beta-isodihydroCadambine, Cadambine, and 3alpha-dihydroCadambine, were isolated from Nauclea cadamba ROXB. growing in Thailand. The stereochemistry at C19 in 3beta-isodihydroCadambine was elucidated to be R by spectroscopic analysis. Treatment of 3alpha-dihydroCadambine with beta-glucosidase in aqueous ammonium acetate solution gave an indolopyridine alkaloid, 16-carbomethoxynaufoline, and an unusually rearranged compound.


