Alpinia hainanensis
Alpinia hainanensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Alpinia hainanensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
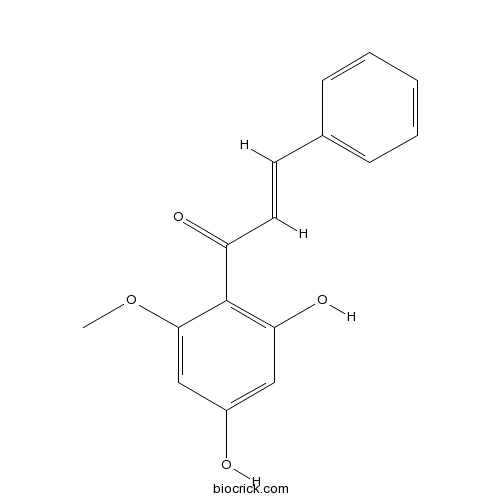
BCN1184
Cardamonin19309-14-9
Instructions
-
BCN2761
Alnustone33457-62-4
Instructions

-
BCN5315
Alpinetin36052-37-6
Instructions

-
BCN5556
Pinocembrin480-39-7
Instructions

-
BCN1321
5-Hydroxy-1,7-diphenyl-6-hepten-3-one87095-74-7
Instructions

Functional conservation and divergence of four ginger AP1/AGL9 MADS-box genes revealed by analysis of their expression and protein-protein interaction, and ectopic expression of AhFUL gene in Arabidopsis.[Pubmed: 25461565]
Alpinia genus are known generally as ginger-lilies for showy flowers in the ginger family, Zingiberaceae, and their floral morphology diverges from typical monocotyledon flowers. However, little is known about the functions of ginger MADS-box genes in floral identity. In this study, four AP1/AGL9 MADS-box genes were cloned from Alpinia hainanensis, and protein-protein interactions (PPIs) and roles of the four genes in floral homeotic conversion and in floral evolution are surveyed for the first time. AhFUL is clustered to the AP1 lineage, AhSEP4 and AhSEP3b to the SEP lineage, and AhAGL6-like to the AGL6 lineage. The four genes showed conserved and divergent expression patterns, and their encoded proteins were localized in the nucleus. Seven combinations of PPI (AhFUL-AhSEP4, AhFUL-AhAGL6-like, AhFUL-AhSEP3b, AhSEP4-AhAGL6-like, AhSEP4-AhSEP3b, AhAGL6-like-AhSEP3b, and AhSEP3b-AhSEP3b) were detected, and the PPI patterns in the AP1/AGL9 lineage revealed that five of the 10 possible combinations are conserved and three are variable, while conclusions cannot yet be made regarding the other two. Ectopic expression of AhFUL in Arabidopsis thaliana led to early flowering and floral organ homeotic conversion to sepal-like or leaf-like. Therefore, we conclude that the four A. hainanensis AP1/AGL9 genes show functional conservation and divergence in the floral identity from other MADS-box genes.
Isolation and characterization of a SEP- like gene from Alpinia hainanensis (Zingiberaceae).[Pubmed: 19685163]
A cDNA clone, AhSEP3 was isolated from the young inflorescences of Alpinia hainanensis. AhSEP3 cDNA is 891 bp long with an open reading frame of 726 bp that encodes a 241-amino acid protein. Sequence comparisons showed that AhSEP3 is very similar to SEP3 homologues. Phylogenetic analyses indicated that AHSEP3 is a new member of AGL2 subfamily. In situ hybridization analyses showed the expression pattern of the AhSEP3 is very similar to those of SEP3 and SEP3 homologs in other plant species, i.e. the signals of AhSEP3 are present in the inner three whorl of the floral organ.


