KokusaginineCAS# 484-08-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 484-08-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10227 | Appearance | Powder |
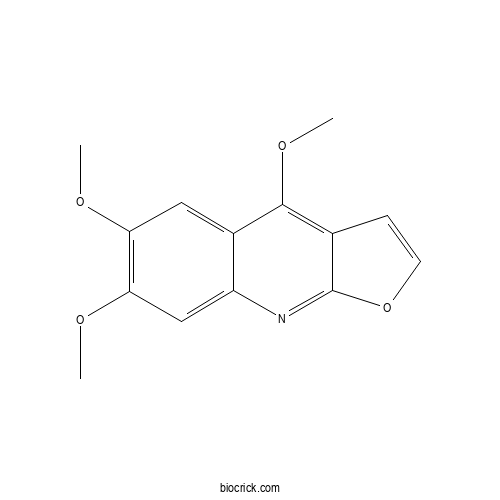
| Formula | C14H13NO4 | M.Wt | 259.3 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 4,6,7-trimethoxyfuro[2,3-b]quinoline | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C2C(=C1)C(=C3C=COC3=N2)OC)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JBRXRVFXQIKPEA-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H13NO4/c1-16-11-6-9-10(7-12(11)17-2)15-14-8(4-5-19-14)13(9)18-3/h4-7H,1-3H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Kokusaginine Dilution Calculator

Kokusaginine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.8565 mL | 19.2827 mL | 38.5654 mL | 77.1307 mL | 96.4134 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7713 mL | 3.8565 mL | 7.7131 mL | 15.4261 mL | 19.2827 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3857 mL | 1.9283 mL | 3.8565 mL | 7.7131 mL | 9.6413 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0771 mL | 0.3857 mL | 0.7713 mL | 1.5426 mL | 1.9283 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0386 mL | 0.1928 mL | 0.3857 mL | 0.7713 mL | 0.9641 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 2,4,6-Trihydroxy-3-prenylacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN0478
CAS No.:27364-71-2
- Ferruginoside C
Catalog No.:BCN0477
CAS No.:213991-03-8
- (±)-8-Gingerol
Catalog No.:BCN0476
CAS No.:77398-92-6
- 2',3'-Dehydromarmesin
Catalog No.:BCN0475
CAS No.:28664-60-0
- Polypodine B 20,22-acetonide
Catalog No.:BCN0474
CAS No.:159858-85-2
- Acrotrione
Catalog No.:BCN0473
CAS No.:2349327-31-5
- 1,4-Dihydro-1-methyl-4-oxonicotinamide
Catalog No.:BCN0472
CAS No.:769-49-3
- 1-O-Cinnamoylglucose
Catalog No.:BCN0471
CAS No.:40004-96-4
- 1-O-p-Coumaroylglucose
Catalog No.:BCN0470
CAS No.:7139-64-2
- 5-endo-Hydroxyborneol
Catalog No.:BCN0469
CAS No.:68738-10-3
- 6,4'-Dihydroxy-5,7-dimethoxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN0468
CAS No.:6951-57-1
- p-O-Farnesylcoumaric acid
Catalog No.:BCN0467
CAS No.:939769-47-8
- 4-(Acetoxymethyl)phenyl glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN0480
CAS No.:188290-72-4
- Isorengyol
Catalog No.:BCN0481
CAS No.:101489-38-7
- Stigmalactam
Catalog No.:BCN0482
CAS No.:289499-72-5
- [6]-Gingerol
Catalog No.:BCN0483
CAS No.:39886-76-5
- Acrovestone
Catalog No.:BCN0484
CAS No.:24177-16-0
- Marionol
Catalog No.:BCN0485
CAS No.:65602-55-3
- Verproside
Catalog No.:BCN0486
CAS No.:50932-20-2
- 5-Hydroxy-6,7,3',4'-tetramethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN0487
CAS No.:21763-80-4
- Piperdardine
Catalog No.:BCN0488
CAS No.:188426-70-2
- 4''-O-Methylcatalposide
Catalog No.:BCN0489
CAS No.:887140-17-2
- Apigenin 7,4'-di-O-alloside
Catalog No.:BCN0490
CAS No.:95693-63-3
- Tsaokoin
Catalog No.:BCN0491
CAS No.:343605-41-4
Outlining In Vitro and In Silico Cholinesterase Inhibitory Activity of Twenty-Four Natural Products of Various Chemical Classes: Smilagenin, Kokusaginine, and Methyl Rosmarinate as Emboldening Inhibitors.[Pubmed:33916300]
Molecules. 2021 Apr 1;26(7). pii: molecules26072024.
Cholinesterase (ChE) inhibition is an important treatment strategy for Alzheimer's disease (AD) as acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) are involved in the pathology of AD. In the current work, ChE inhibitory potential of twenty-four natural products from different chemical classes (i.e., diosgenin, hecogenin, rockogenin, smilagenin, tigogenin, astrasieversianins II and X, astragalosides I, IV, and VI, cyclocanthosides E and G, macrophyllosaponins A-D, kokusaginin, lamiide, forsythoside B, verbascoside, alyssonoside, ipolamide, methyl rosmarinate, and luteolin-7-O-glucuronide) was examined using ELISA microtiter assay. Among them, only smilagenin and Kokusaginine displayed inhibitory action against AChE (IC50 = 43.29 +/- 1.38 and 70.24 +/- 2.87 microg/mL, respectively). BChE was inhibited by only methyl rosmarinate and Kokusaginine (IC50 = 41.46 +/- 2.83 and 61.40 +/- 3.67 microg/mL, respectively). IC50 values for galantamine as the reference drug were 1.33 +/- 0.11 microg/mL for AChE and 52.31 +/- 3.04 microg/mL for BChE. Molecular docking experiments showed that the orientation of smilagenin and Kokusaginine was mainly driven by the interactions with the peripheral anionic site (PAS) comprising residues of hAChE, while Kokusaginine and methyl rosmarinate were able to access deeper into the active gorge in hBChE. Our data indicate that similagenin, Kokusaginine, and methyl rosmarinate could be hit compounds for designing novel anti-Alzheimer agents.
Bio-Guided Fractionation of Ethanol Extract of Leaves of Esenbeckia alata Kunt (Rutaceae) Led to the Isolation of Two Cytotoxic Quinoline Alkaloids: Evidence of Selectivity Against Leukemia Cells.[Pubmed:31597257]
Biomolecules. 2019 Oct 8;9(10). pii: biom9100585.
Bio-guided fractionation performed on the leaves-derived ethanol extract of Esenbeckia alata (Rutaceae), a plant used in traditional medicine, led to the isolation of two alkaloids, Kokusaginine 1 and flindersiamine 2, as main cytotoxic agents. Primary ethanolic extract and raw fractions exhibited cell inhibition against five cancer cell lines at different levels (25-97% inhibition at 50 microg/mL) as well as isolated alkaloids 1-2 (30-90% inhibition at 20 microM). Although alkaloid 2 generally was the most active compound, both alkaloids showed a selective effect on K562, a human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line. The E1-like ubiquitin-activating enzymes (e.g., UBA5) have been recently described as important targets for future treatment of cancer progression, such as leukemia, among others. Therefore, as a rationale to the observed cytotoxic selectivity, an in-silico evaluation by molecular docking and molecular dynamics was also explored. Compounds 1-2 exhibited good performance on the interaction within the active site of UBA5.
Isolation and Antimacrofouling Activity of Indole and Furoquinoline Alkaloids from 'Guatambu' Trees (Aspidosperma australe and Balfourodendron riedelianum).[Pubmed:31515922]
Chem Biodivers. 2019 Nov;16(11):e1900349.
In this work, the antifouling activity of five alkaloids, isolated from trees of the Atlantic rainforest, was studied. The tested alkaloids were olivacine (1), uleine (2) and N-methyltetrahydroellipticine (3) from Aspidosperma australe ('yellow guatambu') and the furoquinoline alkaloids Kokusaginine (4) and flindersiamine (5) from Balfourodendron riedelianum ('white guatambu'). All these compounds can be isolated from their natural sources in high yields in a sustainable way. The five compounds were subjected to laboratory tests (attachment test of the mussel Mytilus edulis platensis) and field trials, by incorporation into soluble matrix paints, and 45 days of exposure of the painted panels in the sea. The results show that compound 3 is a very potent antifoulant, and that compounds 4 and 5 are also very active, while compounds 1 and 2 did not show any significant antifouling activity. These results open the way for the development of environmentally friendly antifouling agents, based on abundant and easy-to-purify compounds that can be obtained in a sustainable way.
Furoquinolines and dihydrooxazole alkaloids with cytotoxic activity from the stem bark of Araliopsis soyauxii.[Pubmed:30654126]
Fitoterapia. 2019 Mar;133:193-199.
Two new furoquinoline alkaloids, maculine B (1) and Kokusaginine B (2) and one new dihydrooxazole alkaloid, veprisazole (3), along with four known compounds namely, N13-methyl-3-methoxyrutaecarpine (4), flindersiamine (5), skimmianine (6) and tilianin (7) were isolated from the methanol extract of the stem bark of Araliopsis soyauxii Engl. by various chromatographic methods. Their structures were determined using spectrometry and spectroscopic techniques including NMR and MS. The cytotoxicity of the new compounds compared to that of doxorubicin, the reference anticancer compound, was determined on a panel of nine cancer cell lines including sensitive and drug resistant phenotypes. The three previously undescribed alkaloids displayed selective activities. Maculine B (1), the most active one among the newly described compounds, exhibited IC50 below 30muM against CCRF-CEM leukemia and U87MG glioblastoma cells.
Determination of antibacterial activity and metabolite profile of Ruta graveolens against Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sobrinus.[Pubmed:30078970]
J Lab Physicians. 2018 Jul-Sep;10(3):320-325.
BACKGROUND: Ruta graveolens is one of the most used phytomedicines. To date, there is no report of determining the bioactivity of R. graveolens against cariogenic causing bacteria (Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sobrinus). OBJECTIVE: The objective of the present study was to determine the antibacterial activity and metabolite profile of R. graveolens against S. mutans and S. sobrinus. MATERIALS AND METHODS: R. graveolens plant material was collected and processed in the month of February. The plant material was extracted by Soxhlet apparatus using methanol solvent. Two strains of S. mutans and two strains of S. sobrinus were isolated from dental caries-active participants and cultured on mitis salivarius-bacitracin agar. The antibacterial susceptibility testing of methanolic extract of R. graveolens was performed by disc diffusion method. The metabolite profile of the plant extract was determined using electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. RESULTS: The methanolic extract of R. graveolens showed a promising antibacterial activity against S. mutans and S. sobrinus. Two compounds named gamma-fagarine and Kokusaginine were identified from the methanolic extract of R. graveolens. CONCLUSION: The study concluded that R. graveolens contains significant antibacterial activity. However, further investigations are suggested to understand the anticaries properties of these pure compounds.
The inhibitory effect of kokusaginine on the growth of human breast cancer cells and MDR-resistant cells is mediated by the inhibition of tubulin assembly.[Pubmed:29903663]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018 Aug 1;28(14):2490-2492.
The emergence of multidrug resistance (MDR) is a significant challenge in breast carcinoma chemotherapy. Kokusaginine isolated from Dictamnus dasycarpus Turcz. has been reported to show cytotoxicity in several human cancer cell lines including breast cancer cells MCF-7. In this study, Kokusaginine showed the potent inhibitory effect on MCF-7 multidrug resistant subline MCF-7/ADR and MDA-MB-231 multidrug resistant subline MDA-MB-231/ADR. Kokusaginine markedly induced apoptosis in a concentration-dependent manner in MCF-7/ADR cells. Furthermore, Kokusaginine reduced P-gp mRNA and protein levels, and suppressed P-gp function especially in MCF-7/ADR cells. In addition, Kokusaginine showed to inhibit tubulin assembly and the binding of colchicine to tubulin by binding directly to tubulin and affects tubulin formation in vitro. Taken together, these results support the potential therapeutic value of Kokusaginine as an anti-MDR agent in chemotherapy for breast carcinoma.
Chalepin: isolated from Ruta angustifolia L. Pers induces mitochondrial mediated apoptosis in lung carcinoma cells.[Pubmed:27729078]
BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Oct 12;16(1):389.
BACKGROUND: Cancer has been one of the leading causes of mortality in this era. Ruta angustifolia L. Pers has been traditionally used as an abortifacient, antihelmintic, emmenagogue and ophthalmic. In Malaysia and Singapore, the local Chinese community used it for the treatment of cancer. METHODS: In this study, the methanol and fractionated extracts (hexane, chloroform, ethyl acetate and water) of R. angustifolia were tested for its cytotoxicity using the sulforhodamide (SRB) cytotoxicity assay against HCT-116, A549, Ca Ski and MRC5 cell lines. Chemical isolation was carried out by using the high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and the isolated compounds were tested for its cytotoxicity against A549 cell line. Cellular and nuclear morphological changes were observed in the cells using phase contrast microscopy and Hoechst/PI fluorescent staining. The externalisation of phosphatidylserine was observed through FITC-labelling Annexin V/PI assay whilst DNA fragmentation was observed through the TUNEL assay. Other indication of apoptosis occuring through the mitochondrial pathway were the attenuation of mitochondrial membrane potential and increase in ROS production. Activation of caspase 9 and 3 were monitored. Western blot analysis was done to show the expression levels of apoptotic proteins. RESULTS: The chloroform extract (without chlorophyll) exhibited the highest cytotoxic activity with IC50 of 10.1 +/- 0.15 mug/ml against A549 cell line. Further chemical investigation was thus directed to this fraction which led to the isolation of 12 compounds identified as graveoline, psoralen, Kokusaginine, methoxysalen, bergapten, arborinine, moskachan B, chalepin, moskachan D, chalepensin, rutamarin and neophytadiene. Among these compounds, chalepin exhibited excellent cytotoxicity against A549 cell line with an IC50 value of 8.69 +/- 2.43 mug/ml (27.64 muM). In western blot analysis, expression of p53, truncated Bid, Bax and Bak while the anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2, survivin, XIAP, Bcl-XL,cFLIP decreased in a time-dependent manner when A549 cells were treated with 36 mug/ml of chalepin. In addition, the level of PARP was found to decrease. CONCLUSION: Hence these findings indicated that chalepin-induced cell death might involve the intrinsic mitochodrial pathway resulting in the upregulation of pro-apoptotic proteins and downregulation of anti-apoptotic proteins. Thus, chalepin could be an excellent candidate for the development of an anticancer agent.
Furoquinoline Alkaloids from the Leaves of Evodia lepta as Potential Cholinesterase Inhibitors and their Molecular Docking.[Pubmed:26434116]
Nat Prod Commun. 2015 Aug;10(8):1359-62.
Nine furoquinoline alkaloids (1-9) were isolated from the leaves of Evodia lepta based on bioassay-guided fractionation and chromatographic techniques. All isolates were evaluated for their cholinesterase (ChEs) inhibitory activities, in which Kokusaginine (7) and melineurine (5) exhibited the highest activity toward AChE and BChE, respectively. Lineweaver-Burk plots indicated that 5 and 7 were mixed mode inhibitors of both ChE enzymes. Molecular docking studies on the binding sites of AChE and BChE were performed in order to afford a molecular insight into the mode of action of these active compounds. From this study these compounds have emerged as promising molecules for Alzheimer's disease therapy.
Inhibition of hepatitis C virus replication by chalepin and pseudane IX isolated from Ruta angustifolia leaves.[Pubmed:25454460]
Fitoterapia. 2014 Dec;99:276-83.
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is highly prevalent among global populations, with an estimated number of infected patients being 170 million. Approximately 70-80% of patients acutely infected with HCV will progress to chronic liver disease, such as liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, which is a substantial cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. New therapies for HCV infection have been developed, however, the therapeutic efficacies still need to be improved. Medicinal plants are promising sources for antivirals against HCV. A variety of plants have been tested and proven to be beneficial as antiviral drug candidates against HCV. In this study, we examined extracts, their subfractions and isolated compounds of Ruta angustifolia leaves for antiviral activities against HCV in cell culture. We isolated six compounds, chalepin, scopoletin, gamma-fagarine, arborinine, Kokusaginine and pseudane IX. Among them, chalepin and pseudane IX showed strong anti-HCV activities with 50% inhibitory concentration (IC(5)(0)) of 1.7 +/- 0.5 and 1.4 +/- 0.2 mug/ml, respectively, without apparent cytotoxicity. Their anti-HCV activities were stronger than that of ribavirin (2.8 +/- 0.4 mug/ml), which has been widely used for the treatment of HCV infection. Mode-of-action analyses revealed that chalepin and pseudane IX inhibited HCV at the post-entry step and decreased the levels of HCV RNA replication and viral protein synthesis. We also observed that arborinine, Kokusaginine and gamma-fagarine possessed moderate levels of anti-HCV activities with IC(5)(0) values being 6.4 +/- 0.7, 6.4 +/- 1.6 and 20.4 +/- 0.4 mug/ml, respectively, whereas scopoletin did not exert significant anti-HCV activities at 30 mug/ml.
Cytotoxic Benzophenanthridine and Furoquinoline Alkaloids from Zanthoxylum buesgenii (Rutaceae).[Pubmed:25349626]
Chem Cent J. 2014 Oct 21;8(1):61.
BACKGROUND: Zanthoxylum buesgenii is a shrub used in Sierra Leone as remedy to cure venereal diseases, arthritis, and rheumatism whereas leaves and barks are employed to treat leprosy and to relieve pain. In South West Region of Cameroon, the plant locally called "Mbem" by Lewoh-Lebang community, is orally given to patients as aphrodisiac decoction and to increase sperm count. Previous chemical studies on Zanthoxylum species reported the identification of lignans, coumarins, diterpenes, sesquiterpenes, steroids, alkaloids and benzopropanoids. Besides, structurally diverse compounds belonging to these classes of secondary metabolites have been reported as trypanocidal, antileishmanial, antimycobacterial and cytotoxic metabolites. RESULTS: We therefore investigated the alkaloidal constituents of Z. buesgenii. In the course of the study, two benzophenanthridines [1-methoxy-12-methyl-12,13-dihydro-[1,3]dioxolo[4',5':4,5]benzo[1,2-c]phenanthrid ine-2,13-diol (1) and isofagaridine (2)] were identified among them one new. Alongside, three known furoquinolines [maculine (3), Kokusaginine (4) and teclearverdoornine (5)] were also obtained and their structures were established on the basis of their NMR data and by comparison with those previously reported. Furthermore, the cytotoxicities of metabolites (1-4) isolated in substantial amount were evaluated against a series of multidrugs-resistant cancer cell lines. While compounds 2-4 showed selective cytotoxicities, compound 1 displayed activities against all cancer cells. CONCLUSIONS: The observed activities corroborate those previously reported on similar benzophenanthridine alkaloids indicating that compounds 1 and 2 can chemically be explored to develop other chemotherapeutic agents. Graphical abstractCytotoxic Benzophenanthridine and Furoquinoline Alkaloids from Zanthoxylum buesgenii (Rutaceae).
Antibacterial constituents of three Cameroonian medicinal plants: Garcinia nobilis, Oricia suaveolens and Balsamocitrus camerunensis.[Pubmed:23574627]
BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013 Apr 10;13:81.
BACKGROUND: Multidrug resistance is a worrying cause of treatment failure in bacterial infections. The search of bioactive constituents from medicinal plants against multidrug resistant (MDR) bacteria has significantly evolved in the two last decades. In the present study, twenty-two compounds (three terpenoids, eleven phenolics and eight alkaloids) isolated from three Cameroonian medicinal plants, namely Garcinia nobilis, Oricia suaveolens and Balsamocitrus camerunensis, as well as the crude extracts were tested for their antibacterial activities against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Gram-negative bacteria amongst which were MDR active efflux pumps expressing phenotypes. METHODS: The microplate alamar blue assay (MABA) and the broth microdilution methods were used to determine the minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC) and minimal bactericidal concentrations (MBC) of the studied samples. RESULTS: The results of the MIC determinations indicate that, the best crude extract was that from G. nobilis (GNB), its inhibitory effects being noted against 12 of the 14 tested bacteria. The extract of GNB also exhibited better anti-tuberculosis (MIC of 128 mug/ml M. tuberculosis against ATCC 27294 strain) and antibacterial (MIC of 64 mug/ml against Escherichia coli ATCC10536) activities compared to the extracts of O. suaveolens and B. camerunensis. Interestingly, 4-prenyl-2-(3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadienyl)-1,3,5,8-tetrahydroxyxanthone (2), isolated from the most active extract GNB, also showed the best activity amongst compounds, inhibiting the growth of all the fourteen tested microorganisms. The lowest MIC value obtained with compound 2 was 8 mug/ml against M. tuberculosis ATCC 27294 and M. tuberculosis clinical MTCS2 strains. Other compounds showed selective activities with 11 of the 14 tested bacteria being sensitive to the xanthone, morusignin I (5) and the alkaloid, Kokusaginine (13). CONCLUSIONS: The results of the present investigation provide evidence that the crude extract from G. nobilis, O. suaveolens and B. camerunensis as well as some of their compounds, and mostly compound 2 (isolated from G. nobilis,) could be considered as interesting natural antibacterial products.
Furoquinoline alkaloids isolated from Balfourodendron riedelianum as photosynthetic inhibitors in spinach chloroplasts.[Pubmed:23416711]
J Photochem Photobiol B. 2013 Mar 5;120:36-43.
In the search for natural inhibitors of plant growth, we investigate the mechanism of action of the natural furoquinoline alkaloids isolated from Balfourodendron riedelianum (Rutaceae): evolitrine (1), Kokusaginine (2), gamma-fagarine (3), skimmianine (4) and maculosidine (5) on the photosynthesis light reactions. Their effect on the electron transport chain on thylakoids was analyzed. Alkaloids 1, 2, 4 and 5 inhibited ATP synthesis, basal, phosphorylating and uncoupled electron transport acting as Hill reaction inhibitors on spinach chloroplasts. Alkaloid 3 was not active. The inhibition and interaction site of alkaloids 1, 2, 4 and 5 on the non-cyclic electron transport chain was studied by polarography and fluorescence of the chlorophyll a (Chl a). The results indicate that the target for 1 was localized on the donor and acceptor side of PS II. In addition alkaloids 2 and 5 affect the PS I electron acceptors on leaf discs.
Activity of selected phytochemicals against Plasmodium falciparum.[Pubmed:22537982]
Acta Trop. 2012 Aug;123(2):96-100.
According to the WHO, in 2008, there were 247 million reported cases of malaria and nearly one million deaths from the disease. Parasite resistance against first-line drugs, including artemisinin and mefloquine, is increasing. In this study the plant-derived compounds aglafolin, rocaglamid, Kokusaginine, arborine, arborinine and tuberostemonine were investigated for their anti-plasmodial activity in vitro. Fresh Plasmodium falciparum isolates were taken from patients in the area of Mae Sot, north-western Thailand in 2008 and the inhibition of schizont maturation was determined for the respective compounds. With inhibitory concentrations effecting 50%, 90% and 99% inhibition (IC(50), IC(90) and IC(99)) of 60.95 nM, 854.41 nM and 7351.49 nM, respectively, rocaglamid was the most active of the substances, closely followed by aglafoline with 53.49 nM, 864.55 nM and 8354.20 nM. The activity was significantly below that of artemisinin, but moderately higher than that of quinine. Arborine, arborinine, tuberostemonine and Kokusaginine showed only marginal activity against P. falciparum characterized by IC(50) and IC(99) values higher than 350 nM and 180 muM, respectively, and regressions with relatively shallow slopes S>14.38. Analogues of rocaglamid and aglafoline merit further exploration of their anti-plasmodial activity.
seco-limonoids and quinoline alkaloids from Raputia heptaphylla and their antileishmanial activity.[Pubmed:21720036]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2011;59(7):855-9.
A novel seco-limonoid, rel-(1S,5R,9S,7R,8S,9R,10S,11R,13S,14R,15R,17R)-11,19-dihydroxy-7-acetoxy-7-deoxo ichangin (raputiolide) (1), and two novel quinolone alkaloids N-methyl-2-phenoxyquinolin-4(1H)-one (heptaphyllone A) (2) and 6-methylbenzofuro[2,3-b]quinolin-4(1H)-one (heptaphyllone B) (3), along with the known seco-limonoid ichangin (4), were isolated from Raputia heptaphylla PITTIER (Rutaceae) stem bark. Five known alkaloids, N-methyl-8-methoxyflindersine (5), skimmianine (6), Kokusaginine (7), dictamnine (8) and flindersiamine (9), were also isolated from R. heptaphylla leaves. Their structures were established on the basis of full spectroscopic data interpretation supported by data from the pertinent literature. seco-Limonoid 1 configuration was determined by enhanced nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy (NOESY) experiments and density functional theory (DFT) molecular modeling. The antileishmanial effect of the isolated compounds was evaluated on Leishmania Viannia panamensis (promastigotes and amastigotes). Whereas alkaloids 2-3, 6-8 and limonoid 4 exhibited no significant parasitocide activity against internalized L. (V.) panamensis amastigotes, limonoid 1 and alkaloid 5 had leishmanicidal activity on intracellular amastigotes (EC(5)(0): 8.7 microg/ml) and promastigotes (EC(50): 14.3 microg/ml), respectively.
Chemical constituents of Melicope ptelefolia.[Pubmed:21485271]
Nat Prod Commun. 2011 Mar;6(3):343-8.
Phytochemical investigations on the methanolic extract of Melicope ptelefolia Champ ex Benth. resulted in the isolation of three new compounds, identified as 3beta-stigmast-5-en-3-ol butyl tridecanedioate (melicoester) (1), (2Z, 6Z, 10Z, 14Z, 18Z, 22Z, 26E)-3', 7', 11', 15', 19', 23', 27', 31'-octamethyldotriaconta-2, 6, 10, 14, 18, 22, 26, 30-octadecanoate (melicopeprenoate) (2) and p-O-geranyl-7"-acetoxy coumaric acid (3). The compounds were isolated along with twenty-one other known compounds, lupeol (4), oleanolic acid (5), Kokusaginine (6) genistein (7), p-O-geranyl coumaric acid (8), 4-stigmasten-3-one (9), 3beta-hydroxystigma-5-en-7-one (10) cis-phytyl palmitate (11), dodecane, dodecan-1-ol, ceryl alcohol, hentriacontanoic acid, eicosane, n-amyl alcohol, caprylic alcohol, octatriacontane, nonatriacontane, hexatriencontan-1-ol, methyl octacosanoate, beta-sitosterol, beta-sitosterol glucoside. Structures of all the compounds were established on the basis of MS and 1D and 2D NMR spectral data, as well as comparison with reported data.


