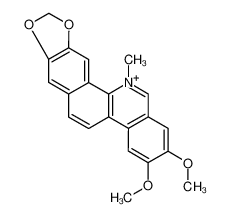
NitidineCAS# 6872-57-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 6872-57-7 | SDF | File under preparation. |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C30H48O5 | M.Wt | 488.7 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Nitidine Dilution Calculator

Nitidine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0462 mL | 10.2312 mL | 20.4625 mL | 40.9249 mL | 51.1561 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4092 mL | 2.0462 mL | 4.0925 mL | 8.185 mL | 10.2312 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2046 mL | 1.0231 mL | 2.0462 mL | 4.0925 mL | 5.1156 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0409 mL | 0.2046 mL | 0.4092 mL | 0.8185 mL | 1.0231 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0205 mL | 0.1023 mL | 0.2046 mL | 0.4092 mL | 0.5116 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- SpicatosideA
Catalog No.:BCX0951
CAS No.:128397-47-7
- Nepetin7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX0950
CAS No.:1627598-00-8
- Aromaticin
Catalog No.:BCX0949
CAS No.:5945-42-6
- Carpesiolin
Catalog No.:BCX0948
CAS No.:63568-73-0
- MangostanaxanthoneIV
Catalog No.:BCX0947
CAS No.:2182593-73-1
- GarcixanthonesB
Catalog No.:BCX0946
CAS No.:2522597-99-3
- 11-hydroxy-1-isomangostin
Catalog No.:BCX0945
CAS No.:164365-71-3
- CompoundK
Catalog No.:BCX0944
CAS No.:160729-91-9
- Lycobetaineacetate
Catalog No.:BCX0943
CAS No.:61221-41-8
- Harmalinehydrochloridedihydrate
Catalog No.:BCX0942
CAS No.:6027-98-1
- 14-hydroxylatedbrassinosteroid
Catalog No.:BCX0941
CAS No.:457603-63-3
- (S)-(-)-Norcoclaurinehydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCX0940
CAS No.:105990-27-0
- (25R)-Spirost-4-en-3,12-dion
Catalog No.:BCX0953
CAS No.:6875-60-1
- ThonningianinB
Catalog No.:BCX0954
CAS No.:271579-12-5
- Dehydroeburicoic acid monoacetate
Catalog No.:BCX0955
CAS No.:77035-42-8
- 10-Hydroxycamptothecin acetate
Catalog No.:BCX0956
CAS No.:951770-22-2
- Liquiritigenin-7-O-apiosyl(1-2)-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0957
CAS No.:135432-48-3
- Furo[3',4':6,7]naphtho[2,3-d]-1,3-dioxol-6(5aH)-one,5,8,8a,9-tetrahydro-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)- (9CI)
Catalog No.:BCX0958
CAS No.:69222-20-4
- 1,5-di-O-p-coumaroylquinicacid
Catalog No.:BCX0959
CAS No.:1239620-73-5
- 1-O-trans-caffeoyl-5-O-trans-p-coumaroylquinicacid
Catalog No.:BCX0960
CAS No.:1401532-34-0
- 1-p-coumaroyl-3-caffeoylquinicacid
Catalog No.:BCX0961
CAS No.:2459224-35-0
- IsochlorogenicacidA 3,5-Dicaffeoylquinicacid
Catalog No.:BCX0962
CAS No.:89919-62-0
- Glyurallin B
Catalog No.:BCX0963
CAS No.:199331-53-8
- Gancaonin L
Catalog No.:BCX0964
CAS No.:129145-50-2
The Therapeutic Potential of Four Main Compounds of Zanthoxylum nitidum (Roxb.) DC: A Comprehensive Study on Biological Processes, Anti-Inflammatory Effects, and Myocardial Toxicity.[Pubmed:38675484]
Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Apr 19;17(4):524.
Zanthoxylum nitidum (Roxb.) DC. (Z. nitidum) is a traditional Chinese medicinal plant that is indigenous to the southern regions of China. Previous research has provided evidence of the significant anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and anticancer properties exhibited by Z. nitidum. The potential therapeutic effects and cardiac toxicity of Z. nitidum remain uncertain. The aim of this research was to investigate the potential therapeutic properties of the four main compounds of Z. nitidum in cardiovascular diseases, their impact on the electrical activity of cardiomyocytes, and the underlying mechanism of their anti-inflammatory effects. We selected the four compounds from Z. nitidum with a high concentration and specific biological activity: Nitidine chloride (NC), chelerythrine chloride (CHE), magnoflorine chloride (MAG), and hesperidin (HE). A proteomic analysis was conducted on the myocardial tissues of beagle dogs following the administration of NC to investigate the role of NC in vivo and the associated biological processes. A bioinformatic analysis was used to predict the in vivo biological processes that MAG, CHE, and HE were involved in. Molecular docking was used to simulate the binding between compounds and their targets. The effect of the compounds on ion channels in cardiomyocytes was evaluated through a patch clamp experiment. Organ-on-a-chip (OOC) technology was developed to mimic the physiological conditions of the heart in vivo. Proteomic and bioinformatic analyses demonstrated that the four compounds of Z. nitidum are extensively involved in various cardiovascular-related biological pathways. The findings from the patch clamp experiments indicate that NC, CHE, MAG, and HE elicit a distinct activation or inhibition of the I(K1) and I(Ca-L) in cardiomyocytes. Finally, the anti-inflammatory effects of the compounds on cardiomyocytes were verified using OOC technology. NC, CHE, MAG, and HE demonstrate anti-inflammatory effects through their specific interactions with prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (PTGS2) and significantly influence ion channels in cardiomyocytes. Our study provides a foundation for utilizing NC, CHE, MAG, and HE in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Dual-Stimuli-Responsive Gut Microbiota-Targeting Nitidine Chloride-CS/PT-NPs Improved Metabolic Status in NAFLD.[Pubmed:38476281]
Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Mar 8;19:2409-2428.
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Nitidine chloride (NC) is a botanical drug renowned for its potent anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, and hepatocellular carcinoma-inhibiting properties; however, its limited solubility poses challenges to its development and application. To address this issue, we have devised a colon-targeted delivery system (NC-CS/PT-NPs) aimed at modulating the dysbiosis of the gut microbiota by augmenting the interaction between NC and the intestinal microbiota, thereby exerting an effect against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. METHODS: The NC-CS/PT-NPs were synthesized using the ion gel method. Subsequently, the particle size distribution, morphology, drug loading efficiency, and release behavior of the NC-CS/PT-NPs were characterized. Furthermore, the impact of NC-CS/PT-NPs on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) induced by a high-fat diet (HFD) in mice was investigated through serum biochemical analysis, ELISA, and histochemical staining. Additionally, the influence of NC-CS/PT-NPs on intestinal microbiota was analyzed using 16S rDNA gene sequencing. RESULTS: The nanoparticles prepared in this study have an average particle size of (255.9+/-5.10) nm, with an encapsulation rate of (72.83+/-2.13) % and a drug loading of (4.65+/-0.44) %. In vitro release experiments demonstrated that the cumulative release rate in the stomach and small intestine was lower than 22.0%, while it reached 66.75% in the colon. In vivo experiments conducted on HFD-induced NAFLD mice showed that treatment with NC-CS/PT-NPs inhibited weight gain, decreased serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST), Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and lipid levels, improved liver and intestinal inflammation, and altered the diversity of gut microbiota in mice. CONCLUSION: This study provides new evidence for the treatment of NAFLD through the regulation of gut microbiota using active ingredients from traditional Chinese medicine.
Nitidine chloride inhibits G2/M phase by regulating the p53/14-3-3 Sigma/CDK1 axis for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment.[Pubmed:38283241]
Heliyon. 2024 Jan 3;10(1):e24012.
BACKGROUND: Liver cancer had become the sixth most common cancer. Nitidine chloride (NC) has demonstrated promising anti-HCC properties; however, further elucidation of its mechanism of action is necessary. METHODS: The anti-HCC targets of NC were identified through the utilization of multiple databases and ChIPs data analysis. The GO and KEGG analyses to determine the specific pathway affected by NC. The Huh 7 and Hep G2 cells were subjected to a 24-h treatment with NC, followed by evaluating the impact of NC on cell proliferation and cell cycle. The involvement of the p53/14-3-3 Sigma/CDK1 axis in HCC cells was confirmed by qPCR and WB analysis of the corresponding genes and proteins. RESULTS: The GO and KEGG analysis showed the targets were related to cell cycle and p53 signaling pathways. In vitro experiments showed that NC significantly inhibited the proliferation of HCC cells and induced G2/M phase arrest. In addition, qPCR and WB experiments showed that the expression of p53 in HCC cells increased after NC intervention, while the expression of 14-3-3 Sigma and CDK1 decreased. CONCLUSION: NC can inhibit the proliferation of HCC cells and induce G2/M cell cycle arrest, potentially by regulating the p53/14-3-3 Sigma/CDK1 axis.
Quantification and discovery of quality markers from Toddalia asiatica by UHPLC-MS/MS coupled with chemometrics.[Pubmed:38191127]
Phytochem Anal. 2024 Jan 8.
INTRODUCTION: Toddalia asiatica (TA) is a classical traditional Chinese medicine used to treat rheumatoid arthritis and contusions. However, research regarding TA quality control is currently limited. OBJECTIVE: We aimed to establish a strategy for identifying quality markers that can be used for the evaluation of the quality of TA. METHOD: A rapid and efficient ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) method was developed for the quantitative determination of 19 compounds in TA from different regions. Then, the extraction process of TA was successively optimized by single-factor optimization and response surface methodology. Moreover, chemometrics was employed to confirm the correlation between quality and target compounds. RESULTS: Utilizing the UHPLC-MS/MS method, separation of the 19 bioactive compounds was achieved within 14 min. The method was validated in terms of linearity (r(2) > 0.9982), precision (0.08%-3.70%), repeatability (0.50%-2.54%), stability (2.26%-5.46%), and recovery (95.8%-113%). The optimal extraction process (extraction solvent, 65% ethanol aqueous solution; solid-liquid ratio, 1:20; extraction time, 25 min) was determined with the total content of 19 bioactive compounds as indicator. Significant disparities were observed in the contents of target compounds across different batches of TA. Besides, all samples could be categorized into two distinct groups, and magnoflorine, (-)-lyoniresinol, Nitidine chloride, norbraylin, skimmianine, and decarine were identified as quality markers. CONCLUSION: In the present study, we developed a strategy to improve the quality control of TA. In consideration of the pharmacodynamic activity and statistical differences, six compounds are proposed as quality markers for TA.
Comparison of the bioactive components and antioxidant activities of wild-type Zanthoxylum nitidum roots from various regions of Southern China.[Pubmed:37990844]
Nat Prod Res. 2023 Nov 22:1-12.
Zanthoxylum nitidum is a traditional Chinese herb, but limited information is available concerning its antioxidant activity of Z. nitidum. In this study, the bioactive components, content, and antioxidant activity of Z. nitidum roots from various regions in southern China were detected and evaluated. The results revealed that the highest Nitidine chloride content found in S13. The S1 contained significantly higher concentrations of hesperidin, total flavonoids, and total phenols than other samples. The samples from S13, S1, and S12 had the strongest comprehensive antioxidant activity. Stoichiometric analysis revealed that samples from various regions were effectively identified and classified. This is the first study to investigate the antioxidant activity of wild-type Z. nitidum in southern China. It lays the groundwork for Z. nitidum harvesting, origin identification, sensible use, as well as the quality evaluation of Z. nitidum resources, particularly in vitro antioxidant activity assessment.
Benzophenanthridine Alkaloid Chelerythrine Elicits Necroptosis of Gastric Cancer Cells via Selective Conjugation at the Redox Hyperreactive C-Terminal Sec(498) Residue of Cytosolic Selenoprotein Thioredoxin Reductase.[Pubmed:37836684]
Molecules. 2023 Sep 28;28(19):6842.
Targeting thioredoxin reductase (TXNRD) with low-weight molecules is emerging as a high-efficacy anti-cancer strategy in chemotherapy. Sanguinarine has been reported to inhibit the activity of TXNRD1, indicating that benzophenanthridine alkaloid is a fascinating chemical entity in the field of TXNRD1 inhibitors. In this study, the inhibition of three benzophenanthridine alkaloids, including chelerythrine, sanguinarine, and Nitidine, on recombinant TXNRD1 was investigated, and their anti-cancer mechanisms were revealed using three gastric cancer cell lines. Chelerythrine and sanguinarine are more potent inhibitors of TXNRD1 than Nitidine, and the inhibitory effects take place in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Site-directed mutagenesis of TXNRD1 and in vitro inhibition analysis proved that chelerythrine or sanguinarine is primarily bound to the Sec(498) residue of the enzyme, but the neighboring Cys(497) and remaining N-terminal redox-active cysteines could also be modified after the conjugation of Sec(498). With high similarity to sanguinarine, chelerythrine exhibited cytotoxic effects on multiple gastric cancer cell lines and suppressed the proliferation of tumor spheroids derived from NCI-N87 cells. Chelerythrine elevated cellular levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Moreover, the ROS induced by chelerythrine could be completely suppressed by the addition of N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC), and the same is true for sanguinarine. Notably, Nec-1, an RIPK1 inhibitor, rescued the chelerythrine-induced rapid cell death, indicating that chelerythrine triggers necroptosis in gastric cancer cells. Taken together, this study demonstrates that chelerythrine is a novel inhibitor of TXNRD1 by targeting Sec(498) and possessing high anti-tumor properties on multiple gastric cancer cell lines by eliciting necroptosis.
Natural plant resource flavonoids as potential therapeutic drugs for pulmonary fibrosis.[Pubmed:37664726]
Heliyon. 2023 Aug 20;9(8):e19308.
Pulmonary fibrosis is an enduring and advancing pulmonary interstitial disease caused by multiple factors that ultimately lead to structural changes in normal lung tissue. Currently, pulmonary fibrosis is a global disease with a high degree of heterogeneity and mortality rate. Nitidine and pirfenidone have been approved for treating pulmonary fibrosis, and the quest for effective therapeutic drugs remains unabated. In recent years, the anti-pulmonary fibrosis properties of natural flavonoids have garnered heightened attention, although further research is needed. In this paper, the resources, structural characteristics, anti-pulmonary fibrosis properties and mechanisms of natural flavonoids were reviewed. We hope to provide potential opportunities for the application of flavonoids in the fight against pulmonary fibrosis.
Nitidine Chloride Triggers Autophagy and Apoptosis of Ovarian Cancer Cells through Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway.[Pubmed:37317923]
Curr Pharm Des. 2023;29(19):1524-1534.
OBJECTIVE: Ovarian cancer (OC) is the eighth most common cancer with high mortality in women worldwide. Currently, compounds derived from Chinese herbal medicine have provided a new angle for OC treatment. METHODS: In this study, the cell proliferation and migration of ovarian cancer A2780/SKOV3 cells were inhibited after being treated with Nitidine chloride (NC) by using MTT and Wound-Healing Assay. Flow cytometry analysis indicated NC-induced apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells, and AO and MDC staining showed that NC treatment induced the appearance of autophagosomes and autophagic lysosomes in ovarian cancer cells. RESULTS: Through the autophagy inhibition experiment of chloroquine, it was proved that NC significantly further promoted apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells. Furthermore, NC proved that it could significantly decrease the expression of autophagy-related genes such as Akt, mTOR, P85 S6K, P70 S6K, and 4E-BP1. CONCLUSION: Therefore, we suggest that NC could trigger autophagy and apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells through Akt/mTOR signaling pathway, and NC may potentially be a target for chemotherapy against ovarian cancer.
Oplodiol and nitidine as potential inhibitors of Plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase: insights from a computational study.[Pubmed:37194452]
J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024 Feb-Mar;42(4):1655-1669.
Many natural products have been shown to possess antiplasmodial activities, but their protein targets are unknown. This work employed molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations to explore the inhibitory activity of some antiplasmodial natural products against wild-type and mutant strains of Plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase (PfDHFR). From the molecular docking study, 6 ligands preferentially bind at the active site of the DHFR domain with binding energies ranging from -6.4 to -9.5 kcal/mol. Interactions of compounds with MET55 and PHE58 were mostly observed in the molecular docking study. From the molecular dynamics study, the binding of 2 of the ligands-Nitidine and oplodiol-was observed to be stable against all tested strains of PfDHFR. The average binding free energy of oplodiol in complex with the various PfDHFR strains was -93.701 kJ/mol whereas that of Nitidine was -106.206 kJ/mol. The impressive in silico activities of the 2 compounds suggest they could be considered for development as potential antifolate agents.Communicated by Ramaswamy H. Sarma.
Comparison of the Ways in Which Nitidine Chloride and Bufalin Induce Programmed Cell Death in Hematological Tumor Cells.[Pubmed:37086379]
Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023 Dec;195(12):7755-7765.
The objective of this work to study the programmed cell death (PCD) in hematological tumor cells induced by Nitidine chloride (NC) and bufalin (BF). Hematological tumor cells were exposed to various doses of NC and BF to measure the level of growth inhibition. While inverted microscope is used to observe cell morphology, western blot technique is used to detect apoptosis-related protein expression levels. The effects of NC and BF on hematological tumor cells were different. Although abnormal cell morphology could be seen under the inverted microscope, the western blot results showed that the two medicines induced PCD through different pathways. Drug resistance varied in intensity across distinct cells. THP-1, Jurkat, and RPMI-8226 each had half maximum inhibitory concentrations (IC50) of 36.23 nM, 26.71 nM, and 40.46 nM in BF, and 9.24 microM, 4.33 microM, and 28.18 microM in NC, respectively. Different hematopoietic malignancy cells exhibit varying degrees of drug resistance, and the mechanisms by which apoptosis of hematologic tumor cells is triggered by NC and BF are also distinct.
Targeting ABCB6 with nitidine chloride inhibits PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to promote ferroptosis in multiple myeloma.[Pubmed:37044150]
Free Radic Biol Med. 2023 Jul;203:86-101.
Since multiple myeloma (MM) remains a cureless malignancy of plasma cells to date, it becomes imperative to develop novel drugs and therapeutic targets for MM. We screened a small molecule library comprising 3633 natural product drugs, which demonstrated that Nitidine Chloride (NC), an extract from traditional Chinese medicine Zanthoxylum nitidum. We used Surface Plasmon Resonance-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Protein Mass Spectrometry (SPR-HPLC-MS), Cellular Thermal Shift Assay (CETSA), molecular docking, and SPR assay to identify the potential targets of NC, in which ABCB6 was the unique target of NC. The effects of ABCB6 on cellular proliferation and drug resistance were determined by CCK8, western blot, flow cytometry, site-mutation cells, transmission electron microscopy, immunohistochemistry staining and xenograft model in vitro and in vivo. NC induced MM cell death by promoting ferroptosis. ABCB6 is the direct target of NC. ABCB6 expression was increased in MM samples compared to normal controls, which was significantly associated with MM relapse and poor outcomes. VGSK was the inferred binding epitope of NC on the ABCB6 protein. In the ABCB6-mutated MM cells, NC did not display cancer resistance, implying the vital role of ABCB6 in NC's bioactivity. Moreover, the silencing of ABCB6 significantly inhibited MM cell growth. Mechanistically, the direct binding of NC to ABCB6 suppressed PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to promote ferroptosis. In conclusion, ABCB6 can be a potential therapeutic target and prognostic biomarker in MM, while NC can be considered a novel drug for MM treatment.
Nitidine chloride regulates cell function of bladder cancer in vitro through downregulating Lymphocyte antigen 75.[Pubmed:36914902]
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Sep;396(9):2071-2085.
Nitidine chloride (NC) is effective on cancer in many tumors, but its effect on bladder cancer (BC) is unknown. We conducted cell function experiments to verify the antineoplastic effect of NC on BC cell lines (5637, T24, and UM-UC-3) in vitro. Then, mRNAs of NC-treated and NC-untreated BC cells were extracted for mRNA sequencing. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs), expression analysis, and drug molecular docking were conducted to discover the target gene of NC. Finally, functional enrichment was analyzed to explore the underlying mechanisms. NC dramatically inhibited proliferation, migration, and invasion, and it induced apoptosis and arrested the S and G2/M phases of BC cell lines. Lymphocyte antigen 75 (LY75) appeared to be the target of NC. LY75 was highly expressed and had the ability to distinguish BC tissue from non-cancerous tissue. Then, drug molecular docking confirmed the targeting relationship between NC and LY75. Gene enrichment analysis showed that the downregulated genes, after being treated with NC, were mainly enriched in pathways relevant to cell pathophysiological processes. NC inhibits BC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, induces apoptosis, and arrests cell cycles by downregulating the expression of LY75. This study provides molecular and theoretical bases for NC treatment of BC.
Disruption of Biofilm Formation and Quorum Sensing in Pathogenic Bacteria by Compounds from Zanthoxylum Gilletti (De Wild) P.G. Waterman.[Pubmed:36811771]
Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023 Oct;195(10):6113-6131.
Microbial resistance is facilitated by biofilm formation and quorum-sensing mediated processes. In this work, the stem bark (ZM) and fruit extracts (ZMFT) of Zanthoxylum gilletii were subjected to column chromatography and afforded lupeol (1), 2,3-epoxy-6,7-methylenedioxyconiferyl alcohol (3), Nitidine chloride (4), Nitidine (7), sucrose (6) and sitosterol-beta-D-glucopyranoside (2). The compounds were characterized using MS and NMR spectral data. The samples were evaluated for antimicrobial, antibiofilm and anti-quorum sensing activities. Highest antimicrobial activity was exhibited by compounds 3, 4 and 7 against Staphylococcus aureus (MIC 200 microg/mL), compounds 3 and 4 against Escherichia coli (MIC = 100 microg/mL) and compounds 4 and 7 against Candida albicans (MIC = 50 microg/mL). At MIC and sub-MIC concentrations, all samples inhibited biofilm formation by pathogens and violacein production in C. violaceum CV12472 except compound 6. Good disruption of QS-sensing in C. violaceum revealed by inhibition zone diameters were exhibited by compounds 3 (11.5 +/- 0.5 mm), 4 (12.5 +/- 1.5 mm), 5 (15.0 +/- 0.8 mm), 7 (12.0 +/- 1.5 mm) as well as the crude extracts from stem barks (16.5 +/- 1.2 mm) and seeds (13.0 +/- 1.4 mm). The profound inhibition of quorum sensing mediated processes in test pathogens by compounds 3, 4, 5 and 7 suggests the methylenedioxy- group that these compounds possess as the possible pharmacophore.
Deciphering the role of Hippo pathway in lung cancer.[Pubmed:36736143]
Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Mar;243:154339.
Hippo pathway has been initially recognized as a regulatory mechanism for modulation of organ size in fruitfly. Subsequently, its involvement in the regulation of homeostasis and tumorigenesis has been identified. This pathway contains some tumor suppressor genes such as hippo (hpo) and warts (wts), as well as a number of oncogenic ones such as yorkie (yki). Recent studies have shown participation of Hippo pathway in the lung carcinogenesis. This pathway can affect lung cancer via different mechanisms. The interaction between some miRNAs and Hippo pathway is a possible mechanism for carcinogenic processes. Moreover, some other types of non-coding RNAs including PVT1, SFTA1P, NSCLCAT1 and circ_0067741 are implicated in this process. Besides, anti-cancer effects of gallic acid, icotinib hydrochloride, curcumin, ginsenoside Rg3, cryptotanshinone, Nitidine chloride, cucurbitacin E, erlotinib, verteporfin, sophoridine, cisplatin and verteporfin in lung cancer are mediated through modulation of Hippo pathway. Here, we summarize the results of recent studies that investigated the role of Hippo signaling in the progression of lung cancer, the impact of non-coding RNAs on this pathway and the effects of anti-cancer agents on Hippo signaling in the context of lung cancer.
A vortex-enhanced magnetic solid phase extraction for the selective enrichment of four quaternary ammonium alkaloids from Zanthoxyli Radix.[Pubmed:36716512]
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2023 Feb 15;1217:123617.
Zanthoxyli Radix, the dried root of Zanthozylum nitidum (Roxb.) DC, one of traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs), exhibits various pharmacological activities such as anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, analgesic activity. A sustainable vortex-enhanced magnetic solid phase extraction (VE-MSPE) method combined with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) was established to enrich and analyze the bioactive quaternary ammonium alkaloids (QAAs) of Zanthoxyli Radix. Fe(3)O(4)@C@CMCS magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) was first synthesized for selectively adsorbing target QAAs (magnolinine, sanguinarine, Nitidine chloride and chelerythrine), which possess excellent adsorption performance after being reused 10 times. The results revealed that the great adsorption rate of Fe(3)O(4)@C@CMCS MNPs for the four QAAs could reach 55.1-78.7 %. In addition, a reliable linear relationship (r >/= 0.9995) and good recovery (97.5-104 %) was obtained. Consequently, the VE-MSPE method applying Fe(3)O(4)@C@CMCS MNPs as a sustainable adsorbent exhibited great potential in the selective enrichment of QAAs in TCM.


