Ginkgolic Acid C17:2CAS# 102811-39-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 102811-39-2 | SDF | File under preparation. |
| PubChem ID | 101926662 | Appearance | Powder |
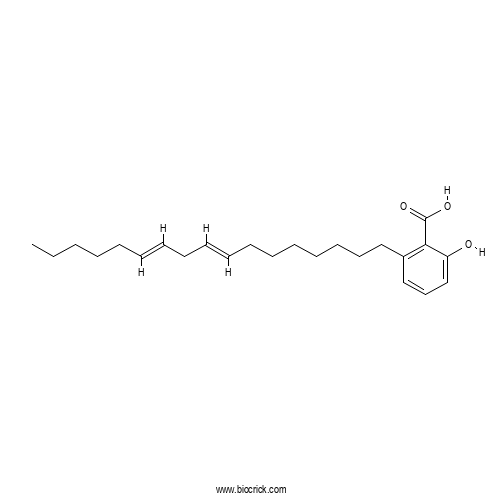
| Formula | C24H36O3 | M.Wt | 372.6 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-[(8E,11E)-heptadeca-8,11-dienyl]-6-hydroxybenzoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CCCCCC=CCC=CCCCCCCCC1=C(C(=CC=C1)O)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OFFQPVDOVYHTBX-AVQMFFATSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H36O3/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-18-21-19-17-20-22(25)23(21)24(26)27/h6-7,9-10,17,19-20,25H,2-5,8,11-16,18H2,1H3,(H,26,27)/b7-6+,10-9+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Ginkgolic Acid C17:2 Dilution Calculator

Ginkgolic Acid C17:2 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6838 mL | 13.4192 mL | 26.8384 mL | 53.6769 mL | 67.0961 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5368 mL | 2.6838 mL | 5.3677 mL | 10.7354 mL | 13.4192 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2684 mL | 1.3419 mL | 2.6838 mL | 5.3677 mL | 6.7096 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0537 mL | 0.2684 mL | 0.5368 mL | 1.0735 mL | 1.3419 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0268 mL | 0.1342 mL | 0.2684 mL | 0.5368 mL | 0.671 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Clinopodiside B
Catalog No.:BCN0871
CAS No.:155762-41-7
- Clinoposaponin VI
Catalog No.:BCN0870
CAS No.:152020-03-6
- Clinoposaponin IX
Catalog No.:BCN0869
CAS No.:159121-99-0
- Clinoposaponin I
Catalog No.:BCN0868
CAS No.:152580-76-2
- Clinoposaponin XI
Catalog No.:BCN0867
CAS No.:159122-01-7
- Clinoposaponin X
Catalog No.:BCN0866
CAS No.:159122-00-6
- Clinoposaponin VIII
Catalog No.:BCN0865
CAS No.:152020-04-7
- Clinoposaponin D
Catalog No.:BCN0864
CAS No.:1822328-43-7
- Secologanin
Catalog No.:BCN0863
CAS No.:19351-63-4
- Heratomol
Catalog No.:BCN0862
CAS No.:61265-07-4
- 1,3,5-tricaffeoylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN0861
CAS No.:1073897-80-9
- Ginsenoside Ra3
Catalog No.:BCN0860
CAS No.:90985-77-6
- Onjisaponin A
Catalog No.:BCN0873
CAS No.:82410-33-1
- Onjisaponin O
Catalog No.:BCN0874
CAS No.:1009314-38-8
- Onjisaponin J
Catalog No.:BCN0875
CAS No.:873334-98-6
- Tenuifoliose J
Catalog No.:BCN0876
CAS No.:147742-15-2
- Tenuifoliose A
Catalog No.:BCN0877
CAS No.:139682-01-2
- Tenuifoliose H
Catalog No.:BCN0878
CAS No.:147742-13-0
- Arillanin A
Catalog No.:BCN0879
CAS No.:154287-47-5
- Onjisaponin Y
Catalog No.:BCN0880
CAS No.:1078708-71-0
- Onjisaponin W
Catalog No.:BCN0881
CAS No.:1078708-68-5
- Onjisaponin R
Catalog No.:BCN0882
CAS No.:1008798-85-3
- Senegin II
Catalog No.:BCN0883
CAS No.:34366-31-9
- Senegin IV
Catalog No.:BCN0884
CAS No.:51005-46-0
[Determination of ginkgolic acids by high performance liquid chromatography].[Pubmed:12914328]
Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2002 Jul;37(7):555-8.
AIM: To establish a simple pre-treated method and high performance liquid chromatographic method for separation and determination of ginkgolic acids in Ginkgo biloba leaves. METHODS: The ginkgolic acids in the German standard sample were identified by LC/DAD/ESI/MS. The methods for pre-treatment and high performance liquid chromatography determination of ginkgolic acids were studied. Ginkgo biloba leaves were extracted with n-hexane in Soxhlet apparatus, then concentrated under vacuum. The ginkgolic acids can be determined directly by HPLC after one-pre-purified-step by silica gel column chromatography. The eluant was petroleum ether-diethyl ether-formic acid (89:11:1). The chromatographic column was Inertsil ODS-2; the mobile phase was methanol-3% acetic acid (92:8); the flow rate was 1.0 mL.min-1; the column temperature was 40 degrees C; the detection wavelength was at 310 nm. RESULTS: There were five kinds of ginkgolic acid (C13:0, C15:1, C17:2, C15:0 and C17:1) in ginkgo biloba leaves. The relative percentage content of ginkgolic acids C15:1 and C17:1 was about 85%. Ginkgolic Acid C17:2 had not been reported in China. The HPLC indicates that there was nearly no impurities except ginkgolic acids after treated by column chromatography. The results showed that the content of ginkgolic acids in the leaves of Ginkgo biloba collected in April, May and June was 1.48%, 1.19% and 1.11% respectively. The average recovery of Ginkgo biloba leaves collected in June was 97.0%, RSD was 1.7% (n = 6). CONCLUSION: The method is accurate, simple and reliable, and can be used for determination of ginkgolic acids in Ginkgo biloba leaves.


