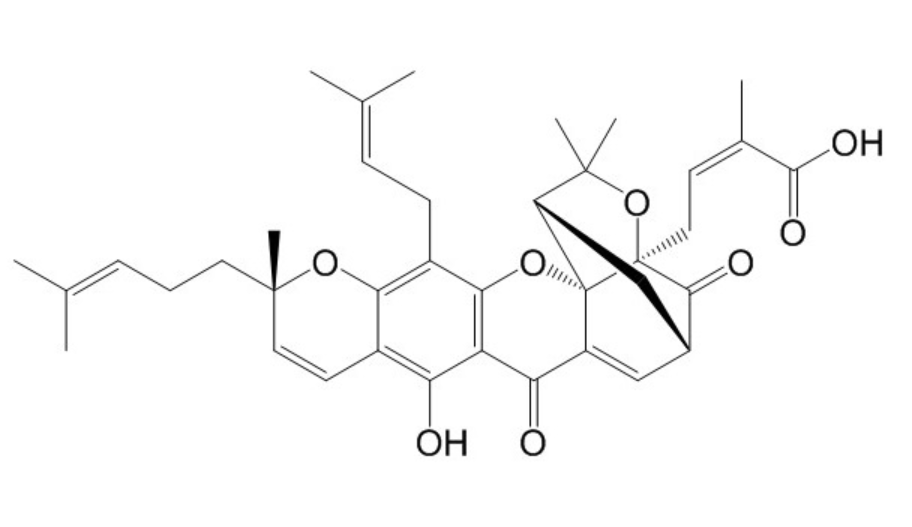
Epigambogic acidCAS# 887606-04-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 887606-04-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C38H44O8 | M.Wt | 628.75 |
| Type of Compound | Xanthones | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Epigambogic acid Dilution Calculator

Epigambogic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5905 mL | 7.9523 mL | 15.9046 mL | 31.8091 mL | 39.7614 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3181 mL | 1.5905 mL | 3.1809 mL | 6.3618 mL | 7.9523 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.159 mL | 0.7952 mL | 1.5905 mL | 3.1809 mL | 3.9761 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0318 mL | 0.159 mL | 0.3181 mL | 0.6362 mL | 0.7952 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0159 mL | 0.0795 mL | 0.159 mL | 0.3181 mL | 0.3976 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Bornyl Acetate
Catalog No.:BCN9108
CAS No.:76-49-3
- Loureirin D
Catalog No.:BCN9107
CAS No.:119425-91-1
- (±)-Vasicine
Catalog No.:BCN9106
CAS No.:6159-56-4
- Macrozamin
Catalog No.:BCN9105
CAS No.:6327-93-1
- 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 2,3-dihydro-3,5,7-trihydroxy-3-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-, (R)-
Catalog No.:BCN9104
CAS No.:118204-64-1
- (3R)-2,3-Dihydro-5,7-dihydroxy-3-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN9103
CAS No.:849727-88-4
- 3-(2-Hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-propanone
Catalog No.:BCN9102
CAS No.:151752-07-7
- Bisisorhapontigenin F
Catalog No.:BCN9101
CAS No.:
- Cyanidin 3-O-arabinoside
Catalog No.:BCN9100
CAS No.:792868-19-0
- α-Terpinene
Catalog No.:BCN9099
CAS No.:99-86-5
- Petunidin 3-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9098
CAS No.:71991-88-3
- Delphinidin 3-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9097
CAS No.:50986-17-9
- Rebaudioside N
Catalog No.:BCN9110
CAS No.:1220616-46-5
- Plantanone B
Catalog No.:BCN9111
CAS No.:55780-30-8
- Kaempferol-3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN9112
CAS No.:476617-49-9
- Kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside 7-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9113
CAS No.:34336-18-0
- Kaempferol 3,7-di-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9114
CAS No.:25615-14-9
- Dehydrocurdione
Catalog No.:BCN9115
CAS No.:38230-32-9
- Isoverticine
Catalog No.:BCN9116
CAS No.:23496-43-7
- Bancroftinone
Catalog No.:BCN9117
CAS No.:14964-98-8
- 5-O-Cinnamoylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9118
CAS No.:6470-68-4
- Valeriandoid F
Catalog No.:BCN9119
CAS No.:1427162-60-4
- Bletilloside A
Catalog No.:BCN9120
CAS No.:2292159-89-6
- Rapanone
Catalog No.:BCN9121
CAS No.:573-40-0
Rapid determination of polyprenylated xanthones in gamboge resin of Garcinia hanburyi by HPLC.[Pubmed:17396587]
J Sep Sci. 2007 Feb;30(3):304-9.
A rapid ion-pair HPLC method was developed and validated for the determination of eight polyprenylated xanthones including three pairs of epimers, namely morellic acid (MA), 30-hydroxygambogic acid (HGA), 30-hydroxyEpigambogic acid (HEGA), isogambogic acid (IGA), epiisogambogic acid (EIGA), gambogenic acid (GNA), gambogic acid (GA), and Epigambogic acid (EGA), in gamboge resin of Garcinia hanburyi. The separation was performed on a narrow bore C8 column with isocratic elution using a mixture of methanol-ACN-40 mM KH2PO4 buffer (37.5:37.5:25 v/v/v, containing 0.1% tetradecyltrimethylammonium bromide). The newly developed method was used to determine the contents of the eight compounds present in the gamboge. Results showed that GA and EGA are the dominant components of gamboge. The content ratio of each epimer pair remained constant, indicating that the content ratio of epimers can be used as a specific characteristic for the quality control of gamboge.
Preparative separation of gambogic acid and its C-2 epimer using recycling high-speed counter-current chromatography.[Pubmed:16887130]
J Chromatogr A. 2006 Sep 15;1127(1-2):298-301.
A recycling counter-current chromatographic system was first set up with a high-speed counter-current chromatography instrument coupled with a column switching valve. This system was first successfully applied to the preparative separation of epimers, gambogic acid and Epigambogic acid from Garcinia hanburyi using n-hexane-methanol-water (5:4:1, v/v/v) as the two-phase solvent system. As a result, 28.2 mg gambogic acid and 18.4 mg Epigambogic acid were separated from 50 mg of mixture. Their purities were both above 97% as determined by HPLC. The chemical structures were then identified by their (1)H NMR and (13)C NMR spectra.
Gambogic acid and epigambogic acid, C-2 epimers with novel anticancer effects from Garcinia hanburyi.[Pubmed:16534739]
Planta Med. 2006 Feb;72(3):281-4.
Gambogic acid, usually isolated as an inseparable stereomeric mixture of C-2 epimers, was newly separated into two epimers (1 and 2) from the gamboges of Garcinia hanburyi. The stereochemistry at C-2 was clearly defined by extensive spectroscopic analysis and direct comparison of NMR and HPLC data with those of the known R-epimer. Both epimers were examined for their cytotoxicities against human leukemia K562 (K562/S) and doxorubicin-resistant K562 (K562/R) cell lines. Different from doxorubicin (IC (50) = 10.78 microM for K562/R and 0.66 microM for K562/S), epimers 1 and 2 exhibited similar activities against both cell lines (IC(50) = 1.32 and 0.89 microM for 1, IC(50) = 1.11 and 0.86 microM for 2). These results suggested that both epimers were not multidrug resistance (MDR) substrates. Furthermore, epimers 1 and 2 were tested for their inhibitory effects against six human cytochrome P-450 enzymes. Epimers 1 and 2 showed little inhibitory effects toward five of the enzymes except CYP2C9. Interestingly, when tested against CYP2C9, S-epimer 2 had an inhibitory effect 20-fold stronger than that of R-epimer 1.


