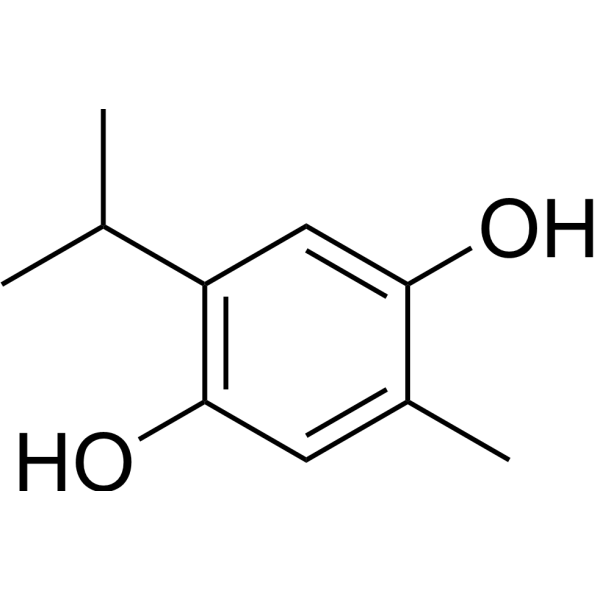
ThymohydroquinoneCAS# 2217-60-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 2217-60-9 | SDF | File under preparation. |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C10H14O2 | M.Wt | 166.22 |
| Type of Compound | Monoterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Thymoquinol,Hydrothymoquinone,4-Hydroxy-5-isopropyl-2-methylphenol,2-Methyl-5-isopropylhydroquinone,... | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Thymohydroquinone Dilution Calculator

Thymohydroquinone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.0161 mL | 30.0806 mL | 60.1612 mL | 120.3225 mL | 150.4031 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.2032 mL | 6.0161 mL | 12.0322 mL | 24.0645 mL | 30.0806 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6016 mL | 3.0081 mL | 6.0161 mL | 12.0322 mL | 15.0403 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1203 mL | 0.6016 mL | 1.2032 mL | 2.4064 mL | 3.0081 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0602 mL | 0.3008 mL | 0.6016 mL | 1.2032 mL | 1.504 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 8-O-4,8-O-4-Dehydrotriferulic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1797
CAS No.:848649-28-5
- Quercetin 3-O-(6-O-(E)-caffeoyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)-α-L-rhamnopyranoside) 7-O-α-L-rhamnopyranos...
Catalog No.:BCX1796
CAS No.:1459767-44-2
- 1,2,6-Tri-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose
Catalog No.:BCX1795
CAS No.:79886-49-0
- Dihydrodehydrodiconiferyl alcohol 9′-O-β-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX1794
CAS No.:106758-58-1
- Kingiside
Catalog No.:BCX1793
CAS No.:25406-67-1
- Ophioglonol
Catalog No.:BCX1792
CAS No.:850894-19-8
- Neochilenin
Catalog No.:BCX1791
CAS No.:22255-19-2
- Transilin
Catalog No.:BCX1790
CAS No.:26931-68-0
- Perilla ketone
Catalog No.:BCX1789
CAS No.:553-84-4
- Ketologanin
Catalog No.:BCX1788
CAS No.:152-91-0
- Pedunculosumoside F
Catalog No.:BCX1787
CAS No.:1283600-08-7
- 3-O-Methylquercetin 7-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-4′-O-β-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX1786
CAS No.:47858-32-2
- (20R,20S)-Verazine
Catalog No.:BCX1799
CAS No.:14320-81-1
- (±)-Acuminatin
Catalog No.:BCX1800
CAS No.:72881-08-4
- Kadsurenin A
Catalog No.:BCX1801
CAS No.:145701-12-8
- Kaempferol 3-O-(6-O-(E)-caffeoyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)-α-L-rhamnopyranoside) 7-O-α-L-rhamnopyrano...
Catalog No.:BCX1802
CAS No.:1459767-45-3
- Soladulcoside A
Catalog No.:BCX1803
CAS No.:137031-53-9
- Jervinone
Catalog No.:BCX1804
CAS No.:469-60-3
- Siderin
Catalog No.:BCX1805
CAS No.:53377-54-1
- Kadsurenin B
Catalog No.:BCX1806
CAS No.:145701-13-9
- (2R,3R,5S)-2-(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-3,5-dihydro-5-methoxy-3-methyl-5-( 2-propenyl) -6(2H)-benzofuran...
Catalog No.:BCX1807
CAS No.:155551-59-0
- 2,5,6-Trihydroxy-3,4-methoxy-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene
Catalog No.:BCX1808
CAS No.:1810733-76-6
- Schisantherin S
Catalog No.:BCX1809
CAS No.:2230512-49-7
- Isolaureline
Catalog No.:BCX1810
CAS No.:475-84-3
Novel thymohydroquinone gallate (THQG) derivative loaded ligand Modified quantum dots as pH-Sensitive Multi-Modal theragnostic agent for cancer treatment.[Pubmed:38735345]
Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2024 May 10:114312.
BACKGROUND: Nanomedicine, as the combination of radiopharmaceutical and nanocarrier (QDs), is developed for treating cancer. Gallic acid is antimutagenic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-carcinogenic. Typical retention time of gallic acid is approximately 4 to 8 h. To increase the retention time gallic acid is converted to prodrug by adding lipophilic moieties, encapsulating in lipophilic nanoparticles, or liposome formation. Similarly, thymoquinone is powerful antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, and anti-inflammatory effect, with reduced DNA damage. METHODS: In this study, a hydrophilic drug (gallic acid) is chemically linked to the hydrophobic drug (Thymohydroquinone) to overcome the limitations of co-delivery of drugs. Thymohydroquinone (THQG) as the combination of gallic acid (GA) and thymoquinone (THQ) is loaded onto the PEI functionalized antimonene quantum dots (AM-QDs) and characterized by FTIR, UV-visible spectroscopy, X-ray powder diffraction, Zeta sizer, SEM and AFM, in-vitro and in-vivo assay, and hemolysis. RESULTS: The calculated drug loading efficiency is 90 %. Drug release study suggests the drug combination is pH sensitive and it can encounters acidic pH, releasing the drug from the nanocarrier. The drug and drug-loaded nanocarrier possesses low cytotoxicity and cell viability on MCF-7 and Cal-27 cell lines. The proposed drug delivery system is radiolabeled with Iodine-131 ((131)I) and Technetium ((99m)Tc) and its deposition in various organs of rats' bodies is examined by SPECT-CT and gamma camera. Hemolytic activity of 2, 4, 6, and 8 mug/ml is 1.78, 4.16, 9.77, and 15.79 %, respectively, reflecting low levels of hemolysis. The system also sustains oxidative stress in cells and environment, decreasing ROS production to shield cells and keep them healthy. CONCLUSIONS: The results of this study suggest that the proposed drug carrier system can be used as a multi-modal theragnostic agent in cancer.
Chemical Composition, Anti-bacterial Activity and Molecular Docking Studies of Essential Oil Isolated from Sa Sam Nam (Launaea sarmentosa).[Pubmed:38692900]
J Oleo Sci. 2024;73(5):787-799.
Launaea sarmentosa, also known as Sa Sam Nam, is a widely used remedy in Vietnamese traditional medicine and cuisine. However, the chemical composition and bioactivity of its essential oil have not been elucidated yet. In this study, we identified 40 compounds (98.6% of total peak area) in the essential oil via GC-MS analysis at the first time. Among them, five main compounds including Thymohydroquinone dimethyl ether (52.4%), (E)-alpha-Atlantone (9.0%), Neryl isovalerate (6.6%), Davanol D2 (isomer 2) (3.9%), and trans-Sesquisabinene hydrate (3.9%) have accounted for 75.8% of total peak area. The anti-bacterial activity of the essential oil against 4 microorganisms including Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa has also investigated via agar well diffusion assay. The results showed that the essential oil exhibited a strong antibacterial activity against Bacillus subtilis with the inhibition zones ranging from 8.2 to 18.7 mm. To elucidate the anti-bacterial effect mechanism of the essential oil, docking study of five main compounds of the essential oil (Thymohydroquinone dimethyl ether, (E)-alpha-Atlantone, Neryl isovalerate, Davanol D2 (isomer 2), and trans-Sesquisabinene hydrate) against some key proteins for bacterial growth such as DNA gyrase B, penicillin binding protein 2A, tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase, and dihydrofolate reductase were performed. The results showed that the main constituents of essential oil were highly bound with penicillin binding protein 2A with the free energies ranging -27.7 to -44.8 kcal/mol, which suggests the relationship between the antibacterial effect of essential oil and the affinity of main compounds with penicillin binding protein. In addition, the free energies of main compounds of the essential oil with human cyclooxygenase 1, cyclooxygenase 2, and phospholipase A2, the crucial proteins related with inflammatory response were less than diclofenac, a non-steroidal antiinflammatory drug. These findings propose the essential oil as a novel and promising anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory medicine or cosmetic products.
An investigation into the usage of black cumin derivatives against cancer and COVID-19 as the nature medicine.[Pubmed:38197611]
J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024 Jan 10:1-8.
Black cumin has been used as a spice and food preservative for years. Thymol, thymoquinone, Thymohydroquinone and dihydrothymoquinone are the most important natural agents in black cumin. In order to determine the most active compound in black cumin the theoretical calculations have been carried out in different phases by using the density functional theory (DFT). The inhibition effect of black cumin derivatives on Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) has been determined and supported the experimental studies without losing time and matter. The chemical activity, stability and solubility of the active substances in black cumin have been theoretically calculated. The chemical active compounds had been investigated in the black seeds when extracted with water. Their stability and polarity in blood and water are important parameters. HDAC2- dihydrothymoquinone interaction has been investigated. It has been determined that the active substances found in black cumin are very effective in protecting ACE2 against COVID-19 and by comparing the docking results of important receptors and selected ligands on COVID-19.Communicated by Ramaswamy H. Sarma.
Essential Oils of the Leaves of Epaltes australis Less. and Lindera myrrha (Lour.) Merr.: Chemical Composition, Antimicrobial, Anti-inflammatory, Tyrosinase Inhibitory, and Molecular Docking Studies.[Pubmed:37819841]
Chem Biodivers. 2023 Dec;20(12):e202301192.
Epaltes australis Less. has been traditionally used to treat fever and snake bites, whereas Lindera myrrha (Lour.) Merr. is well-known for addressing colds, chest pain, indigestion, and worm infestations. This study marks the first report on the chemical compositions and biological potentials of essential oils extracted from the leaves of Epaltes australis and Lindera myrrha. Essential oils obtained by hydro-distillation were analysed using the GC/MS (gas chromatography-mass spectrometry). E. australis exhibited a predominant presence of non-terpenic compounds (46.3 %), with Thymohydroquinone dimethyl ether as the major compound, constituting 44.2 % of the oil. L. myrrha leaf oil contained a good proportion of sesquiterpene hydrocarbons (56.8 %), with principal compounds including (E)-caryophyllene (22.2 %), ledene (9.7 %), selina-1,3,7(11)-trien-8-one (9.6 %), and alpha-pinene (7.0 %). Both essential oils exhibited antimicrobial activity against the bacteria Bacillus subtilis and Clostridium sporogenes, and Escherichia coli, and the fungus Aspergillus brasiliensis. L. myrrha leaf essential oil exhibited potent control over the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae with a MIC of 32 mug/mL. Additionally, L. myrrha leaf oil showed strong anti-inflammatory activity with an IC(50) value of 15.20 mug/mL by inhibiting NO (nitric oxide) production in LPS (lipopolysaccharide)-stimulated RAW2647 murine macrophage cells. Regarding anti-tyrosinase activity, E. australis leaf oil showed the best monophenolase inhibition with the IC(50) of 245.59 mug/mL, while L. myrrha leaf oil successfully inhibited diphenolase with the IC(50) of 152.88 mug/mL. From molecular docking study, selina-1,3,7(11)-trien-8-one showed the highest affinity for both COX-2 (cyclooxygenase-2) and TNF-alpha (tumor necrosis factor-alpha) receptors. Hydrophobic interactions play a great role in the bindings of ligand-receptor complexes.
Nigella sativa Oil Improves Motor Skill Learning of Albino Mice: In Vivo and In Silico Investigations.[Pubmed:37663783]
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Aug 25;2023:8498066.
Experimental evidences demonstrated that Nigella sativa oil (NSO) can restore neuronal integrities and processes by increasing the neuronal density, decreasing apoptosis, preventing inflammatory processes, and improving the neurogenic cells in the hippocampus. This refurbishment enhances the learning process and memory. The antioxidant defense mechanism of NSO slows down the process of neurodegeneration and motor deficit. The present study aimed to investigate the effects of NSO on motor skill learning using the single pellet reaching task method on Swiss albino mice, followed by in silico studies. Mice (total of 16) were randomly divided into the control group and treatment group (n = 8). The treatment group received 1 ml/kg b.w. NSO orally once daily for 7 days, and a control group received 1 ml/kg normal saline instead of NSO in a similar manner. The average success rate due to ingestion of NSO in the treatment group mice increased significantly (P < 0.05) compared to controlled mice. Molecular docking analysis revealed that thymoquinone, carvacrol, Thymohydroquinone, p-cymene, and t-anethole have binding affinities for the alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPA-R) that ranges from (-5.1 to -6.2) kcal/mol, which is comparable to the reference ligand glutamic acid binding affinity with AMPA-R (-6.6 kcal/mol). Thymoquinone and carvacrol formed hydrogen bonds with AMPA receptor at TYR61, SER142, and SER143 residues, comparable to the binding affinity of glutamic acid. ADMET analysis reported that all the compounds have higher bioavailability (>90%) and can cross the BBB easily (logBB> 0.3). Based on our experimental data and in silico report, we concluded that the enhanced motor skill learning effects of NSO are due to presence of potent antioxidants-thymoquinone and carvacrol-which might serve as AMPA receptor agonists. These phytoconstituents may play role in synaptic strengthening and promote experience-dependent motor skill learning.
Therapeutic and Phytochemical Properties of Thymoquinone Derived from Nigella Sativa.[Pubmed:37605475]
Curr Drug Res Rev. 2023 Aug 11.
BACKGROUND: Nigella sativa (N. sativa), commonly known as black seed or black cumin, belongs to the family Ranunculaceae. It contains several phytoconstituents, thymoquinone (TQ), thymol, Thymohydroquinone, carvacrol, and dithymoquinone. TQ is the main phytoconstituent present in N. sativa that is used as an herbal compound, and it is widely used as an antihypertensive, liver tonic, diuretic, digestive, anti-diarrheal, appetite stimulant, analgesic, and antibacterial agent, and in skin disorders. OBJECTIVE: The study focused on collecting data on the therapeutic or pharmacological activities of TQ present in N. sativa seed. METHODS: Antidiabetic, anticancer, immunomodulator, analgesic, antimicrobial, antiinflammatory, hepato-protective, renal protective, and antioxidant properties of TQ have been studied by various scientists. CONCLUSION: TQ seems to have a variety of consequences on how infected cells behave at the cellular level.
Antioxidant Properties of Thymoquinone, Thymohydroquinone and Black Cumin (Nigella sativa L.) Seed Oil: Scavenging of Superoxide Radical Studied Using Cyclic Voltammetry, DFT and Single Crystal X-ray Diffraction.[Pubmed:36978853]
Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Mar 1;12(3):607.
Black cumin seeds and seed oil have long been used in traditional foods and medicine in South Asian, Middle Eastern and Mediterranean countries and are valuable flavor ingredients. An important ingredient of black cumin is the small molecule thymoquinone (TQ), which manifests low toxicity and potential therapeutic activity against a wide number of diseases including diabetes, cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. In this study, the antioxidant activities of black seed oil, TQ and a related molecule found in black cumin, Thymohydroquinone (THQ), were measured using a direct electrochemical method to experimentally evaluate their superoxide scavenging action. TQ and the black seed oil showed good superoxide scavenging ability, while THQ did not. Density Functional Theory (DFT) computational methods were applied to arrive at a chemical mechanism describing these results, and confirmed the experimental Rotating Ring Disk Electrode (RRDE) findings that superoxide oxidation to O(2) by TQ is feasible, in contrast with THQ, which does not scavenge superoxide. Additionally, a thorough inquiry into the unusual cyclic voltammetry pattern exhibited by TQ was studied and was associated with formation of a 1:1 TQ-superoxide radical species, [TQ-O(2)](-)*. DFT calculations reveal this radical species to be involved in the pi-pi mechanism describing TQ reactivity with superoxide. The crystal structures of TQ and THQ were analyzed, and the experimental data reveal the presence of stacking intermolecular interactions that can be associated with formation of the radical species, [TQ-O(2)](-)*. All three of these methods were essential for us to arrive at a chemical mechanism that explains TQ antioxidant activity, that incorporates intermolecular features found in the crystal structure and which correlates with the measured superoxide scavenging activity.
Effects of Active Compounds of Nigella sativa in COVID-19: A Narrative Review.[Pubmed:36815641]
Recent Adv Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2023 Feb 22.
BACKGROUND: SARS-CoV-2 infection that led to the COVID-19 pandemic has changed human health and the economy globally. SARS CoV-2 is a type of Coronaviruses that has caused pneumonia and its complications with many deaths over the past two years. The use of hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine, accepted as generally safe for patients with autoimmune diseases or malaria, was attempted in many trials for COVID-19 treatment. Nigella sativa (NS) (black caraway, also known as black cumin, nigella or Kalonji) is an annual flowering plant of the Ranunculaceae family, chemically composed of the main constituent natural Thymoquinone (TQ) (30%- 48%) in forms of Thymohydroquinone, dithymoquinone (Nigellone) is a native to wider regions, including parts of eastern Europe, west Asia, North of Africa and east of Myanmar. In this review, we explored the Randomized Controlled Trial, Controlled Trial, and Systematic review studies that support Nigella sativa Thymoquinone-targeted SARS-CoV-2 targeting. Therefore, A literature search was performed for publications published on the electronic databases (PubMed, Embase, Scopus, CNKI, and Google Scholar) for Nigella sativa, black seeds, Kalonji, coronavirus, SARS-CoV -2 and COVID-19. This review aimed to find relevant evidence of Nigella sativa preferences as a natural feasible remedy with no side effects in COVID-19. Studies reported the benefits of NS as beneficial, another appropriate remedy for patients with COVID-19. However, all studies have shown limitations, such as limiting clinical symptom outcomes due to regulations imposed by isolation policies and lack of adequate funding. Therefore, the evidence suggests that the chemical contents of NS are a safe and possible treatment for COVID-19 patients that helps to improve COVID-19 infection in patients with no side effects. CONCLUSION: Nigella sativa seeds were one of the well-documented herbal products. Three reviewed randomized controlled trials reported that NS reduced covid-19 risk and could improve immune function. It was also helpful in upper respiratory infections such as asthma and bronchitis, with one RCT showing that honey and NS significantly improved symptoms, viral clearance, and mortality of COVID-19 patients. This review concludes that NS has a positive barrier effect on people at risk of acquiring a COVID-19 infection.
Metabolite Profiling and Bioassay-Guided Fractionation of Zataria multiflora Boiss. Hydroethanolic Leaf Extracts for Identification of Broad-Spectrum Pre and Postharvest Antifungal Agents.[Pubmed:36558036]
Molecules. 2022 Dec 14;27(24):8903.
Hydroethanolic leaf extracts of 14 Iranian Zataria multiflora Boiss. populations were screened for their antifungal activity against five plant pathogenic fungi and metabolically profiled using a non-targeted workflow based on UHPLC/ESI-QTOFMS. Detailed tandem mass-spectrometric analyses of one of the most active hydroethanolic leaf extracts led to the annotation of 68 non-volatile semi-polar secondary metabolites, including 33 flavonoids, 9 hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives, 14 terpenoids, and 12 other metabolites. Rank correlation analyses using the abundances of the annotated metabolites in crude leaf extracts and their antifungal activity revealed four O-methylated flavones, two flavanones, two dihydroflavonols, five Thymohydroquinone glycoconjugates, and five putative phenolic diterpenoids as putative antifungal metabolites. After bioassay-guided fractionation, a number of mono-, di- and tri-O-methylated flavones, as well as three of unidentified phenolic diterpenoids, were found in the most active subfractions. These metabolites are promising candidates for the development of new natural fungicides for the protection of agro-food crops.
Essential Oils from Vietnamese Asteraceae for Environmentally Friendly Control of Aedes Mosquitoes.[Pubmed:36432060]
Molecules. 2022 Nov 17;27(22):7961.
Mosquitoes, in addition to being a biting nuisance, are vectors of several pathogenic viruses and parasites. As a continuation of our work identifying abundant and/or invasive plant species in Vietnam for use as ecologically friendly pesticidal agents, we obtained the essential oils of Blumea lacera, Blumea sinuata, Emilia sonchifolia, Parthenium hysterophorus, and Sphaeranthus africanus; analyzed the essential oils using gas chromatographic techniques; and screened the essential oils for mosquito larvicidal activity against Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. The most active larvicidal essential oils were B. sinuata, which was rich in Thymohydroquinone dimethyl ether (29.4%), (E)-beta-caryophyllene (19.7%), alpha-pinene (8.8%), germacrene D (7.8%), and alpha-humulene (4.3%), (24-h LC(50) 23.4 and 29.1 mug/mL) on Ae. aegypti and Ae. albopictus, respectively, and Emilia sonchifolia, dominated by 1-undecene (41.9%) and germacrene D (11.0%), (24-h LC(50) 30.1 and 29.6 mug/mL) on the two mosquito species. The essential oils of P. hysterophorus and S. africanus were also active against mosquito larvae. Notably, B. sinuata, P. hysterophorus, and S. africanus essential oils were not toxic to the non-target water bug, Diplonychus rusticus. However, E. sonchifolia essential oil showed insecticidal activity (24-h LC(50) 48.1 mug/mL) on D. rusticus. Based on these results, B. sinuata, P. hysterophorus, and S. africanus essential oils appear promising for further investigations.
Molecular insight of phytocompounds from Indian spices and its hyaluronic acid conjugates to block SARS-CoV-2 viral entry.[Pubmed:36093954]
J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023 Sep-Oct;41(15):7386-7405.
Human corona viral infection leads to acute breathing disease and death if not diagnosed and treated properly in time. The disease can be treated with the help of simple natural compounds, which we use in day-to-day life. These natural compounds act against several diseases but their drug targeting mechanism needs to be improved for more efficient and promising applications. In the present study five compounds (gingerol, thymol, Thymohydroquinone, cyclocurcumin, hydrazinocurcumin) from three Indian medicinal plants (ginger, black cumin, turmeric) and its hyaluronic acid (HA) conjugates were docked against initially deposited spike structural proteins (PDB ID 6WPT) and its mutant variant D-614G (PDB ID 6XS6). Docking study result reveals that all the HA conjugates showed the most effective inhibitor of S-protein of initially deposited and D-614G variant forms of SARS-CoV-2. The compounds like Gingerol, Thymol, Thymohydroquinone, Cyclocurcumin, Hydrazinocurcumin, Hydroxychloroquinone, and hyaluronic acid conjugates inhibit the viral protein of both wild-type and mutated S-protein of SARS-CoV-2. The molecular docking studies of phytocompounds with initial deposited and variant spike protein targets show superior binding affinity than with the commercial repurposed viral entry inhibitor hydroxychloroquine. Further, the docking result was modeled using MD simulation study shows excellent simulation trajectories between spike proteins and HA conjugates spices constituents than its free form. DFT analysis was carried out to affirm the reason behind the highest binding affinity of HA conjugates over its free form towards SARS-CoV-2 spike protein targets. Further HA conjugates synthesis and its evaluation against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro studies are needed to prove our novel idea for an anti-viral drug.Communicated by Ramaswamy H. Sarma.
Prevention of doxorubicin-induced experimental cardiotoxicity by Nigella sativa in rats.[Pubmed:36062712]
Rev Port Cardiol. 2022 Feb;41(2):99-105.
INTRODUCTION: Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline cytotoxic chemotherapeutic drug that is commonly used in cancer treatment. A major side effect limiting the clinical use of DOX is cardiotoxicity due to oxidative injury. Nigella sativa (NS) is an annual flowering plant with antioxidant properties. Its seeds contain several bioactive constituents such as saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, thymoquinone, dithymoquinone, Thymohydroquinone, and thymol. In this study, we investigated the effect of NS extract on DOX-induced cardiotoxicity. METHODS: The experimental study animals consisted of 28 male Sprague Dawley rats weighing between 300 and 400 g. Four study groups each of seven rats were defined: controls; NS extract; DOX; and DOX+NS. Control and DOX rats received standard food, while each rat in the NS and DOX+NS groups also received 100 mg/kg NS extract orally. At day 28 of follow-up, rats in the DOX groups were administered a single 10 mg/kg intraperitoneal dose of DOX, while rats in the control and NS groups received a single 10 mg/kg dose of physiological saline solution. All animals were monitored for 35 days. On day 35, the rats were decapitated and serum and cardiac tissue samples were obtained. Troponin and NT-proBNP levels were measured in blood sera, while malondialdehyde (MDA), nitric oxide, total antioxidant capacity (TAC), and total oxidative stress (TOS) levels were quantified in sera and tissue samples. Histological alterations that were assessed in cardiac tissue included myocyte disarray, small vessel disease, myocyte hypertrophy, and fibrosis. RESULTS: The DOX group had significantly higher NT-proBNP, TOS, and MDA, with greater histopathological derangement. TAC was significantly elevated in the DOX+NS group, which also exhibited significantly lower troponin, TOS, and MDA, as well as significantly higher TAC compared to the DOX group. Histopathological examination showed that the significant structural derangement observed in DOX rats was markedly and significantly reduced in DOX+NS rats. CONCLUSION: Our results suggest that NS extract may prevent DOX-induced cardiotoxicity and thus represents a promising cardioprotective agent.
Antioxidant and Prooxidant Effects of Thymoquinone and Its Hydroquinone Metabolite.[Pubmed:36047210]
Biol Pharm Bull. 2022;45(9):1389-1393.
Thymoquinone is a popular health-promoting antioxidant supplement, but it may induce toxicity to cells and organs because of its propensity to promote oxidation of biomolecules under some conditions. Furthermore, as hydroquinones have been found to exhibit more potent antioxidant and prooxidant activities than their parent quinones, the reduced metabolite Thymohydroquinone may have stronger effects than thymoquinone. In this study, the antioxidant and prooxidant activities of thymoquinone and Thymohydroquinone were assessed to determine whether they both act as antioxidants and induce oxidative damage to biomolecules as do other quinones. Using ESR spectroscopy, we demonstrated that Thymohydroquinone exhibits more potent antioxidant activity than does thymoquinone. In addition, Thymohydroquinone was found to act as a prooxidant to induce oxidative damage of isolated plasmid DNA in the presence of free Cu(2+) or Fe(2+)-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). Interestingly, the prooxidant effect of Thymohydroquinone in the presence of Fe(2+) was not observed in the absence of EDTA. Thymohydroquinone thus was demonstrated to have two biologically relevant activities: as an antioxidant and a prooxidant.
The co-adsorption of thymohydroquinone dimethyl ether (THQ) and coumarin present in the aqueous extract of Ayapana triplinervis on mild steel and its protection in hydrochloric acid up to 323 K: computational and physicochemical studies.[Pubmed:35702201]
RSC Adv. 2022 May 12;12(23):14328-14341.
This study evaluates the corrosion inhibition property of the aqueous and alcoholic leaf extracts of the medicinal plant Ayapana triplinervis. The major components in the extracts are Thymohydroquinone dimethyl ether (THQ) and coumarin. It is clear from the weight-loss studies that the water extract of the leaves (AYW) is superior to the alcoholic extract (AYA) in terms of offering corrosion inhibition. The 96% efficiency of 4% (v/v) AYW in 0.5 N HCl at room temperature changes to 84.62% at 323 K. The mixed-type inhibition behaviour of AYW shows slight dominance in the anodic direction. Studies suggest the multilayer adsorption of phytochemicals on the metal surface and that the adsorption follows the Temkin model. Theoretical studies using DFT and BIOVIA Materials Studio investigations establish THQ as a good inhibitor with high adsorption characteristics. Even though the concentration of coumarin in the extract is low, its presence in the extract facilitates the adsorption of THQ on the metal surface, which is evident from the MD simulation study. The changes in the surface topography and elemental composition of the metal specimen in the inhibited and uninhibited solution are monitored by SEM and EDX spectral studies. XPS data support the presence of both THQ and coumarin on the metal surface and the existence of co-ordinate bonding between the metal's d orbital and the O atoms of THQ. Theoretical and experimental studies support the mixed mode of adsorption of THQ as physisorption followed by chemisorption.


