Linifanib (ABT-869)VEGFR/PDGFR inhibitor CAS# 796967-16-3 |
- SKLB610
Catalog No.:BCC3647
CAS No.:1125780-41-7
- Axitinib (AG 013736)
Catalog No.:BCC3729
CAS No.:319460-85-0
- Vandetanib (ZD6474)
Catalog No.:BCC3883
CAS No.:443913-73-3
- Pazopanib (GW-786034)
Catalog No.:BCC1286
CAS No.:444731-52-6
- SU14813 double bond Z
Catalog No.:BCC1972
CAS No.:452105-23-6
- Brivanib Alaninate (BMS-582664)
Catalog No.:BCC1240
CAS No.:649735-63-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 796967-16-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11485656 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C21H18FN5O | M.Wt | 375.41 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | ABT-869; AL-39324 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 72 mg/mL (191.80 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
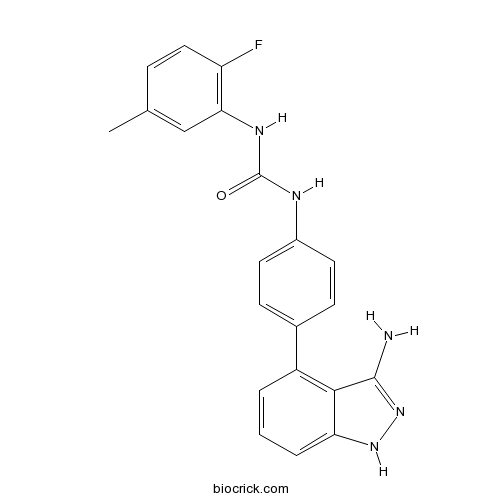
| Chemical Name | 1-[4-(3-amino-1H-indazol-4-yl)phenyl]-3-(2-fluoro-5-methylphenyl)urea | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC(=C(C=C1)F)NC(=O)NC2=CC=C(C=C2)C3=C4C(=CC=C3)NN=C4N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MPVGZUGXCQEXTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H18FN5O/c1-12-5-10-16(22)18(11-12)25-21(28)24-14-8-6-13(7-9-14)15-3-2-4-17-19(15)20(23)27-26-17/h2-11H,1H3,(H3,23,26,27)(H2,24,25,28) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Linifanib is a multitargeted inhibitor of receptor tyrosine kinase with IC50 value of 3 nM, 3 nM, 4 nM, 4 nM and 14 nM for VEGFR1/FLT1, CSF-1R, VEGFR2/KDR, FLT3 and KIT, respectively. | ||||||
| Targets | VEGFR1/FLT1 | CSF-1R | VEGFR2/KDR | FLT3 | KIT | ||
| IC50 | 3 nM | 3 nM | 4 nM | 4 nM | 14 nM | ||

Linifanib (ABT-869) Dilution Calculator

Linifanib (ABT-869) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6638 mL | 13.3188 mL | 26.6375 mL | 53.2751 mL | 66.5939 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5328 mL | 2.6638 mL | 5.3275 mL | 10.655 mL | 13.3188 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2664 mL | 1.3319 mL | 2.6638 mL | 5.3275 mL | 6.6594 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0533 mL | 0.2664 mL | 0.5328 mL | 1.0655 mL | 1.3319 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0266 mL | 0.1332 mL | 0.2664 mL | 0.5328 mL | 0.6659 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Linifanib (ABT-869) is an effective ATP-competitive tyrosine kinase inhibitor against the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor and the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) families, including constitutively active FMS-like receptor tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) [1][2]. It is of IC50 values of 0.55 nmol/L and 6 μmol/L to the cell growth in Ba/F3 FLT3 ITD mutant cells and in Ba/F3 FLT3 WT cells, respectively [1].
FLT3 is important in controlling the proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic cells. Patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) showed activating mutations in FLT3. These mutations caused abnormal cell proliferation [1].
Linifanib at a concentration of 10 nmol/L induced apoptosis in internal tandem duplication (ITD) mutant cells, but showed no effect in WT cells. Treatment with linifanib did not differentiate WT cells from FLT3 mutant cells with mutation at D835V, in inhibiting proliferation or reducing cell viability. In Ba/F3 FLT3 ITD cell lines, linifanib at a concentration of 10 nmol/L, effectively inhibited the phosphorylation of FLT3. 10 nmol/L linifanib reduced the phosphorylation of Akt at Ser473 [1].
Daily orally treatment with linifanib by gavage in NOD/SCID mice with ITD mutant cell decreased the leukemia progression rate compared with the control. On day 7, ITD mutant cells showed rapid progression in control mice, whereas linifanib-treated mice showed no detectable disease. In addition, daily linifanib-treated mice with ITD mutant cells showed significantly longer (P < 0.01) survival duration than control mice with ITD mutant cells only [1].
References:
[1]. Jenny E. Hernandez-Davies, Joan P. Zape, Elliot M. Landaw, et al. The Multitargeted Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Linifanib (ABT-869) Induces Apoptosis through an Akt and Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β–Dependent Pathway. Mol. Cancer Ther., 2011, 10(6):949-59.
[2]. Joyce E. Ohm, Michael R. Shurin, Clemens Esche, et al. Effect of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and FLT3 Ligand on Dendritic Cell Generation In Vivo. Journal of Immunology, 1999, 163:3260-3268.
- Crassicauline A
Catalog No.:BCN2516
CAS No.:79592-91-9
- Alarelin Acetate
Catalog No.:BCC1336
CAS No.:79561-22-1
- Sertraline HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5059
CAS No.:79559-97-0
- 1,7-Diphenyl-4-hepten-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN3592
CAS No.:79559-59-4
- 5-Ethoxychelerthrine
Catalog No.:BCC8105
CAS No.:79559-55-0
- L-165041
Catalog No.:BCC1687
CAS No.:79558-09-1
- 20-HETE
Catalog No.:BCC1301
CAS No.:79551-86-3
- Stelleranol
Catalog No.:BCN8014
CAS No.:795308-62-2
- Norketamine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5859
CAS No.:79499-59-5
- Glaucocalyxin A
Catalog No.:BCN2353
CAS No.:79498-31-0
- 9-Oxo-10,11-dehydroageraphorone
Catalog No.:BCN4333
CAS No.:79491-71-7
- Eleutheroside D
Catalog No.:BCN5336
CAS No.:79484-75-6
- Levonorgestrel
Catalog No.:BCC4792
CAS No.:797-63-7
- H-Hyp(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3249
CAS No.:79775-07-8
- Loratadine
Catalog No.:BCC1262
CAS No.:79794-75-5
- Castanospermine
Catalog No.:BCC6783
CAS No.:79831-76-8
- 1,2,3,6-Tetragalloylglucose
Catalog No.:BCN2159
CAS No.:79886-50-3
- Simvastatin
Catalog No.:BCN2569
CAS No.:79902-63-9
- Forsythoside A
Catalog No.:BCN1195
CAS No.:79916-77-1
- ML130 (Nodinitib-1)
Catalog No.:BCC4611
CAS No.:799264-47-4
- Idazoxan hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6798
CAS No.:79944-56-2
- Boc-His(Bom)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3400
CAS No.:79950-65-5
- Quinovic acid 3-O-beta-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4334
CAS No.:79955-41-2
- Fmoc-D-Ala-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3036
CAS No.:79990-15-1
Linifanib (ABT-869), enhances cytotoxicity with poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor, veliparib (ABT-888), in head and neck carcinoma cells.[Pubmed:24735547]
Oral Oncol. 2014 Jul;50(7):662-9.
OBJECTIVES: PARP inhibitors (PARPi) may provide an opportunity to gain selective killing of tumor cells which have deficiencies in cellular DNA repair systems. We previously demonstrated Linifanib (ABT-869), a multi-receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor of VEGF and PDGF receptor families, radiosensitized Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma cells (HNSCC) via inhibiting STAT3 activation. Given that STAT3 can modulate DNA damage response (DDR) pathway, in this study, we evaluate the effects of linifanib to enhance cytotoxicity with the PARPi, veliparib (ABT-888), in HNSCC. MATERIALS AND METHODS: UMSCC-22A and UMSCC-22B cells were treated with Linifanib (ABT-869) and veliparib (ABT-888). Cell viability, cytotoxicity, apoptosis induction, DNA single strand break (SSB) and double strand break (DSB) damages were examined by MTT assay, colony formation assay, flow cytometry and comet assay. In addition, the expression of DNA homologous recombination repair protein Rad51, gammaH2AX, a double strand break marker and cleaved PARP, an apoptotic cell death marker, were assessed using western immunoblotting. RESULTS: Combination treatment resulted in more cell growth inhibition, induction of apoptosis, DNA damages and double strand breaks, lower expression of Rad51, increase gammaH2AX expression and PARP cleavage. CONCLUSION: These data suggest the possibility of combining targeted therapeutic such as linifanib with veliparib to augment the inhibition of cell growth and apoptosis via synthetic lethality in HNSCC cells. Thus, it may provide a novel therapeutic strategy and improve efficacy and outcome in HNSCC.
Simple, sensitive and rapid determination of linifanib (ABT-869), a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor in rat plasma by UHPLC-MS/MS.[Pubmed:24533632]
Chem Cent J. 2014 Feb 17;8(1):13.
BACKGROUND: Linifanib (ABT-869) is an orally active receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, which simultaneously inhibits vascular endothelial and platelet derived growth factor receptor. The aim of the present study was to develop an UHPLC-MS/MS method for the quantification of linifanib in rat plasma to support the pharmacokinetic and toxicokinetic studies. RESULTS: Linifanib was separated on Acquity UPLC BEH C18 column (50 x 2.1 mm, i.d. 1.7 mum) using acetonitrile-10 mM ammonium acetate (60:40, v/v) as an isocratic mobile phase at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min with sunitinib as internal standard (IS). Detection was performed on tandem mass spectrometer using electrospray ionization source in positive mode by multiple reaction monitoring. The monitored transitions were set at m/z 376.05 > 250.97 for linifanib and m/z 399.12 >283.02 for IS, respectively. Both linifanib and IS were eluted at 0.68 and 0.44 min, respectively with a total run time of 2.0 min only. The calibration curve was found to be linear over the concentration range of 0.40-500 ng/mL. The intra- and inter-day precision value was
Linifanib (ABT-869) Potentiates the Efficacy of Chemotherapeutic Agents through the Suppression of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase-Mediated AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathways in Gastric Cancer.[Pubmed:27387652]
Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 8;6:29382.
Gastric cancer, highly dependent on tumor angiogenesis, causes uncontrolled lethality, in part due to chemoresistance. Here, we demonstrate that Linifanib (ABT-869), a novel multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, markedly augments cytotoxicity of chemotherapies in human gastric cancer. ABT-869 and chemotherapeutic agents exhibited a strong synergy to inhibit the viability of several gastric cancer cell lines, with combination index values ranging from 0.017 to 0.589. Additionally, the combination of ABT-869 and chemotherapeutic agents led to remarkable suppression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Importantly, in a preclinical gastric cancer xenograft mouse model, drug co-treatments led to increased mouse survival as well as a synergistic reduction in tumor size and the inhibition of tumor angiogenesis. Mechanistic studies further revealed that all of the co-treatments containing ABT-869 resulted in decreased activation of the VEGF receptor, the epidermal growth factor receptor and the insulin growth factor receptor. Inhibition of these receptor tyrosine kinases consequently attenuated the activation of the downstream AKT/mTOR signaling pathway both in cultured gastric cancer cells and in gastric cancer xenografts. Collectively, our findings suggest that the addition of ABT-869 to traditional chemotherapies may be a promising strategy for the treatment of human gastric cancer.
Linifanib (ABT-869) enhances radiosensitivity of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells.[Pubmed:23490884]
Oral Oncol. 2013 Jun;49(6):591-7.
OBJECTIVES: Novel targeted therapeutic strategies to overcome radio-resistance of cancer cells traditionally treated with radiation may improve patient survival with the added benefit of reduced systemic toxicity. Herein, we tested the feasibility of Linifanib (ABT-869), a multi-receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor of members of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and platelet derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor families, on radio-sensitization of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC). MATERIALS AND METHODS: UMSCC-22A and UMSCC-22B cells were treated with Linifanib and gamma-radiation response was determined. Cell viability, cytotoxicity, apoptosis induction and cell cycle distribution were examined by MTT assay, colony formation assay and flow cytometry. In addition, expression of STAT3 and downstream signaling proteins were assessed using western immunoblotting. RESULTS: Treatment with Linifanib resulted in cell growth inhibition, G2/M cell cycle arrest, induction of cell death via apoptosis, reduced phosphorylation of STAT3, which has been linked to radio-resistance, lower expression of cyclin D1, survivin and increased PARP cleavage. In addition, Linifanib overcame the radio-resistance of the cell lines and significantly enhanced radiation-induced cytotoxicity (p<0.05). CONCLUSION: These data suggest the possibility of combining targeted therapeutic such as Linifanib with radiation to enhance inhibition of cell growth and apoptosis in HNSCC cells. Thus, it may provide a novel therapeutic strategy and improve efficacy of radiation against HNSCC in the future.


