FlindersineCAS# 523-64-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 523-64-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 68230 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H13NO2 | M.Wt | 227.3 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
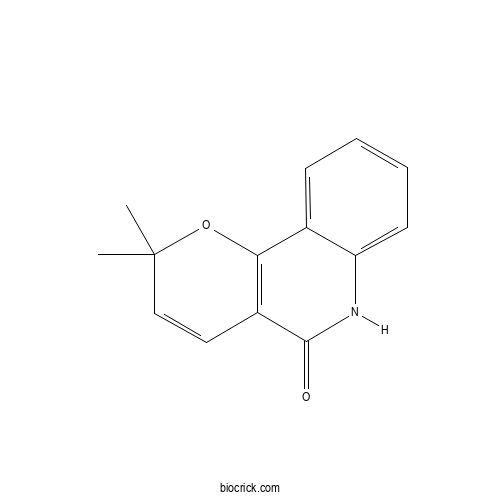
| Chemical Name | 2,2-dimethyl-6H-pyrano[3,2-c]quinolin-5-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1(C=CC2=C(O1)C3=CC=CC=C3NC2=O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PXNMNABLQWUMCX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H13NO2/c1-14(2)8-7-10-12(17-14)9-5-3-4-6-11(9)15-13(10)16/h3-8H,1-2H3,(H,15,16) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Flindersine Dilution Calculator

Flindersine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.3995 mL | 21.9974 mL | 43.9947 mL | 87.9894 mL | 109.9868 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8799 mL | 4.3995 mL | 8.7989 mL | 17.5979 mL | 21.9974 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4399 mL | 2.1997 mL | 4.3995 mL | 8.7989 mL | 10.9987 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.088 mL | 0.4399 mL | 0.8799 mL | 1.7598 mL | 2.1997 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.044 mL | 0.22 mL | 0.4399 mL | 0.8799 mL | 1.0999 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Isorhamnetin 3-O-apiosyl (1->2)[rhamnosyl (1->6)]glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX2105
CAS No.:165605-18-5
- 25R-Tupistroside E
Catalog No.:BCX2104
CAS No.:1448639-95-9
- Stellarin 2
Catalog No.:BCX2103
CAS No.:63975-58-6
- 3',4'-Dimethoxytaxifolin
Catalog No.:BCX2102
CAS No.:179871-73-9
- Kaempferol 3-O-malonylglucoside
Catalog No.:BCX2101
CAS No.:81202-52-0
- 2-Methoxy-2-methyl-6-(4-methylphenyl)-4-heptanone
Catalog No.:BCX2100
CAS No.:70369-29-8
- 4-(3,5-Dihydroxy-7-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)heptyl)benzene-1,2-diol
Catalog No.:BCX2099
CAS No.:884495-94-7
- Wattigenin A
Catalog No.:BCX2098
CAS No.:171485-66-8
- Isorutarin
Catalog No.:BCX2097
CAS No.:53846-51-8
- Tupichinol B
Catalog No.:BCX2096
CAS No.:497142-89-9
- Isosyringalide 3'-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCX2095
CAS No.:110326-99-3
- 6-Hydroxykaempferol 7-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX2094
CAS No.:70056-55-2
- 25(27)-Ene-elephanoside H
Catalog No.:BCX2107
CAS No.:1592406-40-0
- Morindaparvin W
Catalog No.:BCX2108
CAS No.:2596365-67-0
- cis-N-Terrestriamide
Catalog No.:BCX2109
CAS No.:2170469-93-7
- Mangostenone F
Catalog No.:BCX2110
CAS No.:1242438-70-5
- Garcinexanthone C
Catalog No.:BCX2111
CAS No.:1107620-69-8
- O-Methylglycosolone
Catalog No.:BCX2112
CAS No.:41303-25-7
- Tellimagrandin I
Catalog No.:BCX2113
CAS No.:79786-08-6
- 3alpha-Hinokiol
Catalog No.:BCX2114
CAS No.:107740-34-1
- Biflorin
Catalog No.:BCX2115
CAS No.:89701-85-9
- 6-Hydroxy-2-methoxyacetophenone 4-O-beta-D-xylopyranosyl-(1->6)-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX2116
CAS No.:2140317-59-3
- Fischeroside B
Catalog No.:BCX2117
CAS No.:1307257-08-4
- Isolophanthin B
Catalog No.:BCX2118
CAS No.:1370511-57-1
Phytochemical Profiling Studies of Alkaloids and Coumarins from the Australian Plant Geijera parviflora Lindl. (Rutaceae) and Their Anthelmintic and Antimicrobial Assessment.[Pubmed:38786736]
Metabolites. 2024 Apr 30;14(5):259.
Phytochemical profiling followed by antimicrobial and anthelmintic activity evaluation of the Australian plant Geijera parviflora, known for its customary use in Indigenous Australian ceremonies and bush medicine, was performed. In the present study, seven previously reported compounds were isolated including auraptene, 6'-dehydromarmin, geiparvarin, marmin acetonide, Flindersine, and two Flindersine derivatives from the bark and leaves, together with a new compound, chlorogeiparvarin, formed as an artefact during the isolation procedure and isolated as a mixture with geiparvarin. Chemical profiling allowed for a qualitative and quantitative comparison of the compounds in the leaves, bark, flowers, and fruit of this plant. Subsequently, a subset of these compounds as well as crude extracts from the plant were evaluated for their antimicrobial and anthelmintic activities. Anthelmintic activity assays showed that two of the isolated compounds, auraptene and Flindersine, as well as the dichloromethane and methanol crude extracts of G. parviflora, displayed significant activity against a parasitic nematode (Haemonchus contortus). This is the first report of the anthelmintic activity associated with these compounds and indicates the importance of such fundamental explorations for the discovery of bioactive phytochemicals for therapeutic application(s).
Antidiabetic with antilipidemic and antioxidant effects of flindersine by enhanced glucose uptake through GLUT4 translocation and PPARgamma agonism in type 2 diabetic rats.[Pubmed:34861363]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Mar 1;285:114883.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Medicinal plants have been used by the people of developing countries to treat various diseases. WHO also recommends the use of medicines from plants source. In that, diabetes also one of the diseases that have been treated traditionally by several people all over the world. In India, Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam. (Rutaceae) is also a medicinal plant used traditionally for the treatment of diabetes in Ayurveda. Moreover, T. asiatica is also used in a polyherbal formulation to treat diabetes. AIM OF THE STUDY: This study examined the antidiabetic with antilipidemic and antioxidant effects of Flindersine isolated from T. asiatica leaves. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Diabetes was induced in Wistar rats by feeding a high-fat diet (HFD) for 15 days and injecting a single dose of 40 mg/kg b. wt. of Streptozotocin (STZ). Five days post-injection, the grouped diabetic rats were treated with 20 and 40 mg/kg of Flindersine. RESULTS: Flindersine resulted in a clear decline of blood glucose levels during 28 days of treatment in two different doses. Flindersine also significantly (P Flindersine restored the glucose transporter protein 4 (GLUT4), adenosine monophosphate protein kinase (AMPK) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) expressions in adipose tissues and skeletal muscles. CONCLUSION: It has been found that Flindersine has potent antilipidemic and antidiabetic activities by improving insulin sensitivity by enhancing the phosphorylation of AMPK, GLUT4 translocation, and PPARgamma agonism on adipose tissue and skeletal muscles of diabetic rats.
Three quinolinone alkaloid - phenylpropanoid adducts from Melicope pteleifolia.[Pubmed:33648406]
Nat Prod Res. 2022 Aug;36(15):3858-3864.
Preliminary in vitro cytotoxic test on different extracts of Melicope pteleifolia collected at Dak Nong province, Vietnam showed that the n-hexane one was the most potent. From this n-hexane extract, three new quinolinone alkaloid-phenylpropanoid derivatives (1-3) and three known compounds (4-6) were isolated. Based on NMR and HR-MS analysis, their chemical structures were elucidated as melicoptines A-C (1-3), Flindersine (4), 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoic acid (5) and (24S)-methylcholestan-1alpha,3beta-diol (6). Isolated compounds (1-4) were evaluated for their anti-bacterial and cytotoxic activities against human non-small cell lung cancer (A549), human cervical cancer (HeLa), human Burkitt's lymphoma (Raji) and normal fibroblasts (NIH-3T3). All of them were inactive.
Indexing Natural Products for their Antifungal Activity by Filters-based Approach: Disclosure of Discriminative Properties.[Pubmed:30332973]
Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2019;15(3):235-242.
BACKGROUND: A considerable worldwide increase in the rate of invasive fungal infections and resistance toward antifungal drugs was witnessed during the past few decades. Therefore, the need for newer antifungal candidates is paramount. Nature has been the core source of therapeutics for thousands of years, and an impressive number of modern drugs including antifungals were derived from natural sources. In order to facilitate the recognition of potential candidates that can be derived from natural sources, an iterative stochastic elimination optimization technique to index natural products for their antifungal activity was utilized. METHODS: A set of 240 FDA-approved antifungal drugs, which represent the active domain, and a set of 2,892 natural products, which represent the inactive domain, were used to construct predictive models and to index natural products for their antifungal bioactivity. The area under the curve for the produced predictive model was 0.89. When applying it to a database that is composed of active/inactive chemicals, we succeeded to detect 42% of the actives (antifungal drugs) in the top one percent of the screened chemicals, compared with one-percent when using a random model. RESULTS AND CONCLUSION: Eight natural products, which were highly scored as likely antifungal drugs, are disclosed. Searching PubMed showed only one molecule (Flindersine) out of the eight that have been tested was reported as an antifungal. The other seven phytochemicals await evaluation for their antifungal bioactivity in a wet laboratory.
Targeted Isolation of Indolopyridoquinazoline Alkaloids from Conchocarpus fontanesianus Based on Molecular Networks.[Pubmed:27557347]
J Nat Prod. 2016 Sep 23;79(9):2270-8.
A dichloromethane-soluble fraction of the stem bark of Conchocarpus fontanesianus showed antifungal activity against Candida albicans in a bioautography assay. Off-line high-pressure liquid chromatography activity-based profiling of this extract enabled a precise localization of the compounds responsible for the antifungal activity that were isolated and identified as the known compounds Flindersine (17) and 8-methoxyFlindersine (18). As well as the identification of the bioactive principles, the ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry metabolite profiling of the dichloromethane stem bark fraction allowed the detection of more than 1000 components. Some of these could be assigned putatively to secondary metabolites previously isolated from the family Rutaceae. Generation of a molecular network based on MS(2) spectra indicated the presence of indolopyridoquinazoline alkaloids and related scaffolds. Efficient targeted isolation of these compounds was performed by geometric transfer of the analytical high-pressure liquid chromatography profiling conditions to preparative medium-pressure liquid chromatography. This yielded six new indolopyridoquinazoline alkaloids (5, 16, 19-22) that were assigned structurally. The medium-pressure liquid chromatography separations afforded additionally 16 other compounds. This work has demonstrated the usefulness of molecular networks to target the isolation of new natural products and the value of this approach for dereplication. A detailed analysis of the constituents of the stem bark of C. fontanesianus was conducted.
Native Australian plant extracts differentially induce Collagen I and Collagen III in vitro and could be important targets for the development of new wound healing therapies.[Pubmed:26705840]
Fitoterapia. 2016 Mar;109:45-51.
Australian native plants have a long history of therapeutic use in indigenous cultures, however, they have been poorly studied scientifically. We analysed the effects of 14 plant derived compounds from the species Pilidiostigma glabrum, Myoporum montanum, Geijera parviflora, and Rhodomyrtus psidioides for their potential wound healing properties by assessing their ability to induce or suppress Collagen I and Collagen III expression in human skin fibroblasts in culture. The compound 7-geranyloxycoumarin was able to significantly increase Collagen I (23.7%, p<0.0002) expression in comparison to control. Significant suppression of Collagen III was observed for the compounds Flindersine (11.1%, p<0.02), and (N-acetoxymethyl) Flindersine (27%, p<0.00005). The implications of these finding is that these compounds could potentially alter the expression of different collagens in the skin allowing for the potential development of new wound healing therapies and new approaches for treating various skin diseases as well as photo (sun) damaged, and aged skin.
Compounds from Geijera parviflora with prostaglandin E2 inhibitory activity may explain its traditional use for pain relief.[Pubmed:25656002]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Apr 2;163:251-5.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Australian Aboriginal people used crushed leaves of Geijera parviflora Lindl. both internally and externally for pain relief, including for toothache (Cribb and Cribb, 1981). This study tested the hypothesis that this traditional use might be at least in part explained by the presence of compounds with anti-inflammatory activity. MATERIALS AND METHODS: A crude extract (95% EtOH) was prepared from powdered dried leaves. From the CH3Cl fraction of this extract compounds were isolated by bioassay-guided fractionation and tested for: (1) cytotoxicity in RAW 264.7 murine leukemic monocyte-macrophages, (2) prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) inhibitory activity in 3T3 Swiss albino mouse embryonic fibroblast cells, as well as (3) nitric oxide (NO) and (4) tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) inhibitory activity in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Isolated compounds were also tested for (5) antibacterial activity against a panel of Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 and ATCC 25923, Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC 35984, biofilm-forming) and Gram-negative (Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853) strains by broth microdilution. RESULTS: Eleven compounds were isolated, including one new flavone and one new natural product, with a further four compounds reported from this species for the first time. Some of the compounds showed good anti-inflammatory activity in vitro. In particular, Flindersine (1) and N-(acetoxymethyl) Flindersine (3) inhibited PGE2 release with IC50 values of 5.0muM and 4.9muM, respectively, without any significant cytotoxicity. Several other compounds showed moderate inhibition of NO (5, 6, 7) and TNF-alpha (6), with IC50 in the low micromolar range; however much of this apparent activity could be accounted for by the cytotoxicity of these compounds. None of the compounds showed anti-bacterial activity. CONCLUSIONS: The inhibition of PGE2, an important mediator of inflammation and pain, by Flindersine and a derivative thereof, along with the moderate anti-inflammatory activity shown by several other compounds isolated from Geijera parviflora leaf extract, support the traditional use of this plant for pain relief by Australian Aboriginal people.
Antidiabetic and antioxidant activities of Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam. leaves in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats.[Pubmed:22842651]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Sep 28;143(2):515-23.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: The leaves of Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam. have been utilized traditionally for the cure of diabetes. AIM OF THE STUDY: The present study was aimed to assess the antidiabetic and antioxidant effects of T. asiatica leaves in Streptozotocin (STZ) induced diabetic rats. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The phytochemical screening, total phenolic content, HPLC analysis, acute toxicity study and oral glucose tolerance test were carried out. Glucose lowering effect of the hexane, ethyl acetate and methanol extracts of T. asiatica leaves was studied in STZ-induced diabetic rats. The antidiabetic and antioxidant activities were studied for the ethyl acetate extract. The effects of extracts on blood glucose, body weight, plasma insulin, total protein, liver glycogen, plasma enzymes (SGOT, SGPT and ALP) and activities of SOD, CAT and GPx were analyzed. RESULTS: T. asiatica leaves ethyl acetate extract (TALEe) showed highly significant blood glucose lowering effect. Phytochemical evaluation of TALEe showed the presence of alkaloids, terpenoids, cumarins, flavonoids and phenolic compounds. The total phenolic content of TALEe was 126 mg of gallic acid equivalents/g extract. HPLC analysis revealed the presence of Flindersine and ulopterol. Acute toxicity study of TALEe revealed no death or toxicity. The oral glucose tolerance test showed lowered area under curve (AUC(glucose)) values in TALEe treated rats. After treatment with TALEe (250 and 500 mg/kg) for 28 days there was a significant decrease in blood glucose, plasma enzymes (SGOT, SGPT and ALP) and significant increase in body weight, total protein, serum insulin and liver glycogen levels in treated diabetic rats. The activities of antioxidant enzymes SOD, CAT and GPx were reversed to near normal in treated diabetic rats. Histopathology of pancreas in TALEe treated groups showed regeneration of beta-cells. CONCLUSION: The results of the experiments showed that TALEe exerted significant antidiabetic and antioxidant effects in STZ-induced diabetic rats justifying its traditional use.
Antimicrobial activity of Ulopterol isolated from Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam.: a traditional medicinal plant.[Pubmed:22265751]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Mar 6;140(1):161-5.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: The leaves of Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam. (Rutaceae) are widely used in folk medicine in India to treat various ailments like cough, malaria, indigestion, influenza lung diseases and rheumatism, fever, stomach ailments, cholera and diarrhea. In our earlier communication we have reported the antimicrobial study on the various extracts of the leaves and the isolation and identification of Flindersine, a quinolone alkaloid as the major active principle. In the present study, we report the antibacterial and antifungal activities of Ulopterol, a coumarin isolated as another major active antimicrobial principle. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The leaves were successively extracted with hexane, chloroform, ethyl acetate, methanol and water. The extracts were studied for their antimicrobial activity against selected bacteria and fungi by using disc-diffusion method. The ethyl acetate extract which was found to possess highest antimicrobial activity was subjected to activity guided fractionation by column chromatography over silica gel. This resulted in the isolation of the coumarin, Ulopetrol, an active principle besides Flindersine which was reported by us earlier. The structure of the compound was elucidated using physical and spectroscopic data. Flindersine and Ulopterol were quantified by HPLC. RESULTS: Ulopterol showed activity against the bacteria viz. Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterobacter aerogenes, Shigella flexneri, Klebsiella pneumoniae (ESBL-3967), Escherichia coli (ESBL-3984) and fungi viz. Aspergillus flavus, Candida krusei and Botrytis cinerea. Quantification by HPLC showed the content of Flindersine and Ulopterol to be 0.361% and 0.266% respectively on dry weight basis of the leaves. CONCLUSIONS: Ethyl acetate extract (successive extraction) contained Ulopterol, a coumarin, besides Flindersine, a quinolone alkaloid, as a major active principle in the antimicrobial studies. This is the first report of the antimicrobial activity of Ulopterol and also its first report from the plant.
Secondary metabolites and cytotoxic activities from the stem bark of Zanthoxylum nitidum.[Pubmed:19551734]
Chem Biodivers. 2009 Jun;6(6):846-57.
A dihydrobenzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloid, epizanthocadinanine A (1), together with 27 known compounds, including eight benzo[c]phenanthridines, i.e., oxynitidine (2), oxyavicine (3), oxychelerythrine (4), dihydrochelerythrine (5), 6-acetonyldihydrochelerythrine (6), norchelerythrine (7), decarine (8), and arnottianamide (9); two 2-quinolones, i.e., Flindersine (10) and 4-methoxy-1-methyl-2-quinolone (11); two furoquinolines, i.e., skimmianine (12) and gamma-fagarine (13); three aporphines, i.e., liriodenine (14), N-acetyldehydroanonaine (15), and N-acetylanonaine (16); six lignans, i.e., sesamin (17), episesamin (18), piperitol-3,3-dimethylallyl ether (19), xanthoxylol-3,3-dimethylallyl ether (20), savinin (21), and 2,3-bis(3,4-methylenedioxybenzyl)but-2-en-4-olide (22); three terpenoids, i.e., alpha-cadinol (23), anticopalol (24), and spathulenol (25); one coumarin, i.e., aesculetin dimethyl ether (26); and two steroids, i.e., beta-sitosterol (27) and beta-sitostenone (28) were isolated from the stem bark of Zanthoxylum nitidum. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of extensive 1D- and 2D-NMR as well as MS analyses. Moreover, the recently reported structures 2'-4' of rhoifolines B and A, and '8-methoxynorchelerythrine', resp., isolated as new compounds from Z. rhoifolium and Z. nitidum, resp., could be assigned the revised structures 2-4 by reinvestigation of the spectroscopic data. In addition, the cytotoxicity of the isolates was evaluated on the MCF-7, NCI-H460, and SF-268 cell lines. Among these isolates, liriodenine (14) was the most active compound against the MCF-7, NCI-H460, and SF-268 cell lines with IC(50) values of 2.19, 2.38, and 3.19 microg/ml, resp.
Cytotoxic activity and cell cycle analysis of quinoline alkaloids isolated from Haplophyllum canaliculatum Boiss.[Pubmed:19551611]
Planta Med. 2009 Nov;75(14):1509-16.
Bioassay-guided fractionation of Haplophyllum canaliculatum Boiss. (Rutaceae) extract resulted in isolation of five quinoline alkaloids: 7-isopentenyloxy-gamma-fagarine, atanine, skimmianine, Flindersine and perfamine. This is the first isolation of these compounds from this endemic species. The antitumor activity of these five isolates was evaluated against RAJI, Jurkat, KG-1a, HEP-2, MCF-7, HL-60 and HL-60/MX1 tumor cell lines. The highest cytotoxic effect was observed on acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines. 7-Isopentenyloxy-gamma-fagarine, atanine, skimmianine and Flindersine exhibited very high cytotoxicity against the RAJI cell line with IC(50) values of 1.5, 14.5, 15.6 and 14.9 microg/mL, respectively and 7-isopentenyloxy-gamma-fagarine, atanine and skimmianine exhibited very high cytotoxicity against the Jurkat cell line with IC(50) values of 3.6, 9.3 and 11.5 microg/mL, respectively. 7-Isopentenyloxy-gamma-fagarine was also highly cytotoxic against the MCF-7 cell line (IC(50) = 15.5 microg/mL), while atanine, skimmianine, Flindersine and perfamine showed moderate to low activity against these cells. All alkaloids had moderate to low cytotoxicity against KG-1a and HEP-2. Investigation of the toxic potential of the alkaloids on HL-60 and HL-60/MX1 showed a significantly higher effect against HL-60/MX1, a multidrug-resistant cell line, compared with the control etoposide (p < 0.05). In all cytotoxicity experiments, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were used as a control for normal hematopoietic cells. Flow cytometry analysis of the compounds resulted in the arrest of cell cycle progression at the sub-G1 phase of the RAJI and Jurkat cell lines in a dose-dependent manner. According to computational analyses, the similar cytotoxic trend in the cell lines could be indicative of the fact that these compounds may act through parallel mechanisms.
Antibacterial and antifungal activity of Flindersine isolated from the traditional medicinal plant, Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam.[Pubmed:19481384]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2009 Jun 25;123(3):494-8.
AIM OF THE STUDY: The leaves and root of Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam. (Rutaceae) are widely used as a folk medicine in India. Hexane, chloroform, ethyl acetate, methanol and water extracts of Toddalia asiatica leaves and isolated compound Flindersine were tested against bacteria and fungi. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Antibacterial and antifungal activities were tested against bacteria and fungi using disc-diffusion method and minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs). The compound was confirmed using X-ray crystallography technique. RESULTS: Antibacterial and antifungal activities were observed in ethyl acetate extract. One active principle Flindersine (2,6-dihydro-2,2-dimethyl-5H-pyrano [3,2-c] quinoline-5-one-9cl) was isolated from the ethyl acetate extract. The MIC values of the compound against bacteria Bacillus subtilis (31.25 microg/ml), Staphylococcus aureus (62.5 microg/ml), Staphylococcus epidermidis (62.5 microg/ml), Enterococcus faecalis (31.25 microg/ml), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (250 microg/ml), Acinetobacter baumannii (125 microg/ml) and fungi Trichophyton rubrum 57 (62.5 microg/ml), Trichophyton mentagrophytes (62.5 microg/ml), Trichophyton simii (62.5 microg/ml), Epidermophyton floccosum (62.5 microg/ml), Magnaporthe grisea (250 microg/ml) and Candida albicans (250 microg/ml) were determined. CONCLUSIONS: Ethyl acetate extract showed promising antibacterial and antifungal activity and isolated compound Flindersine showed moderate activity against bacteria and fungi.
Static and dynamic interaction of a naturally occurring photochromic molecule with bovine serum albumin studied by UV-visible absorption and fluorescence spectroscopy.[Pubmed:19367911]
J Phys Chem B. 2008 Dec 25;112(51):16793-801.
In this work, the interaction of a naturally occurring chromene, Flindersine (FL), and bovine serum albumin (BSA) has been investigated by UV-vis absorption and fluorescence spectroscopy, time-resolved lifetime measurements, steady state photochemistry, and semiempirical calculations. The interplay of FL with tryptophan (Trp) has been studied in parallel. The interaction of FL with BSA causes fluorescence quenching of BSA through both static and dynamic quenching mechanisms. FL binds BSA with a stoichiometry that varies from 1.09:1 to 0.80:1 as the temperature increases from 293 to 308 K. The reaction is characterized by negative enthalpy (deltaH degrees = -193 kJ mol(-1)) and negative entropy (deltaS degrees = -550 J K(-1) mol(-1)), indicating that the predominant forces in the FL-BSA complex are hydrogen bonding and van der Waals forces. The binding distance between the protein and the photochrome was calculated as 2.5 nm, according to the Foerster theory on resonance energy transfer. The effect of FL concentration on the BSA fluorescence was analyzed according to the maximum entropy method. FL also quenches the emission of Trp with a mechanism that, based on the experimental evidence, excludes both static and dynamic effects. An alternative relaxation pathway, consisting in an electron transfer from a prefluorescent state of Trp to FL, is put forward. The photobehavior of FL is affected by the interplay with BSA but not with Trp. When FL is complexed with BSA, it becomes a more fluorescent and more reactive species. Semiempirical calculations of the lowest optically active electronic transitions of hypothetical FL photoproducts suggest the most likely structure for the photoproduct.


