Pterosin ACAS# 35910-16-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 35910-16-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 135017 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H20O3 | M.Wt | 248.3 |
| Type of Compound | Sesquiterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
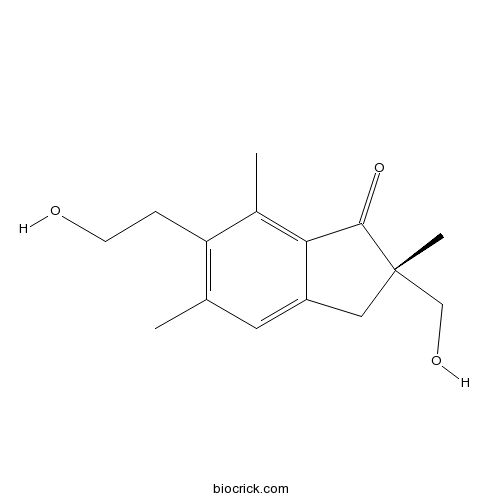
| Chemical Name | (2S)-6-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2,5,7-trimethyl-3H-inden-1-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(=C2C(=C1)CC(C2=O)(C)CO)C)CCO | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BDZJLPDYMKPKGC-HNNXBMFYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H20O3/c1-9-6-11-7-15(3,8-17)14(18)13(11)10(2)12(9)4-5-16/h6,16-17H,4-5,7-8H2,1-3H3/t15-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Pterosin A is a novel activator of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase, which is crucial for regulating blood glucose homeostasis, 2. Pterosin A has potential anti-diabetic activity, it can significantly reverse the increased serum insulin and insulin resistance (IR) in dexamethasone-IR mice and in db/db mice. |
| Targets | ROS | GLUT | AMPK | Akt | p38MAPK | GSK-3 |

Pterosin A Dilution Calculator

Pterosin A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.0274 mL | 20.1369 mL | 40.2739 mL | 80.5477 mL | 100.6847 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8055 mL | 4.0274 mL | 8.0548 mL | 16.1095 mL | 20.1369 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4027 mL | 2.0137 mL | 4.0274 mL | 8.0548 mL | 10.0685 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0805 mL | 0.4027 mL | 0.8055 mL | 1.611 mL | 2.0137 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0403 mL | 0.2014 mL | 0.4027 mL | 0.8055 mL | 1.0068 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Pteroside A
Catalog No.:BCN8146
CAS No.:35910-15-7
- 3,3-Dimethoxy-5α-androstan-17-one
Catalog No.:BCC8594
CAS No.:3591-19-3
- Onjisaponin B
Catalog No.:BCN2741
CAS No.:35906-36-6
- Boc-His(Tos)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3402
CAS No.:35899-43-5
- Ligustroside
Catalog No.:BCN5310
CAS No.:35897-92-8
- Boc-Arg-OH.HCl.H2O
Catalog No.:BCC3053
CAS No.:35897-34-8
- Vestitol
Catalog No.:BCN5309
CAS No.:35878-41-2
- Novokinin
Catalog No.:BCC6051
CAS No.:358738-77-9
- Apocynol A
Catalog No.:BCN4642
CAS No.:358721-33-2
- H-Trp-OBzl.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3113
CAS No.:35858-81-2
- Etazolate hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6648
CAS No.:35838-58-5
- 3-Epicabraleahydroxylactone
Catalog No.:BCN5308
CAS No.:35833-72-8
- NECA
Catalog No.:BCC5804
CAS No.:35920-39-9
- Vicenin -1
Catalog No.:BCN3012
CAS No.:35927-38-9
- Pterosin C
Catalog No.:BCN7104
CAS No.:35938-43-3
- Triciribine
Catalog No.:BCC3872
CAS No.:35943-35-2
- Pteroside D
Catalog No.:BCN5311
CAS No.:35943-38-5
- Anchustrigosine
Catalog No.:BCC8185
CAS No.:
- 3-Hydroxy-11-ursen-28,13-olide
Catalog No.:BCN5312
CAS No.:35959-05-8
- 3-Acetoxy-11-ursen-28,13-olide
Catalog No.:BCN5313
CAS No.:35959-08-1
- Inotodiol
Catalog No.:BCN3331
CAS No.:35963-37-2
- Triptotin F
Catalog No.:BCN3482
CAS No.:359630-36-7
- Pterosin G
Catalog No.:BCN8148
CAS No.:35964-50-2
- 3,6-Ditigloyloxynortropane
Catalog No.:BCN1877
CAS No.:359723-70-9
Antidiabetic effects of pterosin A, a small-molecular-weight natural product, on diabetic mouse models.[Pubmed:23069626]
Diabetes. 2013 Feb;62(2):628-38.
The therapeutic effect of Pterosin A, a small-molecular-weight natural product, on diabetes was investigated. Pterosin A, administered orally for 4 weeks, effectively improved hyperglycemia and glucose intolerance in streptozotocin, high-fat diet-fed, and db/db diabetic mice. There were no adverse effects in normal or diabetic mice treated with Pterosin A for 4 weeks. Pterosin A significantly reversed the increased serum insulin and insulin resistance (IR) in dexamethasone-IR mice and in db/db mice. Pterosin A significantly reversed the reduced muscle GLUT-4 translocation and the increased liver phosphoenolpyruvate carboxyl kinase (PEPCK) expression in diabetic mice. Pterosin A also significantly reversed the decreased phosphorylations of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and Akt in muscles of diabetic mice. The decreased AMPK phosphorylation and increased p38 phosphorylation in livers of db/db mice were effectively reversed by Pterosin A. Pterosin A enhanced glucose uptake and AMPK phosphorylation in cultured human muscle cells. In cultured liver cells, Pterosin A inhibited inducer-enhanced PEPCK expression, triggered the phosphorylations of AMPK, acetyl CoA carboxylase, and glycogen synthase kinase-3, decreased glycogen synthase phosphorylation, and increased the intracellular glycogen level. These findings indicate that Pterosin A may be a potential therapeutic option for diabetes.
Chemical constituents analysis and antidiabetic activity validation of four fern species from Taiwan.[Pubmed:25622260]
Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jan 22;16(2):2497-516.
Pterosins are abundant in ferns, and Pterosin A was considered a novel activator of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase, which is crucial for regulating blood glucose homeostasis. However, the distribution of pterosins in different species of ferns from various places in Taiwan is currently unclear. To address this question, the distribution of pterosins, glucose-uptake efficiency, and protective effects of Pterosin A on beta-cells were examined. Our results showed that three novel compounds, 13-chloro-spelosin 3-O-beta-d-glucopyranoside (1), (3R)-Pterosin D 3-O-beta-d-(3'-p-coumaroyl)-glucopyranoside (2), and (2R,3R)-Pterosin L 3-O-beta-d-(3'-p-coumaroyl)-glucopyranoside (3), were isolated for the first time from four fern species (Ceratopteris thalictroides, Hypolepis punctata, Nephrolepis multiflora, and Pteridium revolutum) along with 27 known compounds. We also examined the distribution of these pterosin compounds in the mentioned fern species (except N. multiflora). Although all Pterosin Analogs exhibited the same effects in glucose uptake assays, Pterosin A prevented cell death and reduced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. This paper is the first report to provide new insights into the distribution of pterosins in ferns from Taiwan. The potential anti-diabetic activity of these novel phytocompounds warrants further functional studies.


