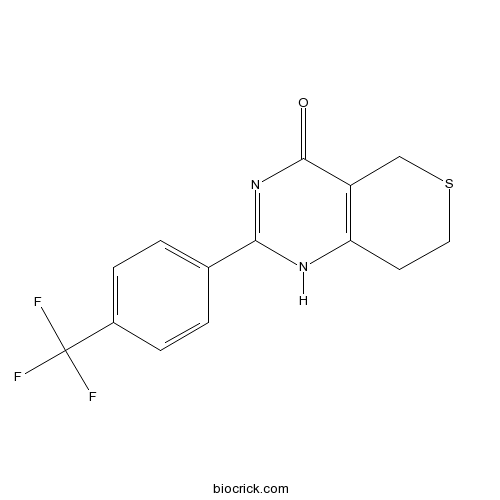
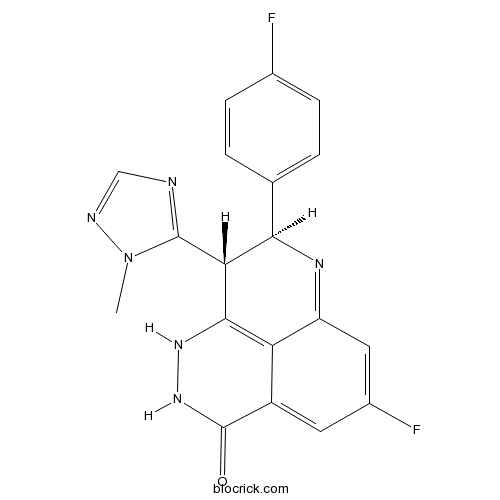
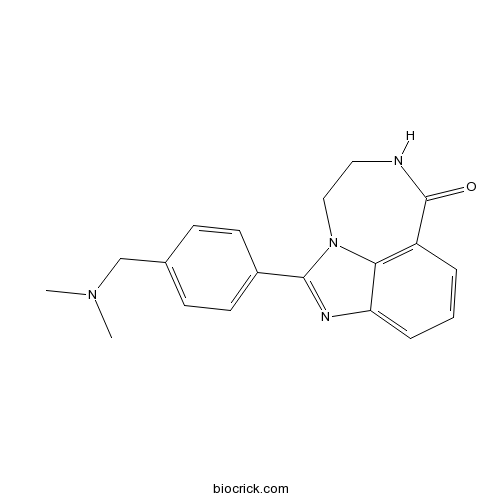
PARP
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs) is a large family of proteins with a conserved catalytic domain that catalyze an immediate DNA-damage-dependent post-translational modification of histones and other nuclear proteins leading to the survival of injured proliferating cells. So far, a total number of 18 human PARP proteins encoded by different genes have been identified, including PARP-1 to PARP-4, PARP-5a, PARP-5b, PARP-5c and PARP-6 to PARP-16. The general structural of PARP proteins has been revealed through the extensive study of the founding family member PARP-1, which is characterized by the presence of four functional domains, including a DNA-binding domain, a caspase-cleaved domain, an automodification domain and a catalytic domain.