TriciribineAkt inhibitor,highly selective CAS# 35943-35-2 |
- GDC-0068 (RG7440)
Catalog No.:BCC1271
CAS No.:1001264-89-6
- MK-2206 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1274
CAS No.:1032350-13-2
- AZD5363
Catalog No.:BCC1073
CAS No.:1143532-39-1
- A-443654
Catalog No.:BCC1321
CAS No.:552325-16-3
- AKT inhibitor VIII
Catalog No.:BCC1334
CAS No.:612847-09-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 35943-35-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 65399 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C13H16N6O4 | M.Wt | 320.3 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Triciribine, NSC 154020, TCN | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in 1eq. HCl and to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
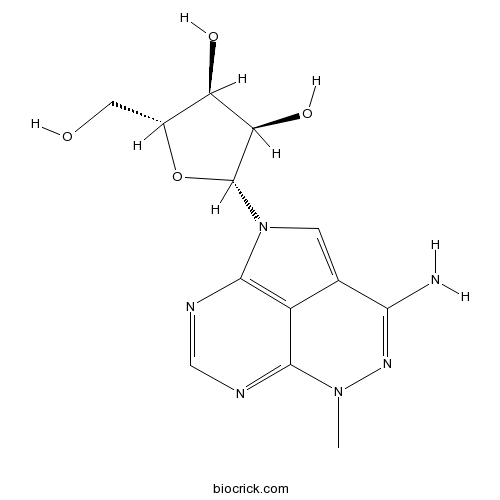
| SMILES | CN1C2=NC=NC3=C2C(=CN3C4C(C(C(O4)CO)O)O)C(=N1)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HOGVTUZUJGHKPL-HTVVRFAVSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H16N6O4/c1-18-11-7-5(10(14)17-18)2-19(12(7)16-4-15-11)13-9(22)8(21)6(3-20)23-13/h2,4,6,8-9,13,20-22H,3H2,1H3,(H2,14,17)/t6-,8-,9-,13-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective inhibitor of Akt (protein kinase B) signaling; displays minimal inhibition of PKC, PKA, SGK and p38 pathways. Inhibits phosphorylation and activation of downstream targets of Akt including Bad, GSK-3β and AFX. Induces apoptosis and growth arrest in vitro, preferentially in human cancer cells with elevated levels of Akt. Potently and selectively inhibits growth of Akt-overexpressing tumors in mice. Inhibits DNA synthesis and displays antiviral activity against HIV-1 and -2. |

Triciribine Dilution Calculator

Triciribine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1221 mL | 15.6104 mL | 31.2207 mL | 62.4415 mL | 78.0518 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6244 mL | 3.1221 mL | 6.2441 mL | 12.4883 mL | 15.6104 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3122 mL | 1.561 mL | 3.1221 mL | 6.2441 mL | 7.8052 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0624 mL | 0.3122 mL | 0.6244 mL | 1.2488 mL | 1.561 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0312 mL | 0.1561 mL | 0.3122 mL | 0.6244 mL | 0.7805 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Triciribine is an inhibitor of DNA synthesis for Akt and HIV-1 with IC50 values of 130 nM and 20 nM, respectively. [1,2]
Protein kinase B (PKB), also known as Akt, is a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase that plays a key role in multiple cellular processes such as glucose metabolism, apoptosis, cell proliferation, transcription and cell migration. Once PH domain of Akt bind phospholipids ,the activated Akt can then go on to activate or deactivate its myriad substrates via its kinase activity. e.g. Nuclear Factor-kB, Bcl-2 family proteins and murine double minute 2 (MDM2).[3] Studies show that tumor cells have constantly active Akt depending on Akt for survival [4], so Akt inhibitors may treat cancers.
Triciribine, also known as API-2, suppresses the phosphorylation level and kinase activity of Akt, result in induce apoptosis and cell growth in cancer cell. Triciribine can specifically inhibit the most common astrocytic tumor cells inhibitory efficiency was very low (13.6 mM [5] GI50). Triciribine can inhibit HIV-1, IC50 20 nM. The amount of inhibition of 0.1 M can produce >90% ratio, dosage of 5 M could completely inhibit coenocytic. In the same cell line cytotoxicity test results showed when the concentration of Triciribine for the selective index of 46 M to 2250 using HIV-1 infected CEM-SS, H9, and B and U1 persistent infection of H9III cells of p24 core antigen, Triciribine can significantly inhibit HIV-1 induced generation, reverse transcriptase and the generation of infectious virus, this inhibition is dose dependent characteristics [6]. Triciribine inhibits human prostate cancer cell line PC-3 in the Akt 308 bit acid and serine 473 phosphorylation and Akt activity. Triciribine make PC-3 cells more sensitive to apoptosis induced by TRAIL- and anti-CD95, but to DNA damage caused by chemotherapy is still resistance [7]. Triciribine also can selectively inhibit Akt1, Akt2, and Akt3 without inhibiting known upstream activators, PDK1 and PI3K, of Akt. Additionally, Triciribine has antineoplastic and antiviral activity at low micromolar and submicromolar concentrations, and has been demonstrated to inhibit incorporation of amino acids into proteins and purine nucleotide synthesis.
Reference:
1 Gursel DB, et al. “Control of proliferation in astrocytoma cells by the receptor tyrosine kinase/PI3K/AKT signaling axis and the use of PI-103 and TCN as potential anti-astrocytoma therapies”. Nero Oncol, 2011, 13(6), 610-621.
2 Kucera LS, et al, AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses, 1993, 9(4), 307-314.
3 Song G, Ouyang G, Bao S. "The activation of Akt/PKB signaling pathway and cell survival". J. Cell. Mol. Med, 2005, 9 (1): 59-71.
4 Lindhurst MJ, Sapp JC, Teer JK, Johnston JJ, Finn EM, Peters K et al. "A mosaic activating mutation in AKT1 associated with the Proteus syndrome". N. Engl. J. Med, 2011, 365 (7): 611-9.
5 Gursel DB, et al, Nero Oncol, 2011, 13(6), 610-621.
6 Dieterle A, et al, Int J Cancer , 2009, 125(4), 932-941.
7 Yang L, et al, Cancer Res, 2004, 64(13), 4394-4399.
- Pterosin C
Catalog No.:BCN7104
CAS No.:35938-43-3
- Vicenin -1
Catalog No.:BCN3012
CAS No.:35927-38-9
- NECA
Catalog No.:BCC5804
CAS No.:35920-39-9
- Pterosin A
Catalog No.:BCN8147
CAS No.:35910-16-8
- Pteroside A
Catalog No.:BCN8146
CAS No.:35910-15-7
- 3,3-Dimethoxy-5α-androstan-17-one
Catalog No.:BCC8594
CAS No.:3591-19-3
- Onjisaponin B
Catalog No.:BCN2741
CAS No.:35906-36-6
- Boc-His(Tos)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3402
CAS No.:35899-43-5
- Ligustroside
Catalog No.:BCN5310
CAS No.:35897-92-8
- Boc-Arg-OH.HCl.H2O
Catalog No.:BCC3053
CAS No.:35897-34-8
- Vestitol
Catalog No.:BCN5309
CAS No.:35878-41-2
- Novokinin
Catalog No.:BCC6051
CAS No.:358738-77-9
- Pteroside D
Catalog No.:BCN5311
CAS No.:35943-38-5
- Anchustrigosine
Catalog No.:BCC8185
CAS No.:
- 3-Hydroxy-11-ursen-28,13-olide
Catalog No.:BCN5312
CAS No.:35959-05-8
- 3-Acetoxy-11-ursen-28,13-olide
Catalog No.:BCN5313
CAS No.:35959-08-1
- Inotodiol
Catalog No.:BCN3331
CAS No.:35963-37-2
- Triptotin F
Catalog No.:BCN3482
CAS No.:359630-36-7
- Pterosin G
Catalog No.:BCN8148
CAS No.:35964-50-2
- 3,6-Ditigloyloxynortropane
Catalog No.:BCN1877
CAS No.:359723-70-9
- [Ala17]-MCH
Catalog No.:BCC6024
CAS No.:359784-84-2
- Glycodeoxycholic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7250
CAS No.:360-65-6
- Nandrolone decanoate
Catalog No.:BCC9087
CAS No.:360-70-3
- 2',4'-Dihydroxy-6'-methoxyacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN5314
CAS No.:3602-54-8
Phase I clinical, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic study of the Akt-inhibitor triciribine phosphate monohydrate in patients with advanced hematologic malignancies.[Pubmed:23993427]
Leuk Res. 2013 Nov;37(11):1461-7.
Akt, a serine/threonine protein kinase, is constitutively phosphorylated and hyperactivated in multiple cancers, including acute myeloid leukemia. High levels are linked to poor survival and inferior responses to chemotherapy, making Akt inhibition an attractive therapeutic target. In this phase I/II study of TCN-PM, a small-molecule Akt inhibitor, TCN-PM therapy was well tolerated in patients with advanced hematological malignancies, and reduced levels of phosphorylation of Akt and its substrate Bad were shown, consistent with inhibition of this survival pathway and induction of cell death. Further investigation of TCN-PM alone or in combination in patients with high Akt levels is warranted.
The Akt inhibitor, triciribine, ameliorates chronic hypoxia-induced vascular pruning and TGFbeta-induced pulmonary fibrosis.[Pubmed:26033700]
Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Aug;172(16):4173-88.
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Interstitial lung disease accounts for a group of chronic and progressive disorders associated with severe pulmonary vascular remodelling, peripheral vascular rarefaction and fibrosis, thus limiting lung function. We have previously shown that Akt is necessary for myofibroblast differentiation, a critical event in organ fibrosis. However, the contributory role of the Akt-mTOR pathway in interstitial lung disease and the therapeutic benefits of targeting Akt and mTOR remain unclear. EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH: We investigated the role of the Akt-mTOR pathway and its downstream molecular mechanisms in chronic hypoxia- and TGFbeta-induced pulmonary vascular pruning and fibrosis in mice. We also determined the therapeutic benefits of the Akt inhibitor Triciribine and the mTOR inhibitor rapamycin for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis in mice. KEY RESULTS: Akt1(-) (/) (-) mice were protected from chronic hypoxia-induced peripheral vascular pruning. In contrast, hyperactivation of Akt1 induced focal fibrosis similar to TGFbeta-induced fibrosis. Pharmacological inhibition of Akt, but not the Akt substrate mTOR, inhibited hypoxia- and TGFbeta-induced pulmonary vascular rarefaction and fibrosis. Mechanistically, we found that Akt1 modulates pulmonary remodelling via regulation of thrombospondin1 (TSP1) expression. Hypoxic Akt1(-) (/) (-) mice lungs expressed less TSP1. Moreover, TSP1(-) (/) (-) mice were resistant to adMyrAkt1-induced pulmonary fibrosis. CONCLUSIONS AND IMPLICATIONS: Our study identified Akt1 as a novel target for the treatment of interstitial lung disease and provides preclinical data on the potential benefits of the Akt inhibitor Triciribine for the treatment of interstitial lung disease.
Addition of the Akt inhibitor triciribine overcomes antibody resistance in cells from ErbB2/Neu-positive/PTEN-deficient mammary tumors.[Pubmed:24452693]
Int J Oncol. 2014 Apr;44(4):1277-83.
Trastuzumab resistance is a challenging problem in ErbB2/HER2-positive breast cancers. Multiple mechanisms of resistance have been proposed and, thus, may require the development of more personalized therapies. In this study, we report the establishment of a mouse mammary cancer cell line, designated MT104T, obtained from spontaneous tumors in genetically engineered FVB/N-ErbB2/Neu-positive-PTEN-deficient mice. The critical molecular phenotype of MT104T cells was confirmed by genotyping and western blot analysis. This cell line was tumorigenic in immunologically intact syngeneic mice, forming tumors of generally similar histology as its origin. PTEN loss led to hyperactivation of Akt and conferred resistance to anti-ErbB2/Neu antibody treatment in MT104T cells. Addition of the Akt inhibitor Triciribine (TCN) inhibited the viability of MT104T cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner as evaluated by MTT assay. ErbB2/Neu antibody and TCN combination treatment greatly induced apoptosis of MT104T cells as indicated by Annexin V-FITC staining. Moreover, this combination treatment also significantly reduced both Akt and Erk activities, which are responsible for the inhibitory effect on MT104T cells. Therefore, MT104T cells could represent an alternative model system to investigate the nature of ErbB2positive breast cancer and for the experimental therapeutics studies of this disease. Our findings also suggest that combination of TCN may be a potential strategy for the treatment of trastu-zumab-resistant breast cancer mediated by PTEN loss or PI3K hyperactivation, which may facilitate the development of more personalized therapies for breast cancer patients.
Triciribine Phosphate Monohydrate, an AKT Inhibitor, Enhances Gemcitabine Activity in Pancreatic Cancer Cells.[Pubmed:26254348]
Anticancer Res. 2015 Sep;35(9):4599-604.
BACKGROUND: Pancreatic cancer is a highly lethal cancer due to early metastasis and resistance to current chemotherapeutic agents. Abnormal protein kinase B (AKT) activation is an important mechanism of chemoresistance to gemcitabine, the most widely used agent in pancreatic cancer. MATERIAL AND METHODS: In the study, we tested the hypothesis that combining an AKT inhibitor with gemcitabine would augment anti-tumor activity. We treated human pancreatic cancer MiaPaCa-2 cells with gemcitabine and the AKT inhibitor Triciribine, alone and in combination, and evaluated treatment effects using trypan blue assay, 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5 diphenyl tetrazolium (MTT) assay, and cell death enzyme-linked immunosorbant assay. Colorimetric data of MTT assay were computationally analyzed for synergism of the combination therapy by CalcuSyn2 (Biosoft, Great Shelford, Cambridge, UK). RESULTS: Both gemcitabine and Triciribine inhibited cell growth in a dose-dependent manner. Triciribine synergistically enhanced the cytotoxic activity of gemcitabine. The combination index (CI) provides the synergistic, additive, or antagonistic effects of the two-drug combination. CI at the 50% effective dose at 1:500 ratio of gemcitabine to Triciribine was 0.74, indicating the synergistic effect of the drugs. The combination treatment with the non-apoptotic dose of each agent distinctly induced apoptosis, with gemcitabine in combination with Triciribine, synergistically inhibiting pancreatic cancer cell growth and inducing apoptosis. CONCLUSION: These findings support the use of Triciribine to overcome activated AKT-mediated resistance of pancreatic cancer to gemcitabine.
Akt/protein kinase B signaling inhibitor-2, a selective small molecule inhibitor of Akt signaling with antitumor activity in cancer cells overexpressing Akt.[Pubmed:15231645]
Cancer Res. 2004 Jul 1;64(13):4394-9.
Accumulated studies have shown that activation of the Akt pathway plays a pivotal role in malignant transformation and chemoresistance by inducing cell survival, growth, migration, and angiogenesis. Therefore, Akt is believed to be a critical target for cancer intervention. Here, we report the discovery of a small molecule Akt pathway inhibitor, Akt/protein kinase B signaling inhibitor-2 (API-2), by screening the National Cancer Institute Diversity Set. API-2 suppressed the kinase activity and phosphorylation level of Akt. The inhibition of Akt kinase resulted in suppression of cell growth and induction of apoptosis in human cancer cells that harbor constitutively activated Akt due to overexpression of Akt or other genetic alterations such as PTEN mutation. API-2 is highly selective for Akt and does not inhibit the activation of phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase, phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1, protein kinase C, serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase, protein kinase A, signal transducer and activators of transcription 3, extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2, or c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase. Furthermore, API-2 potently inhibited tumor growth in nude mice of human cancer cells in which Akt is aberrantly expressed/activated but not of those cancer cells in which it is not. These findings provide strong evidence for pharmacologically targeting Akt for anticancer drug discovery.
Phosphorylation of triciribine is necessary for activity against HIV type 1.[Pubmed:9788672]
AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1998 Oct 10;14(15):1315-22.
Triciribine (TCN) is a tricyclic nucleoside with known antineoplastic and antiviral activity. It is a potent and selective inhibitor of HIV-1 and HIV-2, including strains known to be resistant to AZT or TIBO. TCN is phosphorylated to its 5'-monophosphate (TCN-P) by intracellular adenosine kinase (AK), but is not converted to di- or triphosphates. We now report that 5'-phosphorylation is requisite for the activity of TCN against HIV-1. CEM cells incubated with TCN at concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 330 microM gave intracellular TCN-P concentrations from 27 to 775 microM, respectively. There was no difference in the amount of intracellular TCN-P detected in uninfected compared with HIV-1-infected CEM cells. The antiviral effect of TCN against HIV-1 was strongly antagonized by the AK inhibitor 5-iodotubercidin (ITu). In contrast, TCN and ITu only exhibited additive cytotoxicity. The 5'-deoxy analog of TCN, which cannot be phosphorylated, had no antiviral effect against HIV-1 at a concentration more than 100 times higher than the IC50 of TCN. Similarly, TCN was not active against HIV-1 in an AK-deficient cell line (AA-2) at concentrations shown to inhibit the virus by >95% in CEM cells. Consistent with its AK-deficient phenotype, this cell line phosphorylated TCN to only 3% of the extent observed in CEM cells. We conclude that TCN must be phosphorylated to TCN-P for activity against HIV-1.
Dual mechanisms of inhibition of DNA synthesis by triciribine.[Pubmed:2379153]
Cancer Res. 1990 Aug 15;50(16):4891-9.
The inhibition of DNA synthesis in Triciribine (TCN)-treated L1210 cells was shown to involve two mechanisms, with different concentration dependence. (a) Initiation of new replicons and possibly of Okazaki fragments was inhibited when the cells were treated with 0.1 microM TCN. The inhibition of replicon initiation was shown by the rate of alkaline elution of [3H]DNA from 15-min-[3H]thymidine-labeled cells being slower if the cells had been pretreated with TCN, indicating that the average size of actively replicating DNA strands was increased. (b) At 1 microM TCN elongation of previously initiated DNA chains was also inhibited. This conclusion was suggested by the decrease in the rate of alkaline elution of [3H]DNA, during postlabeling incubation, being less if TCN was included in the medium. The mechanism of inhibition of DNA synthesis by TCN was shown not to involve DNA strand breakage or cross-linking, inhibition of polyamine biosynthesis, inhibition of purine de novo biosynthesis, inhibition of DNA polymerase alpha or DNA primase, or inhibition of ligation of Okazaki fragments. The effects of TCN on the incorporation of [3H]thymidine into Okazaki fragments and higher molecular weight DNA suggested the possibilities of inhibition of Okazaki fragment initiation and/or DNA polymerase delta.


