Phoyunnanin ECAS# 886747-60-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 886747-60-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Brown powder |
| Formula | C30H26O6 | M.Wt | 482.5 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Phoyunnanin E Dilution Calculator

Phoyunnanin E Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0725 mL | 10.3627 mL | 20.7254 mL | 41.4508 mL | 51.8135 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4145 mL | 2.0725 mL | 4.1451 mL | 8.2902 mL | 10.3627 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2073 mL | 1.0363 mL | 2.0725 mL | 4.1451 mL | 5.1813 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0415 mL | 0.2073 mL | 0.4145 mL | 0.829 mL | 1.0363 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0207 mL | 0.1036 mL | 0.2073 mL | 0.4145 mL | 0.5181 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Leeaoside
Catalog No.:BCN9323
CAS No.:1015063-56-5
- Hymexelsin
Catalog No.:BCN9322
CAS No.:117842-09-8
- Giffonin P
Catalog No.:BCN9321
CAS No.:1830306-93-8
- Dicliripariside A
Catalog No.:BCN9320
CAS No.:491613-65-1
- Jinflexin D
Catalog No.:BCN9319
CAS No.:2055155-78-5
- 10-Hydroxyligstroside
Catalog No.:BCN9318
CAS No.:35897-94-0
- 3-epi-Isocucurbitacin B
Catalog No.:BCN9317
CAS No.:89647-62-1
- Flazin
Catalog No.:BCN9316
CAS No.:100041-05-2
- 10-Hydroxymajoroside
Catalog No.:BCN9315
CAS No.:259753-12-3
- Aspyridone A
Catalog No.:BCN9314
CAS No.:935863-26-6
- 2,3-Dimethoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN9313
CAS No.:42833-49-8
- Hydroxytyrosol 4-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9312
CAS No.:54695-80-6
- Icterogenin
Catalog No.:BCN9325
CAS No.:561-47-7
- 4a-Demethoxysampsone B
Catalog No.:BCN9326
CAS No.:1292798-98-1
- Cucurbitacin A 2-O-β-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN9327
CAS No.:1135141-76-2
- Lantanilic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9328
CAS No.:60657-41-2
- Methyl lucidenate E2
Catalog No.:BCN9329
CAS No.:98665-12-4
- Hancokinol
Catalog No.:BCN9330
CAS No.:132294-77-0
- 7β-Hydroxycucurbitacin B
Catalog No.:BCN9331
CAS No.:1135141-79-5
- 3α,30-Diacetoxy-12α-hydroxy-23-oxoeupha-7,24-dien-21,16β-olid-28-oic acid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN9332
CAS No.:215160-96-6
- Sampsone B
Catalog No.:BCN9333
CAS No.:1309125-17-4
- Aureusidin
Catalog No.:BCN9334
CAS No.:38216-54-5
- Thymol isobutyrate
Catalog No.:BCN9335
CAS No.:5451-67-2
- 1-Methyleffusol
Catalog No.:BCN9336
CAS No.:144106-78-5
Phoyunnanin E Induces Apoptosis of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells via p53 Activation and Down-regulation of Survivin.[Pubmed:30396948]
Anticancer Res. 2018 Nov;38(11):6281-6290.
BACKGROUND/AIM: Lung cancer is by far the most common cause of cancer mortality, accounting for nearly 20% of all global cancer deaths. Therefore, potent and effective compounds for treatment of this cancer type are essential. Phoyunnanin E, isolated from Dendrobium venustum (Orchidaceae), has promising pharmacological activities; however, it is unknown if Phoyunnanin E affects apoptosis of lung cancer cells. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The apoptosis-inducing activity of Phoyunnanin E on H460 lung cancer cells was investigated by Hoechst 33342, and annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate/propidium iodide staining. The underlying mechanism was determined via monitoring apoptosis-regulatory proteins by western blot analysis. The apoptotic effect of the compound was confirmed in H23 lung cancer cells. RESULTS: Phoyunnanin E significantly induced apoptotic cell death of H460 lung cancer cells, as indicated by condensed and fragmented nuclei with the activation of caspase-3 and -9 and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage. Phoyunnanin E mediated apoptosis via a p53-dependent pathway by increasing the accumulation of cellular p53 protein. As a consequence, anti-apoptotic proteins including induced myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein (MCL1) and B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2) were found to be significantly depleted, while pro-apoptotic BCL-2-associated X protein (BAX) protein was up-regulated. Furthermore, it was found that expression of an inhibitor of apoptosis, survivin, markedly reduced in response to Phoyunnanin E treatment. The apoptosis-inducting effect was also found in Phoyunnanin E-treated H23 lung cancer cells. CONCLUSION: These results indicate the promising effect of Phoyunnanin E in induction of apoptosis, that may be useful for the development of novel anticancer agents.
Phoyunnanin E inhibits migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells via suppression of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and integrin alphav and integrin beta3.[Pubmed:29284478]
BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Dec 29;17(1):553.
BACKGROUND: The conversion of the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells into cells with a mesenchymal phenotype-so-called epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-has been shown to enhance the capacity of the cells to disseminate throughout the body. EMT is therefore becoming a potential target for anti-cancer drug discovery. Here, we showed that Phoyunnanin E, a compound isolated from Dendrobium venustum, possesses anti-migration activity and addressed its mechanism of action. METHODS: The cytotoxic and proliferative effects of Phoyunnanin E on human non-small cell lung cancer-derived H460, H292, and A549 cells and human keratinocyte HaCaT cells were investigated by MTT assay. The effect of Phoyunnanin E on EMT was evaluated by determining the colony formation and EMT markers. The migration and invasion of H460, H292, A549 and HaCaT cells was evaluated by wound healing assay and transwell invasion assay, respectively. EMT markers, integrins and migration-associated proteins were examined by western blot analysis. RESULTS: Phoyunnanin E at the concentrations of 5 and 10 muM, which are non-toxic to H460, H292, A549 and HaCaT cells showed good potential to inhibit the migratory activity of three types of human lung cancer cells. The anti-migration effect of Phoyunnanin E was shown to relate to the suppressed EMT phenotypes, including growth in anchorage-independent condition, cell motility, and EMT-specific protein markers (N-cadherin, vimentin, slug, and snail). In addition to EMT suppression, we found that Phoyunnanin E treatment with 5 and 10 muM could decrease the cellular level of integrin alphav and integrin beta3, these integrins are frequently up-regulated in highly metastatic tumor cells. We further characterized the regulatory proteins in cell migration and found that the cells treated with Phoyunnanin E exhibited a significantly lower level of phosphorylated focal adhesion kinase (p-FAK) and phosphorylated ATP-dependent tyrosine kinase (p-AKT), and their downstream effectors (including Ras-related C3 botulinum (Rac-GTP); Cell division cycle 42 (Cdc42); and Ras homolog gene family, member A (Rho-GTP)) in comparison to those of the non-treated control. CONCLUSIONS: We have determined for the first time that Phoyunnanin E could inhibit the motility of lung cancer cells via the suppression of EMT and metastasis-related integrins. This new information could support further development of this compound for anti-metastasis approaches.
Chemical constituents of Dendrobium venustum and their antimalarial and anti-herpetic properties.[Pubmed:25115090]
Nat Prod Commun. 2014 Jun;9(6):825-7.
A MeOH extract from the whole plant Dendrobium venustum exhibited significant antimalarial and anti-herpetic activities. Bioassay-guided isolation of the plant extract resulted in the isolation of seven known phenolic compounds. Densiflorol B (3) and Phoyunnanin E (6) showed the strongest antimalarial activity and a high selectivity index, whereas gigantol (2), batatasin III (5) and phoyunnanin C (7) exhibited moderate activity. Compounds 2 and 5 also showed weak activity against the Herpes simplex virus. This study is the first report on the chemical and biological activities of D. venustum.
New stilbenoids from Pholidota yunnanensis and their inhibitory effects on nitric oxide production.[Pubmed:16394543]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2006 Jan;54(1):21-5.
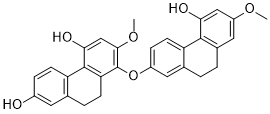
Six new stilbenoids, a (bibenzyldihydrophenanthrene) ether designated phoyunnanin D (1), a bis(dihydrophenanthrene) ether designated Phoyunnanin E (2), and four stilbenes designated phoyunbene A-D (3-6), were isolated from the air-dried whole plant of Pholidota yunnanensis ROLFE. The new compounds were identified as 7-[2-(3-hydroxyphenethyl)-4-hydroxy-6-methoxyphenoxy]-4-hydroxy-2-methoxy-9,10-di hydrophenanthrene (1), 1-[(9,10-dihydro-4-hydroxy-2-methoxy-7-phenanthrenyl)oxy]-4,7-dihydroxy-2-methoxy -9,10-dihydrophenanthrene (2), trans-3,3'-dihydroxy-2',4',5-trimethoxystilbene (3), trans-3,4'-dihydroxy-2',3',5-trimethoxystilbene (4), trans-3,3'-dihydroxy-2',5-dimethoxystilbene (5), and trans-3-hydroxy-2',3',5-trimethoxystilbene (6) based on spectroscopic evidence. Furthermore, the inhibitory effects of compounds 1-6 on nitric oxide production in a murine macrophage-like cell line (RAW 264.7) activated by lipopolysaccharide and interferon-gamma were examined.


