Loureirin DCAS# 119425-91-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 119425-91-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 13939318 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H16O5 | M.Wt | 288.3 |
| Type of Compound | Chalcones/Dihydrochalcones | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
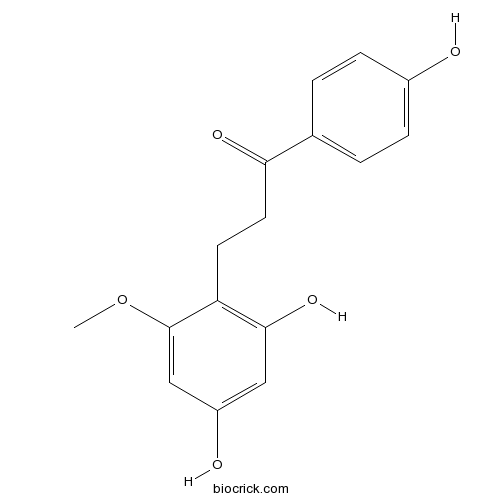
| Chemical Name | 3-(2,4-dihydroxy-6-methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-1-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=CC(=C1CCC(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AQMBVNGTZRFEPF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H16O5/c1-21-16-9-12(18)8-15(20)13(16)6-7-14(19)10-2-4-11(17)5-3-10/h2-5,8-9,17-18,20H,6-7H2,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Loureirin D Dilution Calculator

Loureirin D Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4686 mL | 17.343 mL | 34.6861 mL | 69.3722 mL | 86.7152 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6937 mL | 3.4686 mL | 6.9372 mL | 13.8744 mL | 17.343 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3469 mL | 1.7343 mL | 3.4686 mL | 6.9372 mL | 8.6715 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0694 mL | 0.3469 mL | 0.6937 mL | 1.3874 mL | 1.7343 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0347 mL | 0.1734 mL | 0.3469 mL | 0.6937 mL | 0.8672 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- (±)-Vasicine
Catalog No.:BCN9106
CAS No.:6159-56-4
- Macrozamin
Catalog No.:BCN9105
CAS No.:6327-93-1
- 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 2,3-dihydro-3,5,7-trihydroxy-3-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-, (R)-
Catalog No.:BCN9104
CAS No.:118204-64-1
- (3R)-2,3-Dihydro-5,7-dihydroxy-3-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN9103
CAS No.:849727-88-4
- 3-(2-Hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-propanone
Catalog No.:BCN9102
CAS No.:151752-07-7
- Bisisorhapontigenin F
Catalog No.:BCN9101
CAS No.:
- Cyanidin 3-O-arabinoside
Catalog No.:BCN9100
CAS No.:792868-19-0
- α-Terpinene
Catalog No.:BCN9099
CAS No.:99-86-5
- Petunidin 3-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9098
CAS No.:71991-88-3
- Delphinidin 3-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9097
CAS No.:50986-17-9
- Malvidin 3-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9096
CAS No.:18470-06-9
- Febrifugine dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN9095
CAS No.:32434-42-7
- Bornyl Acetate
Catalog No.:BCN9108
CAS No.:76-49-3
- Epigambogic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9109
CAS No.:887606-04-4
- Rebaudioside N
Catalog No.:BCN9110
CAS No.:1220616-46-5
- Plantanone B
Catalog No.:BCN9111
CAS No.:55780-30-8
- Kaempferol-3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN9112
CAS No.:476617-49-9
- Kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside 7-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9113
CAS No.:34336-18-0
- Kaempferol 3,7-di-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9114
CAS No.:25615-14-9
- Dehydrocurdione
Catalog No.:BCN9115
CAS No.:38230-32-9
- Isoverticine
Catalog No.:BCN9116
CAS No.:23496-43-7
- Bancroftinone
Catalog No.:BCN9117
CAS No.:14964-98-8
- 5-O-Cinnamoylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9118
CAS No.:6470-68-4
- Valeriandoid F
Catalog No.:BCN9119
CAS No.:1427162-60-4
[Identification of active components in Longxue Tongluo Capsules against ischemic brain injury based on component-activity relationship].[Pubmed:30868826]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019 Jan;44(1):150-157.
Ten fractions(A-J) were prepared by separation of Longxue Tongluo Capsules(LTC) by using silica gel column chromatography and orthogonal experimental design,showing similar chemical profiles with different abundances of peaks.These ten samples were assessed with UHPLC-QE OrbitrapHRMS for 97 common peaks.For the pharmacological activity experiment,three kinds of in vitro cell models including lipopolysaccharide(LPS)-induced BV-2 microglial cells NO release model,oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation(OGD/R)-treated HUVEC vascular endothelial cells injury model,and OGD/R-treated PC-12 nerve cells injury model were employed to evaluated the bioactivity of each fraction.Based on the contribution of each identified component,grey relation analysis and partial least squares(PLS) analysis were performed to establish component-activity relationship of LTC,identify the potential active components.After that,validation of the potential active components in LTC was carried out by using the same models.The results indicated that 4 phenolic compounds including 7,4'-dihydroxyhomoisoflavanone,loureirin C,4,4'-dihydroxy-2,6-dimethoxydihydrochalcone,and homoisosocotrin-4'-ol,might be the active components for anti-neuroinflammation effect;five phenolic compounds such as 3,5,7,4'-tetrahydroxyhomoisoflavanone,Loureirin D,7,4'-dihydroxyhomoisoflavane,and 5,7-dihydroxy-4'-methoxy-8-methyflavane,might have positive effects on the vascular endothelial injury;three phenolic compounds including 5,7,4'-trihydroxyflavanone,7,4'-dihydroxy-5-methoxyhomoisoflavane,and Loureirin D,might be the active components in LTC against neuronal injury.
Stimulation of dragon's blood accumulation in Dracaena cambodiana via fungal inoculation.[Pubmed:23518260]
Fitoterapia. 2013 Jun;87:31-6.
Dragon's blood is a rare and precious traditional medicine used by different cultures since ancient times. However, studies on enhancing the rapid accumulation of dragon's blood in Dracaena cambodiana and determining its formation mechanism are unavailable. In this study, the activities of two fungi, namely, BJDC01 and BJDC05, and their effect on promoting the accumulation of five main compositions of dragon's blood in D. cambodiana were investigated for the first time. Results of field tests conducted for ten months indicated that the contents of Loureirin D, 4,4'-dihydroxy-2'-dimethoxychalcone, Loureirin A and Loureirin B in two fungal-inoculated materials were 1.67 to 2.85 times greater than those of natural samples, and thus were significantly higher than those of the control groups. The content of 4,4'-dihydroxy-2'6'-dimethoxydihydrochalcone in each fungal-inoculated sample was close to that of the natural sample, and was more than twice of each of the control group. By combining the results of morphological characterizations, both BJDC01 and BJDC05 can stimulate the accumulation of the compositions of dragon's blood. This stimulation may be considered as a defense response of D. cambodiana tree against the invasion of foreign fungi. Thus, this study provides a potential way of producing dragon's blood via the inoculation of two fungal elicitors.


