MentholCAS# 89-78-1 |
- D-Isomenthol
Catalog No.:BCN8540
CAS No.:23283-97-8
- D-Menthol
Catalog No.:BCN4973
CAS No.:15356-60-2
- DL-Menthol
Catalog No.:BCN5950
CAS No.:15356-70-4
- L-Menthol
Catalog No.:BCN4971
CAS No.:2216-51-5
- Neoisomenthol
Catalog No.:BCC8169
CAS No.:20752-34-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 89-78-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6566020 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C10H20O | M.Wt | 156.27 |
| Type of Compound | Monoterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
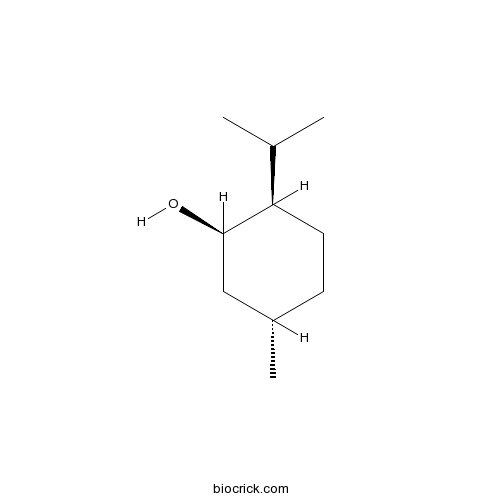
| Chemical Name | (1R,2R,5S)-5-methyl-2-propan-2-ylcyclohexan-1-ol | ||
| SMILES | CC1CCC(C(C1)O)C(C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NOOLISFMXDJSKH-IVZWLZJFSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H20O/c1-7(2)9-5-4-8(3)6-10(9)11/h7-11H,4-6H2,1-3H3/t8-,9+,10+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Menthol Dilution Calculator

Menthol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.3992 mL | 31.9959 mL | 63.9918 mL | 127.9836 mL | 159.9795 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.2798 mL | 6.3992 mL | 12.7984 mL | 25.5967 mL | 31.9959 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6399 mL | 3.1996 mL | 6.3992 mL | 12.7984 mL | 15.998 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.128 mL | 0.6399 mL | 1.2798 mL | 2.5597 mL | 3.1996 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.064 mL | 0.32 mL | 0.6399 mL | 1.2798 mL | 1.5998 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Quininic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9044
CAS No.:86-68-0
- Allocryptopine
Catalog No.:BCN9043
CAS No.:485-91-6
- (+)-Secoisolariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN9042
CAS No.:145265-02-7
- Peimisine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN9041
CAS No.:900498-44-4
- DL-α-Tocopherol
Catalog No.:BCN9040
CAS No.:10191-41-0
- Fluoranthene
Catalog No.:BCN9039
CAS No.:206-44-0
- Ganoderic acid E
Catalog No.:BCN9038
CAS No.:
- D-(+)-Lactose Monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCN9037
CAS No.:64044-51-5
- Kizuta saponin K11
Catalog No.:BCN9036
CAS No.:97240-03-4
- 1-Naphthaleneacetic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9035
CAS No.:86-87-3
- Isopongachromene
Catalog No.:BCN9034
CAS No.:
- Cichoric acid
Catalog No.:BCN9033
CAS No.:6537-80-0
- Atractyloside potassium salt
Catalog No.:BCN9046
CAS No.:17754-44-8
- Deslanoside
Catalog No.:BCN9047
CAS No.:17598-65-1
- 1αH,5αH-guaia-6-ene-4β,10β-diol
Catalog No.:BCN9048
CAS No.:2013537-81-8
- Hydroquinone
Catalog No.:BCN9049
CAS No.:123-31-9
- Bisisorhapontigenin D
Catalog No.:BCN9050
CAS No.:
- Mirificin-4'-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9051
CAS No.:168035-01-6
- DL-Tartaric acid
Catalog No.:BCN9052
CAS No.:133-37-9
- 5'-Cytidylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9053
CAS No.:63-37-6
- Xanthosine
Catalog No.:BCN9054
CAS No.:146-80-5
- 5'-Guanylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9055
CAS No.:85-32-5
- Flavokawain A
Catalog No.:BCN9056
CAS No.:37951-13-6
- Warfarin sodium
Catalog No.:BCN9057
CAS No.:129-06-6
Agonists of orally expressed TRP channels stimulate salivary secretion and modify the salivary proteome.[Pubmed:32651226]
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020 Jul 10. pii: RA120.002174.
Natural compounds that can stimulate salivary secretion are of interest in developing treatments for xerostomia, the perception of a dry mouth, that affects between 10 and 30% of the adult and elderly population. Chemesthetic transient receptor potential (TRP) channels are expressed in the surface of the oral mucosa. The TRPV1 agonists capsaicin and piperine have been shown to increase salivary flow when introduced into the oral cavity but the sialogogic properties of other TRP channel agonists have not been investigated. In this study we have determined the influence of different TRP channel agonists on the flow and protein composition of saliva. Mouth rinsing with the TRPV1 agonist nonivamide or Menthol, a TRPM8 agonist, increased whole mouth saliva (WMS) flow and total protein secretion compared to unstimulated saliva, the vehicle control mouth rinse or cinnamaldehyde, a TRPA1 agonist. Nonivamide also increased the flow of labial minor gland saliva but parotid saliva flow rate was not increased. The influence of TRP channel agonists on the composition and function of the salivary proteome was investigated using a multi-batch quantitative mass spectrometry method novel to salivary proteomics. Inter-personal and inter-mouth rinse variation was observed in the secreted proteomes and, using a novel bioinformatics method, inter-day variation was identified with some of the mouth rinses. Significant changes in specific salivary proteins were identified after all mouth rinses. In the case of nonivamide, these changes were attributed to functional shifts in the WMS secreted, primarily the over representation of salivary and non-salivary cystatins which was confirmed by immunoassay. This study provides new evidence of the impact of TRP channel agonists on the salivary proteome and the stimulation of salivary secretion by a TRPM8 channel agonist, which suggests that TRP channel agonists are potential candidates for developing treatments for sufferers of xerostomia.
The actual and anticipated effects of a menthol cigarette ban: a scoping review.[Pubmed:32641026]
BMC Public Health. 2020 Jul 9;20(1):1055.
BACKGROUND: The United States (US) Food and Drug Administration (FDA), under the 2009 Family Smoking Prevention and Tobacco Control Act, banned characterizing flavors in cigarettes; however, Mentholated tobacco products were exempt. Since 2009, over 20 US jurisdictions and numerous countries around the world have extended this restriction to Menthol. Currently, the FDA is reconsidering its position on a nation-wide Menthol cigarette ban. However, the effects of such a ban remain unclear. We conducted a scoping review to explore the impact of a Menthol cigarette ban on individual behaviors (initiation, cessation, and product switching), sales, and compliance. METHODS: We conducted a search of the international literature using PubMed, EBSCO, and Web of Science (to November 25, 2019). We retrieved articles relevant to the impacts of an implemented or hypothetical Menthol ban. We also included studies of flavored tobacco product bans due to their potential relevance in gauging compliance and product substitutability. RESULTS: The search identified 493 articles, of which 24 were included. Studies examined the effects of implemented Menthol bans (n = 6), hypothetical Menthol bans (n = 12) and implemented flavor bans that exclude Menthol (n = 6). Menthol bans were found to reduce sales and increase smoking cessation with only partial substitution for non-Menthol cigarettes. US smokers' reactions to a hypothetical ban indicate that about 25-64% would attempt to quit smoking and 11-46% would consider switching to other tobacco products, including 15-30% to e-cigarettes. Flavor ban studies indicate reductions in initiation of 6%. Ban compliance was high, but studies indicate that the tobacco industry and retailers have attempted to circumvent their impact via packaging changes and online sales. CONCLUSION: Our review finds that extending the US cigarette flavor ban to Menthol products would promote smoking cessation and reduce initiation. This evidence supports further action by the FDA towards Mentholated tobacco products. However, few studies have been conducted in the vaping era.
A modified quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe method with hydrophobic natural deep eutectic solvent as extractant and analyte protectant for analyzing pyrethroid residues in tomatoes.[Pubmed:32640110]
J Sep Sci. 2020 Jul 8.
In this work, a novel quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe technique with hydrophobic natural deep eutectic solvent as both extractant and analyte protectant was developed and combined with GC-MS/MS to analyze pyrethroid residues in tomatoes. Eight hydrophobic natural deep eutectic solvents were firstly evaluated as analyte protectants and those with decanoic acid or lactic acid as hydrogen bond donor were demonstrated to be effective in compensating for the matrix effects of pyrethroids in the GC system. Hence, they were added to solvent standards for correcting the quantitation errors instead of matrix-matched calibration standards. Then the abilities of these acid-based deep eutectic solvents to extract pyrethriods from tomatoes were evaluated. Results showed the recoveries of all pyrethroids reached to over 80% with only 5ml Menthol: decanoic acid (1:1) used, and good phase separation was easily achieved without the addition of inorganic salt in the extraction step, indicating hydrophobic natural deep eutectic solvent could be a green substitute for acetonitrile in the quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe extraction. Compared with the conventional method, the proposed protocol improved the recoveries, reduced the matrix effects and simplified the extraction step, demonstrating to be an effective, fast and green method.
Safety and efficacy of Biomin((R)) DC-P as a zootechnical feed additive for chickens for fattening, chickens reared for laying and minor avian species to the point of lay.[Pubmed:32626346]
EFSA J. 2019 Jun 11;17(6):e05724.
The additive (trade name Biomin((R))DC-P) is a blend of five individual compounds (carvacrol, thymol, d-carvone, methyl salicylate and l-Menthol) encapsulated with a hydrogenated vegetable oil. The additive is intended for use in feed for various poultry species at a minimum concentration of 65 mg/kg complete feed and a recommended maximum level of 105 mg/kg complete feed. The results of a tolerance study show that Biomin((R)) DC-P is safe for chickens for fattening at the maximum recommended application rate of 105 mg/kg complete feed; this conclusion is extended to include chickens reared for laying and extrapolated to minor poultry species The active components of a previously evaluated additive (Biomin((R))DC-C) were shown to be not genotoxic; owing to the similarity on composition, this conclusion can be also applied to Biomin((R))DC-P. Notwithstanding the uncertainties identified in the residue study, after applying a worst-case scenario to calculate potential exposure of consumers to Menthol and carvone, and since that the components of the additive are considered safe for their use as food and feed flavourings, the FEEDAP Panel concludes that the use of the additive in animal nutrition is considered safe for consumers. The FEEDAP Panel considered that exposure of users by inhalation is unlikely, but cannot conclude on the effects of Biomin((R))DC-P on skin and eyes. The use of Biomin((R))DC-P is not expected to pose a risk for the environment. Biomin((R))DC-P has a potential to increase the growth performance of chickens for fattening when incorporated into feed at a minimum application rate of 65 mg/kg complete feed; the conclusion can be extended to chickens reared for laying and extrapolated to minor poultry species reared up to the point of lay.
Menthol as an Ergogenic Aid for the Tokyo 2021 Olympic Games: An Expert-Led Consensus Statement Using the Modified Delphi Method.[Pubmed:32623642]
Sports Med. 2020 Jul 4. pii: 10.1007/s40279-020-01313-9.
INTRODUCTION: Menthol topical application and mouth rinsing are ergogenic in hot environments, improving performance and perception, with differing effects on body temperature regulation. Consequently, athletes and federations are beginning to explore the possible benefits to elite sport performance for the Tokyo 2021 Olympics, which will take place in hot (~ 31 degrees C), humid (70% RH) conditions. There is no clear consensus on safe and effective Menthol use for athletes, practitioners, or researchers. The present study addressed this shortfall by producing expert-led consensus recommendations. METHOD: Fourteen contributors were recruited following ethical approval. A three-step modified Delphi method was used for voting on 96 statements generated following literature consultation; 192 statements total (96/96 topical application/mouth rinsing). Round 1 contributors voted to "agree" or "disagree" with statements; 80% agreement was required to accept statements. In round 2, contributors voted to "support" or "change" their round 1 unaccepted statements, with knowledge of the extant voting from round 1. Round 3 contributors met to discuss voting against key remaining statements. RESULTS: Forty-seven statements reached consensus in round 1 (30/17 topical application/rinsing); 14 proved redundant. Six statements reached consensus in round 2 (2/4 topical application/rinsing); 116 statements proved redundant. Nine further statements were agreed in round 3 (6/3 topical application/rinsing) with caveats. DISCUSSION: Consensus was reached on 62 statements in total (38/24 topical application/rinsing), enabling the development of guidance on safe Menthol administration, with a view to enhancing performance and perception in the heat without impairing body temperature regulation.
Healthcare Utilization of Menthol and Non-menthol Cigarette Smokers.[Pubmed:32623471]
Nicotine Tob Res. 2020 Jul 5. pii: 5867536.
OBJECTIVE: To study the association between healthcare utilization and Menthol cigarette use and whether the association differed between African American (AA) and non-African American (non-AA) smokers. METHODS: We analyzed the three most recent 2005, 2010, and 2015 National Health Interview Survey Cancer Control Supplements. After incorporating propensity score weights adjusting for observed differences between Menthol and non-Menthol users, we estimated Zero-Inflated Poisson models on hospital nights, emergency department (ED) visits, doctor visits, and home visits as a function of Menthol use status and other covariates separately for current cigarette smokers and recent quitters (former smokers quitting cigarette smokingMenthol smokers smoked fewer cigarettes per day (CPD) than current non-Menthol smokers, they did not differ from current non-Menthol smokers in healthcare utilization. Among recent quitters, those who used to smoke Menthol cigarettes had higher odds of having hospital nights than those who used to smoke non-Menthol cigarettes. However, we did not find any significant association between Menthol use and other healthcare utilization-ED visits, doctor visits and home visits -- among recent quitters. Moreover, compared to non-AA recent quitters, AA recent quitters had higher odds of having home visits, but fewer home visits, if they used to smoke Menthol cigarettes. CONCLUSION: Menthol use was associated with greater hospitalization among recent quitters, and the association between home visits and Menthol use differed between AA and non-AA recent quitters.
Productive, metabolic and anatomical parameters of menthol mint are influenced by light intensity.[Pubmed:32609271]
An Acad Bras Cienc. 2020 Jun 26;92(suppl 1):e20180321.
The cultivation of aromatic species to obtain essential oils has great economic importance, presenting an increasing demand from different industrial sectors, especially to Menthol mint (Mentha arvensis L.) essential oil, rich in Menthol (70-80%). Consortium cultivation has been an important practice in agricultural systems whose land use is necessary, consequently promoting strong competition for light in reduced space. Thus, this study aimed verifying if different light intensities might promote chemical, metabolical and anatomical alterations in Menthol mint. Plants were grown in greenhouse at different average of light intensities (137, 254, 406 and 543 micromol photons m2 s1). Samples were collected 43 days after germination and submitted to following analyses: Gravimetric test, photosynthetic pigments, soluble fractions, enzymatic activity, N-total, trichome density and histochemistry and chemometric test based on essential oil chemical profile. Fresh mass gain, trichome density, essential oil content and soluble sugars were positively influenced by light intensity increase. On the other hand, total-N, NO3--N and pigments content have decreased influenced by light intensity increase. In the secretion from the trichomes, phenolic substances were reported, as well as lipophilic ones in the peltate ones. The increase of oxygenated monoterpenes was favored by light intensity decrease.
Microbiological quality and safety of commercialized thalassotherapy products based on marine mud and algae extracts in Tunisia.[Pubmed:32607726]
Arch Microbiol. 2020 Jun 30. pii: 10.1007/s00203-020-01957-1.
A total of 15 samples of thalassotherapy products, distributed in Tunisia in their intact and final state of production, was analyzed to determine their microbiological safety status. The result shows the absence of pathogenic bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus, Candida albicans, Salmonella, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and coliforms). The incidence of contamination by Gram-positive Bacilli (mesophelic bacteria, aerobic and anaerobic spore forming bacteria, anaerobic sulphite-reducing bacteria) was found to be higher in products composed by mud and extract of alga. The biochemical and molecular identification of the major contaminant show that Bacilli were the most covered from 75% of the thalassotherapy products. Mineral analysis (organic matter, Fe, Mg, Ca, Na d K, Al, Si and Ti) shows strong composition on Aluminum and Silica. Cytotoxicity study of six thalassotherapy products and three essential oil extracts (Menthol, Clove and Eucalyptus) did not show any cytotoxic effect. Furthermore, antibacterial acitivity of 5 essentila oils, against 30 isolates of the genus Bacillus and 10 reference strains, has been characterized showing an interesting bactericidal potential of the extract of Menthol and Eucalyptus.
Prolonged-release of menthol through a superhydrophilic multilayered structure of balangu (Lallemantia royleana)-gelatin nanofibers.[Pubmed:32600715]
Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020 Oct;115:111115.
This study aimed to develop a sandwich structure based on electrospun mats derived from gelatin (central layer) and Balangu seed gum (outer layers) and to compare its capability for prolonging the Menthol release in the oral phase compared to the gelatin monolayer mat. The mesh-like structure and the smooth and uniform surface of the electrospun mats designed in this study were authenticated by Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM). By designing the sandwich structure, the dissolution time and contact angle of the mats were increased and their bioadhesive strength decreased. The swelling degree of the gelatin mat (453.25 +/- 32.56%) was significantly higher than that of the sandwich mat (297.71 +/- 22.68%) (p < 0.05). Successful entrapment and the thermal stability of the produced mats were proved by X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) tests. The release kinetics in the human simulated saliva showed that the burst release of Menthol from the structure of electrospun gelatin mats, due to its fast-dissolving nature, was well prolonged by the designed sandwich system. The Fickian Case-I release was the main mechanism in the Menthol release and the Peppas-Sahlin was the most suitable model governing the release of Menthol from these structures.
Negative Modulation of TRPM8 Channel Function by Protein Kinase C in Trigeminal Cold Thermoreceptor Neurons.[Pubmed:32580281]
Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 22;21(12). pii: ijms21124420.
TRPM8 is the main molecular entity responsible for cold sensing. This polymodal ion channel is activated by cold, cooling compounds such as Menthol, voltage, and rises in osmolality. In corneal cold thermoreceptor neurons (CTNs), TRPM8 expression determines not only their sensitivity to cold, but also their role as neural detectors of ocular surface wetness. Several reports suggest that Protein Kinase C (PKC) activation impacts on TRPM8 function; however, the molecular bases of this functional modulation are still poorly understood. We explored PKC-dependent regulation of TRPM8 using Phorbol 12-Myristate 13-Acetate to activate this kinase. Consistently, recombinant TRPM8 channels, cultured trigeminal neurons, and free nerve endings of corneal CTNs revealed a robust reduction of TRPM8-dependent responses under PKC activation. In corneal CTNs, PKC activation decreased ongoing activity, a key parameter in the role of TRPM8-expressing neurons as humidity detectors, and also the maximal cold-evoked response, which were validated by mathematical modeling. Biophysical analysis indicated that PKC-dependent downregulation of TRPM8 is mainly due to a decreased maximal conductance value, and complementary noise analysis revealed a reduced number of functional channels at the cell surface, providing important clues to understanding the molecular mechanisms of how PKC activity modulates TRPM8 channels in CTNs.
Monitoring peppermint washout in the breath metabolome by secondary electrospray ionization-high resolution mass spectrometry.[Pubmed:32575094]
J Breath Res. 2020 Jun 23.
In this study, a secondary electrospray ionization-high resolution mass spectrometer (SESI-HRMS) system was employed to profile the real-time exhaled metabolome of ten subjects who had ingested a peppermint oil capsule. In total, six time points were sampled during the experiment. Using an untargeted way of profiling breath metabolome, 2333 m/z unique metabolite features were determined in positive mode, and 1322 in negative mode. To benchmark the performance of the SESI-HRMS setup, several additional checks were done, including determination of the technical variation, the biological variation of one subject within three days, the variation within a time point, and the variation across all samples, taking all m/z features into account. Reproducibility was good, with the median technical variation being 18% and the median variation within biological replicates being 34%. Both variations were lower than the variation across individuals. Washout profiles of compounds from the peppermint oil, including menthone, limonene, pulegone, Menthol and menthofuran were determined in all subjects. Metabolites of the peppermint oil were also determined in breath, for example, cis/trans-carveol, perillic acid and Menthol glucuronide. Butyric acid was found to be the major metabolite that reduce the uptake rate of limonene. Pathways related to limonene metabolism were examined, and meaningful pathways were identified from breath metabolomics data acquired by SESI using an untargeted analysis.
Enzymatic Synthesis of Glucose Monodecanoate in a Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent.[Pubmed:32570792]
Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 18;21(12). pii: ijms21124342.
Environmentally friendly and biodegradable reaction media are an important part of a sustainable glycolipid production in the transition to green chemistry. Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) are an ecofriendly alternative to organic solvents. So far, only hydrophilic DESs were considered for enzymatic glycolipid synthesis. In this study, a hydrophobic DES consisting of (-)-Menthol and decanoic acid is presented for the first time as an alternative to hydrophilic DES. The yields in the newly introduced hydrophobic DES are significantly higher than in hydrophilic DESs. Different reaction parameters were investigated to optimize the synthesis further. Twenty milligrams per milliliter iCalB and 0.5 M glucose resulted in the highest initial reaction velocity for the esterification reaction, while the highest initial reaction velocity was achieved with 1.5 M glucose in the transesterification reaction. The enzyme was proven to be reusable for at least five cycles without significant loss of activity.


