Flavokawain ACAS# 37951-13-6 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

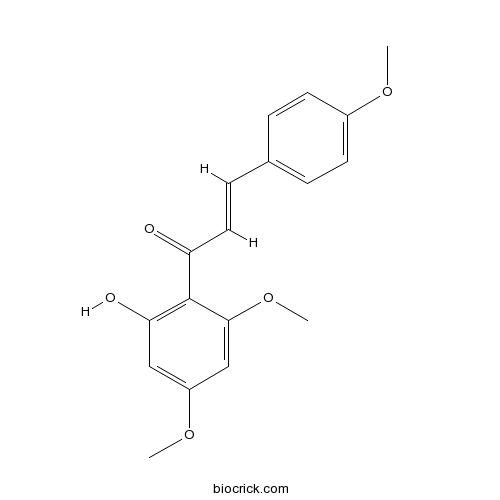
| Cas No. | 37951-13-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5355469 | Appearance | Orange powder |
| Formula | C18H18O5 | M.Wt | 314.34 |
| Type of Compound | Chalcones/Dihydrochalcones | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Flavokavin A; 2'-Hydroxy 4,4',6'-trimethoxychalcone; 4-Methoxyflavokawain B;3420-72-2;64680-84-8 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in chloroform | ||
| Chemical Name | (E)-1-(2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC=C(C=C1)C=CC(=O)C2=C(C=C(C=C2OC)OC)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CGIBCVBDFUTMPT-RMKNXTFCSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H18O5/c1-21-13-7-4-12(5-8-13)6-9-15(19)18-16(20)10-14(22-2)11-17(18)23-3/h4-11,20H,1-3H3/b9-6+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Flavokawain A Dilution Calculator

Flavokawain A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1813 mL | 15.9063 mL | 31.8127 mL | 63.6254 mL | 79.5317 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6363 mL | 3.1813 mL | 6.3625 mL | 12.7251 mL | 15.9063 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3181 mL | 1.5906 mL | 3.1813 mL | 6.3625 mL | 7.9532 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0636 mL | 0.3181 mL | 0.6363 mL | 1.2725 mL | 1.5906 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0318 mL | 0.1591 mL | 0.3181 mL | 0.6363 mL | 0.7953 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 5'-Guanylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9055
CAS No.:85-32-5
- Xanthosine
Catalog No.:BCN9054
CAS No.:146-80-5
- 5'-Cytidylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9053
CAS No.:63-37-6
- DL-Tartaric acid
Catalog No.:BCN9052
CAS No.:133-37-9
- Mirificin-4'-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9051
CAS No.:168035-01-6
- Bisisorhapontigenin D
Catalog No.:BCN9050
CAS No.:
- Hydroquinone
Catalog No.:BCN9049
CAS No.:123-31-9
- 1αH,5αH-guaia-6-ene-4β,10β-diol
Catalog No.:BCN9048
CAS No.:2013537-81-8
- Deslanoside
Catalog No.:BCN9047
CAS No.:17598-65-1
- Atractyloside potassium salt
Catalog No.:BCN9046
CAS No.:17754-44-8
- Menthol
Catalog No.:BCN9045
CAS No.:89-78-1
- Quininic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9044
CAS No.:86-68-0
- Warfarin sodium
Catalog No.:BCN9057
CAS No.:129-06-6
- N-Phenethylbenzamide
Catalog No.:BCN9058
CAS No.:3278-14-6
- Trimethyl phosphate
Catalog No.:BCN9059
CAS No.:512-56-1
- Glucodigifucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9060
CAS No.:2446-63-1
- (±)-Naringenin
Catalog No.:BCN9061
CAS No.:67604-48-2
- α-L-Rhamnopyranose
Catalog No.:BCN9062
CAS No.:6014-42-2
- D-Ribose
Catalog No.:BCN9063
CAS No.:50-69-1
- Alizarin 1-methyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN9064
CAS No.: 6170-06-5
- Eugenol acetate
Catalog No.:BCN9065
CAS No.:93-28-7
- Citral
Catalog No.:BCN9066
CAS No.:5392-40-5
- 10-hydroxydec-2-enoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9067
CAS No.:14113-05-4
- Citronellal
Catalog No.:BCN9068
CAS No.:106-23-0
Skp2 Depletion Reduces Tumor-Initiating Properties and Promotes Apoptosis in Synovial Sarcoma.[Pubmed:32623326]
Transl Oncol. 2020 Jul 2;13(10):100809.
Synovial sarcoma (SS) is an aggressive soft-tissue cancer with a poor prognosis and a propensity for local recurrence and distant metastasis. In this study, we investigated whether S phase kinase-associated protein (Skp2) plays an oncogenic role in tumor initiation, progression, and metastasis of SS. Our study revealed that Skp2 is frequently overexpressed in SS specimens and SS18-SSX transgenic mouse tumors, as well as correlated with clinical stages. Next, we identified that genetic depletion of Skp2 reduced mesenchymal and stemness markers, and inhibited the invasive and proliferative capacities of SS cell lines. Furthermore, Skp2 depletion markedly suppressed the growth of SS xenografts tumors. Treatment of SS cell lines with the skp2 inhibitor Flavokawain A (FKA) reduced Skp2 expression in a dose-dependent manner and resulted in cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. FKA also suppressed the invasion and tumor-initiating properties in SS, similar to the effects of Skp2 knockdown. In addition, a combination of FKA and conventional chemotherapy showed a synergistic therapeutic efficacy. Taken together, our results suggest that Skp2 plays an essential role in the biology of SS by promoting the mesenchymal state and cancer stemness. Given that chemotherapy resistance is often associated with cancer stemness, strategies of combining Skp2 inhibitors with conventional chemotherapy in SS may be desirable.
Suppression of LPS-Induced Inflammation by Chalcone Flavokawain A through Activation of Nrf2/ARE-Mediated Antioxidant Genes and Inhibition of ROS/NFkappaB Signaling Pathways in Primary Splenocytes.[Pubmed:32617135]
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Jun 12;2020:3476212.
Oxidative stress is an important contributing factor for inflammation. Piper methysticum, also known as Kava-kava, is a shrub whose root extract has been consumed as a drink by the pacific islanders for a long time. Flavokawain A (FKA) is a novel chalcone derived from the kava plant that is known to have medicinal properties. This study was aimed at demonstrating the antioxidant molecular mechanisms mediated by FKA on lipopolysaccharide- (LPS-) induced inflammation in BALB/c mouse-derived primary splenocytes. In vitro data show that the nontoxic concentrations of FKA (2-30 muM) significantly suppressed the proinflammatory cytokine (TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, and IL-6) release but induced the secretion of interleukin-10 (IL-10), an anti-inflammatory cytokine. It was also shown that FKA pretreatment significantly downregulated the LPS-induced ROS production and blocked the activation of the NFkappaB (p65) pathway leading to the significant suppression of iNOS, COX-2, TNF-alpha, and IL-1beta protein expressions. Notably, FKA favored the nuclear translocation of Nrf2 leading to the downstream expression of antioxidant proteins HO-1, NQO-1, and gamma-GCLC via the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway signifying the FKA's potent antioxidant mechanism in these cells. Supporting the in vitro data, the ex vivo data obtained from primary splenocytes derived from the FKA-preadministered BALB/c mice (orally) show that FKA significantly suppressed the proinflammatory cytokine (TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, and IL-6) secretion in control-, LPS-, or Concanavalin A- (Con A-) stimulated cells. A significant decrease in the ratios of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6/IL-10; TNF-alpha/IL-10) showed that FKA possesses strong anti-inflammatory properties. Furthermore, BALB/c mice induced with experimental pancreatitis using cholecystokinin- (CCK-) 8 showed decreased serum lipase levels due to FKA pretreatment. We conclude that with its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, chalcone Flavokawain A could be a novel therapeutic agent in the treatment of inflammation-associated diseases.
Flavokawain A inhibits prostate cancer cells by inducing cell cycle arrest and cell apoptosis and regulating the glutamine metabolism pathway.[Pubmed:32361091]
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020 Jul 15;186:113288.
Flavokawain A (FKA), a major chalcone in kava extracts, has exhibited anti-proliferative and apoptotic effects in the prostate cancer. However, the molecular mechanism of FKA remains unclear. In this study, FKA induces cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in a G2M phase to prostate cancer cells. FKA interferes with tubulin polymerization and inhibits survivin expression in PC3 cells. Molecular docking simulation experiment finds that FKA can bind to colchicine binding sites that inhibit tubulin polymerization. FKA treatment regulates the glutamine metabolism pathway in PC3 cells by reducing intracellular glutamine, glutamic and proline. FKA treatment also decreases the GSH content by decreasing the activity of GSH synthetase (GSS) and increasing the activity of glutathione thiol transferase (GSTP1), which subsequently induces ROS production and PC3 cell apoptosis.
Bioassay-Guided Isolation and in Silico Study of Antibacterial Compounds From Petroleum Ether Extract of Peperomia blanda (Jacq.) Kunth.[Pubmed:31117526]
J Chem Inf Model. 2019 May 28;59(5):1858-1872.
Bioassay-guided isolation protocol was performed on petroleum ether extract of Peperomia blanda (Jacq.) Kunth using column chromatographic techniques. Five compounds were isolated and their structures were elucidated via one-dimensional (1D) and two-dimensional (2D) NMR, gas chromatography mass sectroscopy (GCMS), liquid chromatography mass spectroscopy (LCMS), and ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) analyses. Dindygulerione E (a new compound), and two compounds isolated from P. blanda for the first time-namely, dindygulerione A and Flavokawain A-are reported herein. Antimicrobial activity was screened against selected pathogenic microbes, and minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) were recorded within the range of 62-250 mug/mL. Assessment of the pharmacotherapeutic potential has also been done for the isolated compounds, using the Prediction of Activity spectra for Substances (PASS) software, and different activities of compounds were predicted. Molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation and molecular mechanics/Poisson-Boltzmann Surface Area (MM-PBSA) calculations have proposed the binding affinity of these compounds toward methylthioadenosine phosphorylase enzyme, which may explain their inhibitory actions.
Chalcone flavokawain A attenuates TGF-beta1-induced fibrotic pathology via inhibition of ROS/Smad3 signaling pathways and induction of Nrf2/ARE-mediated antioxidant genes in vascular smooth muscle cells.[Pubmed:30549180]
J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Feb;23(2):775-788.
TGF-beta1 plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of vascular fibrotic diseases. Chalcones are reportedly cancer chemo-preventive food components that are rich in fruits and vegetables. In this study, Flavokawain A (FKA, 2-30 muM), a naturally occurring chalcone in kava extracts, was evaluated for its anti-fibrotic and antioxidant properties in TGF-beta1-stimulated vascular smooth muscle (A7r5) cells, as well as its underlying molecular mechanism of action. Immunofluorescence data showed down-regulated F-actin expression with FKA treatment in TGF-beta1-stimulated A7r5 cells. Western blotting demonstrated that FKA treatment suppressed the expression of alpha-SMA and fibronectin proteins under TGF-beta1 stimulation. Findings from wound-healing and invasion experiments showed that FKA inhibits TGF-beta1-mediated migration and invasion. Western blotting demonstrated that treatment with FKA down-regulated MMP-9 and MMP-2 and up-regulated TIMP-1 expression. Further evidence showed that FKA decreased TGF-beta1-mediated phosphorylation and the transcriptional activity of Smad3. TGF-beta1-induced excessive ROS production was remarkably reversed by FKA treatment in A7r5 cells, and inhibition by FKA or N-acetylcysteine (NAC) substantially diminished TGF-beta1-induced p-Smad3 activation and wound-healing migration. Interestingly, FKA-mediated antioxidant properties were associated with increased nuclear translocation of Nrf2 and elevated antioxidant response element (ARE) luciferase activity. Activation of Nrf2/ARE signaling was accompanied by the induction of HO-1, NQO-1 and gamma-GCLC genes in FKA-treated A7r5 cells. Notably, silencing of Nrf2 (siRNA transfection) significantly diminished the FKA-mediated antioxidant effects, indicating that FKA may inhibit TGF-beta1-induced fibrosis through suppressing ROS generation in A7r5 cells. Our results suggested that anti-fibrotic and antioxidant activities of the chalcone Flavokawain A may contribute to the development of food-based chemo-preventive drugs for fibrotic diseases.
Down-regulation of Skp2 expression inhibits invasion and lung metastasis in osteosarcoma.[Pubmed:30250282]
Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 24;8(1):14294.
Osteosarcoma (OS), the most common primary cancer of bone, exhibits a high propensity for local invasion and distant metastasis. This study sought to elucidate the role of S phase kinase-associated protein (Skp2) in osteosarcoma invasion and metastasis and to explore Flavokawain A (FKA), a natural chalcone from kava extract, as a potential Skp2 targeting agent for preventing osteosarcoma progression. Skp2 was found to be overexpressed in multiple osteosarcoma cell lines, including 5 standard and 8 primary patient-derived cell lines. Patients whose tumors expressed high levels of Skp2 sustained a significantly worse metastasis-free (p = 0.0095) and overall survival (p = 0.0013) than those with low Skp2. Skp2 knockdown markedly reduced in vitro cellular invasion and in vivo lung metastasis in an orthotopic mouse model of osteosarcoma. Similar to Skp2 knockdown, treatment with FKA also reduced Skp2 expression in osteosarcoma cell lines and blocked the invasion of osteosarcoma cells in vitro and lung metastasis in vivo. Together, our findings suggest that Skp2 is a promising therapeutic target in osteosarcoma, and that FKA may be an effective Skp2-targeted therapy to reduce osteosarcoma metastasis.
Kavalactone yangonin induces autophagy and sensitizes bladder cancer cells to flavokawain A and docetaxel via inhibition of the mTOR pathway.[Pubmed:28959001]
J Biomed Res. 2017 Sep 26;31(5):408-418.
Consumption of kava (Piper methysticum Forst) has been linked to reduced cancer risk in the South Pacific Islands. Kavalactones are major bioactive components in kava root extracts, which have recently demonstrated anti-cancer activities. However, molecular mechanisms of kavalactones' anti-cancer action remain largely unknown. We have identified two kavalactones, yangonin and 5' 6'-dehydrokawain, as potent inducers of autophagic cell death in bladder cancer cells. The effect of yangonin inducing autophagy is associated with increased expression of beclin and ATG5. In addition, yangonin increases the expression of LKB1 and decreases the phosphorylation of Akt, PRAS40, rpS6, p70S6K and 4E-BP1, leading to increased binding of 4E-BP1 to m7 GTP. The growth inhibitory effects of yangonin were attenuated inTSC1 or LKB1 knockout mouse embryonic fibroblasts, suggesting that TSC1 and LKB1 expression may contribute to optimal growth inhibition by yangonin. Furthermore, yangonin reduces the viability of bladder cancer cell lines derived from different stages of human bladder cancer, and acts synergistically with apoptosis-inducing agents such as docetaxel and Flavokawain A. Our results support a novel anti-bladder cancer mechanism by yangonin and further studies are needed to assess the potential use of yangonin for bladder cancer prevention and treatment.
Induction of G2M Arrest by Flavokawain A, a Kava Chalcone, Increases the Responsiveness of HER2-Overexpressing Breast Cancer Cells to Herceptin.[Pubmed:28335434]
Molecules. 2017 Mar 14;22(3). pii: molecules22030462.
HER2/neu positive breast tumors predict a high mortality and comprise 25%-30% of breast cancer. We have shown that Flavokawain A (FKA) preferentially reduces the viabilities of HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cell lines (i.e., SKBR3 and MCF7/HER2) versus those with less HER2 expression (i.e., MCF7 and MDA-MB-468). FKA at cytotoxic concentrations to breast cancer cell lines also has a minimal effect on the growth of non-malignant breast epithelial MCF10A cells. FKA induces G2M arrest in cell cycle progression of HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cell lines through inhibition of Cdc2 and Cdc25C phosphorylation and downregulation of expression of Myt1 and Wee1 leading to increased Cdc2 kinase activities. In addition, FKA induces apoptosis in SKBR3 cells by increasing the protein expression of Bim and BAX and decreasing expression of Bcl(2), BclX/L, XIAP, and survivin. FKA also downregulates the protein expression of HER-2 and inhibits AKT phosphorylation. Herceptin plus FKA treatment leads to an enhanced growth inhibitory effect on HER-2 overexpressing breast cancer cell lines through downregulation of Myt1, Wee1, Skp2, survivin, and XIAP. Our results suggest FKA as a promising and novel apoptosis inducer and G2 blocking agent that, in combination with Herceptin, enhances for the treatment of HER2-overexpressing breast cancer.
Flavokawain derivative FLS induced G2/M arrest and apoptosis on breast cancer MCF-7 cell line.[Pubmed:27358555]
Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Jun 10;10:1897-907.
Known as naturally occurring biologically active compounds, Flavokawain A and B are the leading chalcones that possess anticancer properties. Another flavokawain derivative, (E)-1-(2'-Hydroxy-4',6'-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-(4-methylthio)phenyl)prop-2-ene-1-one (FLS) was characterized with (1)H-nuclear magnetic resonance, electron-impact mas spectrometry, infrared spectroscopy, and ultraviolet ((1)H NMR, EI-MS, IR, and UV) spectroscopic techniques. FLS cytotoxic efficacy against human cancer cells (MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, and MCF-10A) resulted in the reduction of IC50 values in a time- and dose-dependent mode with high specificity on MCF-7 (IC50 of 36 muM at 48 hours) against normal breast cell MCF-10A (no IC50 detected up to 180 muM at 72 hours). Light, scanning electron, and fluorescent microscopic analysis of MCF-7 cells treated with 36 muM of FLS displayed cell shrinkage, apoptotic body, and DNA fragmentation. Additionally, induction of G2/M cell arrest within 24 hours and apoptosis at subsequent time points was discovered via flow cytometry analysis. The roles of PLK-1, Wee-1, and phosphorylation of CDC-2 in G2/M arrest and proapoptotic factors (Bax, caspase 9, and p53) in promotion of apoptosis of FLS against MCF-7 cells were discovered using fluorometric, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, and Western blot analysis. Interestingly, the presence of SCH3 (thiomethyl group) on ring B structure contributed to the selective cytotoxicity against MCF-7 cells compared to other chalcones, Flavokawain A and B. Overall, our data suggest potential therapeutic value for flavokawain derivative FLS to be further developed as a new anticancer drug.
[Study on chemical constituents from Chloranthus multistachys].[Pubmed:28901072]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016 Jun;41(12):2273-2279.
To investigate the chemical constituents from the shoots of Chloranthus multistachys.All compounds wereisolated by using a combination of various chromatographic techniques including silica gel, ODS, Sephadex LH-20, reversed-phase HPLC, and other methods.Their structures were elucidated by the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), mass spectrometry, and other modernspectroscopies.As a result, 19 compounds were isolated from the shoots of C.multistachys and identified as zederoneepoxide(1), chlomultin C(2), curcolonol(3), sarcaglaboside A(4), zedoarofuran(5), (1E,4Z)-8-hydroxy-6-oxogermacra-1(10), 4,7(11)-trieno-12,8-lactone(6), chloranoside A(7), istanbulin A(8), (8alpha)-6,8-dihydroxycadina-7(11),10(15)-dien-12-oicacid-gamma-lactone(9), codonolactone(10), lasianthuslactone A(11), 12,15-epoxy-5alphaH,9betaH-labda-8(17),13-dien-19-oicacid(12), 12R,15-dihydroxylabda-8(17),13E-dien-19-oicacid(13), N-transcinnamoyltyramine(14), trans-N-p-coumaroyltyramine(15), dibutyl phthalate (16), Flavokawain A(17), bergenin(18), and enedione(19).Compounds 1, 2, 4, 7-10, 12-19 were isolated from C.multistachys for the first time and compounds 14-19 were obtained from the genus Chloranthus for the first time.


