Tumulosic acidCAS# 508-24-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 508-24-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 12314446 | Appearance | Powder |
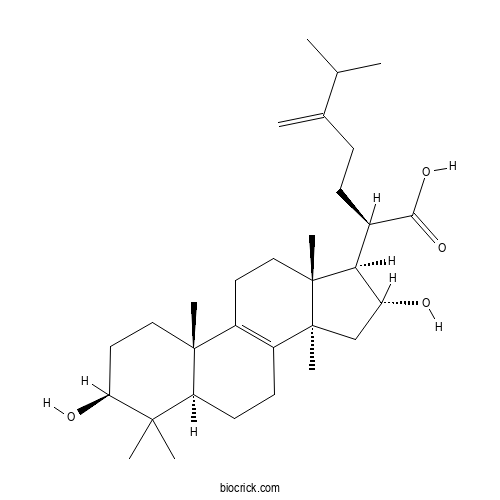
| Formula | C31H50O4 | M.Wt | 486.7 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2R)-2-[(3S,5R,10S,13R,14R,16R,17R)-3,16-dihydroxy-4,4,10,13,14-pentamethyl-2,3,5,6,7,11,12,15,16,17-decahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-6-methyl-5-methylideneheptanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)C(=C)CCC(C1C(CC2(C1(CCC3=C2CCC4C3(CCC(C4(C)C)O)C)C)C)O)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XADJANKGURNTIA-YEXRKOARSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C31H50O4/c1-18(2)19(3)9-10-20(27(34)35)26-23(32)17-31(8)22-11-12-24-28(4,5)25(33)14-15-29(24,6)21(22)13-16-30(26,31)7/h18,20,23-26,32-33H,3,9-17H2,1-2,4-8H3,(H,34,35)/t20-,23-,24+,25+,26+,29-,30-,31+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Tumulosic acid Dilution Calculator

Tumulosic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0547 mL | 10.2733 mL | 20.5465 mL | 41.0931 mL | 51.3663 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4109 mL | 2.0547 mL | 4.1093 mL | 8.2186 mL | 10.2733 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2055 mL | 1.0273 mL | 2.0547 mL | 4.1093 mL | 5.1366 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0411 mL | 0.2055 mL | 0.4109 mL | 0.8219 mL | 1.0273 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0205 mL | 0.1027 mL | 0.2055 mL | 0.4109 mL | 0.5137 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 3'-Hydroxy-5,7,4',5'-Tetramethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN0768
CAS No.:29976-51-0
- Platycodin J
Catalog No.:BCN0767
CAS No.:1325614-80-9
- Dipsacus saponin X
Catalog No.:BCN0759
CAS No.:146100-01-8
- 7-O-(4-beta-D-glucopyranosyloxy-3-methoxybenzoyl)secologanolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN0758
CAS No.:469899-55-6
- Eucomic acid
Catalog No.:BCN0757
CAS No.:42151-32-6
- ZP-amide C
Catalog No.:BCN0756
CAS No.:412316-38-2
- Ternatumoside II
Catalog No.:BCN0755
CAS No.:1473419-87-2
- Dihydrophaseic acid 4'-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN0754
CAS No.:78914-56-4
- 5,6,7,3',4'-Pentamethoxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN0753
CAS No.:104193-93-3
- Ternstroside F
Catalog No.:BCN0766
CAS No.:914649-36-8
- Ternstroside E
Catalog No.:BCN0765
CAS No.:914649-31-3
- Ternstroside D
Catalog No.:BCN0764
CAS No.:914649-26-6
- Meliotocarpan D
Catalog No.:BCN0770
CAS No.:83013-81-4
- (-)-5'-Methoxyisolariciresinol 3alpha-O-beta-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN0771
CAS No.:143236-03-7
- 4'-Hydroxy-3',5,5',6,7,8-hexamethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN0772
CAS No.:85644-03-7
- 3'-Hydroxy-5,7,4'-trimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN0773
CAS No.:33554-52-8
- Lariciresinol 4'-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN0774
CAS No.:107110-16-7
- Tetillapyrone
Catalog No.:BCN0775
CAS No.:363136-43-0
- 4'-Hydroxy-5,7,3'-trimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN0776
CAS No.:1239-68-5
- (2S)-5,7,3',4'-tetramethoxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN0777
CAS No.:74628-43-6
- (Z)-3,11-dimethy-7-methylene-9,14-epoxy-1,6,10-dodecatrien-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN0778
CAS No.:1392202-57-1
- Quercetin 3,7-diglucoside
Catalog No.:BCN0779
CAS No.:6892-74-6
- 6alpha-Hydroxydehydropachymic acid
Catalog No.:BCN0780
CAS No.:176390-67-3
- 3',4',5',5,7-Pentamethoxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN0781
CAS No.:479672-30-5
LC-ESI-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of eleven bioactive compounds in rat plasma after oral administration of Ling-Gui-Zhu-Gan Decoction and its application to a pharmacokinetics study.[Pubmed:30172532]
Talanta. 2018 Dec 1;190:450-459.
A sensitive and robust LC-MS/MS method has been developed and validated to simultaneous determine the concentrations of Tumulosic acid, dehydroTumulosic acid, polyporenic acid C, cinnamic acid, Atractylenolide I, Atractylenolide II, Atractylenolide III, glycyrrhizic acid, glycyrrhetinic acid, liquiritigenin and isoliquiritin in plasma from rats who received Ling-Gui-Zhu-Gan Decoction extract oral administration. The samples were prepared by a liquid-liquid extraction procedure using ethyl ether as the extraction solvent and schisandrin as the internal standard. Chromatographic separation was achieved using a Thermo Hypersil GOLD C18 column (2.1mmx100mm, 1.9microm) and a gradient mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile-water with 0.1% formic acid. All of the analytes were quantified using negative and positive multiple reaction monitoring mode. The method was validated for selectivity, linearity, accuracy, precision, recovery, matrix effect and sample stability under various storage conditions, whose values are all fell in the acceptable limits. We report the lowest limit of quantification for Tumulosic acid, dehydroTumulosic acid and polyporenic acid C as 2ng/mL. This is the first study for simultaneous determination of so many analytes in rat plasma after oral administration of Ling-Gui-Zhu-Gan Decoction. This validated method was successfully used to study the pharmacokinetics of multiple compounds in rat plasma after oral administration of Ling-Gui-Zhu-Gan Decoction.
Inhibition of Human Kallikrein 5 Protease by Triterpenoids from Natural Sources.[Pubmed:29077044]
Molecules. 2017 Oct 27;22(11). pii: molecules22111829.
Stratum corneum tryptic enzyme kallikrein 5 (KLK5) is a serine protease that is involved in the cell renewal and maintenance of the skin barrier function. The excessive activation of KLK5 causes an exacerbation of dermatoses, such as rosacea and atopic dermatitis. Some triterpenoids are reported to suppress the serine proteases. We aimed to investigate whether bioactive triterpenoids modulate the KLK5 protease. Nineteen triterpenoids occurring in medicinal crude drugs were evaluated using an enzymatic assay to measure the anti-KLK5 activity. The KLK5-dependent cathelicidin peptide LL-37 production in human keratinocytes was examined using immunoprecipitation and Western blotting. Screening assays for evaluating the anti-KLK5 activity revealed that ursolic acid, oleanolic acid, saikosaponin b(1), Tumulosic acid and pachymic acid suppressed the KLK5 protease activity, although critical molecular moieties contributing to anti-KLK5 activity were unclarified. Ursolic acid and Tumulosic acid suppressed the proteolytic processing of LL-37 in keratinocytes at Tumulosic acid, modulate the KLK5 protease activity and cathelicidin peptide production. Triterpenoids may affect the skin barrier function via the regulation of proteases.
[Chemical constituents of Poria cocos].[Pubmed:24956845]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2014 Mar;39(6):1030-3.
The chemical constituents of Poria cocos were studied by means of silica gel, ODS column chromatography, Sephadex LH-20 and preparative HPLC. Thirteen compounds were isolated from this plant. By analysis of the ESI-MS and NMR data, the structures of these compounds were determined as Tumulosic acid (1), dehydroTumulosic acid (2), 3beta, 5alpha-dihydroxy-ergosta-7, 22-dien-6-one (3), 3beta, 5alpha, 9alpha-trihydroxy-ergosta-7, 22-diene -6-one (4), ergosta-7, 22-diene-3-one (5), 6, 9-epoxy-ergosta-7,22-diene-3-ol (6), ergosta-4,22-diene-3-one (7), 3beta, 5alpha, 6beta-trihydroxyl-ergosta-7,22-diene (8), ergosta-5, 6-epoxy-7,22-dien-3-ol (9), beta-sitosterol (10), ribitol (11), mannitol (12), and oleanic acid 3-O-acetate (13), respectively. Compounds 3-13 were isolated from the P. cocos for the first time.
A UFLC-MS/MS method with a switching ionization mode for simultaneous quantitation of polygalaxanthone III, four ginsenosides and tumulosic acid in rat plasma: application to a comparative pharmacokinetic study in normal and Alzheimer's disease rats.[Pubmed:23893636]
J Mass Spectrom. 2013 Aug;48(8):904-13.
A fast, sensitive and reliable ultra fast liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UFLC-MS/MS) method has been developed and validated for simultaneous quantitation of polygalaxanthone III (POL), ginsenoside Rb1 (GRb1), ginsenoside Rd (GRd), ginsenoside Re (GRe), ginsenoside Rg1 (GRg1) and Tumulosic acid (TUM) in rat plasma after oral administration of Kai-Xin-San, which plays an important role for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The plasma samples were extracted by liquid-liquid extraction using ethyl acetate-isopropanol (1:1, v/v) with salidrdoside as internal standard (IS). Good chromatographic separation was achieved using gradient elution with the mobile phase consisting of methanol and 0.01% acetic acid in water. The tandem mass spectrometric detection was performed in multiple reaction monitoring mode on 4000Q UFLC-MS/MS system with turbo ion spray source in a negative and positive switching ionization mode. The lower limits of quantification were 0.2-1.5 ng/ml for all the analytes. Both intra-day and inter-day precision and accuracy of analytes were well within acceptance criteria (+/-15%). The mean absolute extraction recoveries of analytes and IS from rat plasma were all more than 60.0%. The validated method has been successfully applied to comparing pharmacokinetic profiles of analytes in normal and AD rat plasma. The results indicated that no significant differences in pharmacokinetic parameters of GRe, GRg1 and TUM were observed between the two groups, while the absorption of POL and GRd in AD group were significantly higher than those in normal group; moreover, the GRb1 absorbed more rapidly in model group. The different characters of pharmacokinetics might be caused by pharmacological effects of the analytes.
Triterpenes from the fungus Poria cocos and their inhibitory activity on nitric oxide production in mouse macrophages via blockade of activating protein-1 pathway.[Pubmed:22083926]
Chem Biodivers. 2011 Nov;8(11):2135-43.
Two new triterpenes, 29-hydroxydehydroTumulosic acid (1) and 29-hydroxydehydropachymic acid (2), together with six known compounds, dehydropachymic acid (3), dehydroTumulosic acid (4), 29-hydroxypolyporenic acid C (5), polyporenic acid C (6), Tumulosic acid (7), and pachymic acid (8), were isolated from the dried sclerotia of Poria cocos. In the in vitro bioassays, these isolated compounds reduced, in a dose-dependent manner, nitric oxide (NO) production from lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW 264.7 cells, with compounds 5 and 6, the IC(50) values of which were 16.8+/-2.7 and 18.2+/-3.3 muM, respectively, exhibiting the greatest inhibition activity. Further Western blot analysis conducted on cells pre-treated with compounds 5 and 6, and luciferase assays on activator protein 1-dependent gene expression revealed that the inhibited NO release was attributed to the reduced expression of iNOs (=inducible NO synthase) enzymes, which might be regulated via the blockade of activator protein-1 signaling pathway.
Comparative pharmacokinetics of three triterpene acids in rat plasma after oral administration of Poria extract and its formulated herbal preparation: GuiZhi-FuLing capsule.[Pubmed:22008604]
Fitoterapia. 2012 Jan;83(1):117-24.
A sensitive liquid chromatographic-mass spectrometric technique coupled with liquid-liquid extraction method was developed and validated for simultaneous determination of dehydro-Tumulosic acid, Tumulosic acid and polyporic acid C in rat plasma. The analytes were separated on a Kromasil C(18) column with a total running time of 12.5 min. Author had compared the pharmacokinetics of dehydro-Tumulosic acid, Tumulosic acid and polyporic acid C after oral administration of the extract of Poria and its formulated herbal preparation (GuiZhi-FuLing capsule). The improved pharmacokinetic profiles of the three compounds were found in the GuiZhi-FuLing capsule, indicating the more effective absorption and the slower elimination, compared with the Poria extract. Furthermore, this study revealed that as far as the Poria extract was concerned, it is very valuable to be used as a clinical instruction of GF capsule.
Cytotoxic and anti-oxidant activities of lanostane-type triterpenes isolated from Poria cocos.[Pubmed:18827390]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2008 Oct;56(10):1459-62.
A new lanostane-type triterpene, 29-hydroxypolyporenic acid C (8), was isolated from the dried sclerotia of Poria cocos together with eight other known compounds pachymic acid (1), dehydropachymic acid (2), 3-acetyloxy-16alpha-hydroxytrametenolic acid (3), polyporenic acid C (4), 3-epi-dehydropachymic acid (5), 3-epi-dehydroTumulosic acid (6), Tumulosic acid (7), and dehydroTumulosic acid (9). The compounds were identified by spectral analysis and comparison with spectroscopic data reported in the literatures. Although none of the nine (1 to 9) compounds showed promising antioxidant activity, 1 through 6 and 8 showed good cytotoxicity against human lung cancer cell line A549 and human prostate cancer cell line DU145. Interestingly, all these compounds exhibited better cytotoxicity towards A549 than DU145 cells.
Cytotoxicity and DNA topoisomerases inhibitory activity of constituents from the sclerotium of Poria cocos.[Pubmed:15460443]
Arch Pharm Res. 2004 Aug;27(8):829-33.
The bioactivity-guided fractionation of the methylene chloride extract of the sclerotium of Poria cocos led to the isolation of (S)-(+)-turmerone (1), ergosterol peroxide (2), polyporenic acid C (3), dehydropachymic acid (4), pachymic acid (5), and Tumulosic acid (6). Compounds 4-6 exhibited moderate cytotoxicities, with IC50 values of 20.5, 29.1, and 10.4 microM, respectively, against a human colon carcinoma cell line. However, 3-6 not only showed inhibitory activities as potent as etoposide used as a positive control on DNA topoisomerase II (36.1, 36.2, 43.9 and 66.7% inhibition at a concentration of 20 microM, respectively), but also inhibition of DNA topoisomerase I (55.8, 60.7, 43.5, and 83.3% inhibition at a concentration of 100 microM, respectively).
Inhibition of tumor-promoting effects by poricoic acids G and H and other lanostane-type triterpenes and cytotoxic activity of poricoic acids A and G from Poria cocos.[Pubmed:11975480]
J Nat Prod. 2002 Apr;65(4):462-5.
The structures of two novel 3,4-seco-lanostane-type triterpenes isolated from the sclerotium of Poria cocos were established to be 16alpha-hydroxy-3,4-seco-lanosta-4(28),8,24-triene-3,21-dioic acid (1; poricoic acid G) and 16alpha-hydroxy-3,4-seco-24-methyllanosta-4(28),8,24(24(1))-triene-3,21-dioic acid (2; poricoic acid H) on the basis of spectroscopic methods. These two, and eight other known compounds isolated from the sclerotium, poricoic acid B (3), poricoic acid A (4), Tumulosic acid (5), dehydroTumulosic acid (6), 3-epidehydroTumulosic acid (7), polyporenic acid C (8), 25-hydroxy-3-epidehydroTumulosic acid (9), and dehydroabietic acid methyl ester (10), showed potent inhibitory effects on Epstein-Barr virus early antigen (EBV-EA) activation induced by the tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA). Evaluation of the cytotoxicity of compounds 1 and 4 against human cancer cell lines revealed that 1 was significantly cytotoxic to leukemia HL-60 cells [GI(50) (concentration that yields 50% growth) value 39.3 nM], although it showed only moderate cytotoxicity to the other cells. Compound 4 exhibited moderate cytotoxicity to all of the cancer cell lines tested.


