Anoectochilus roxburghii
Anoectochilus roxburghii
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
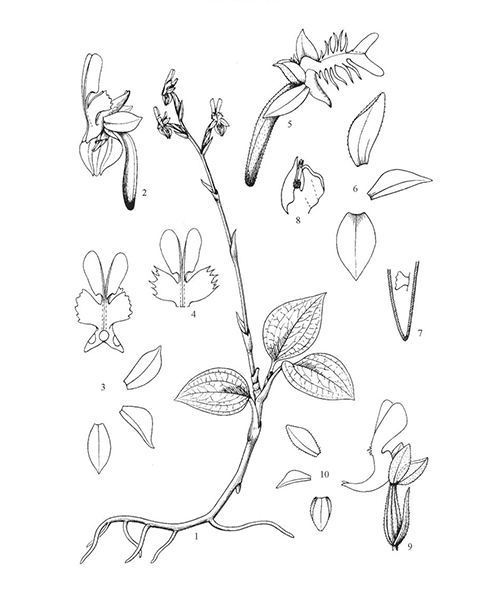

Natural products/compounds from Anoectochilus roxburghii
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5816
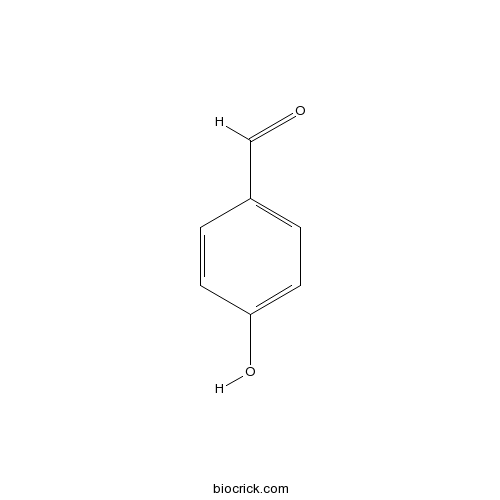
4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde123-08-0
Instructions
-
BCN3181
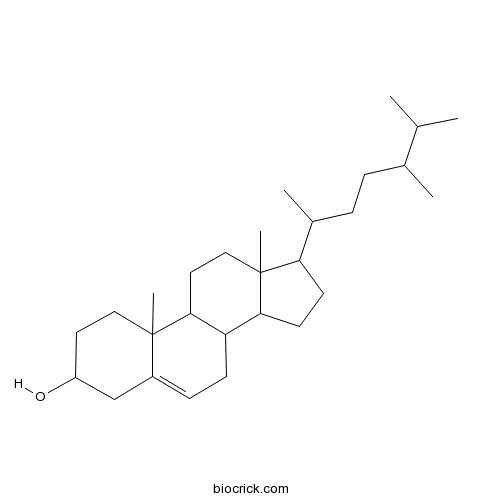
Campesterol474-62-4
Instructions
-
BCN5551
Isorhamnetin480-19-3
Instructions

-
BCN2916
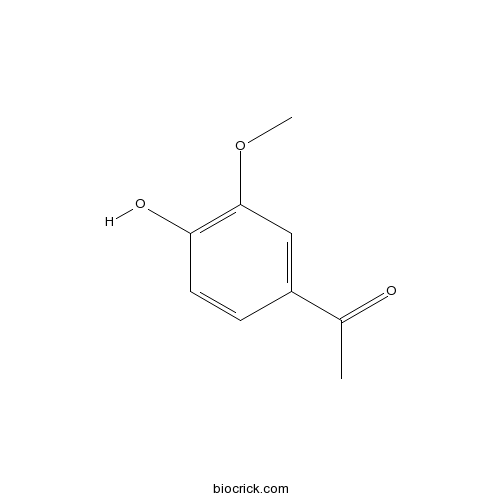
Acetovanillone498-02-2
Instructions
-
BCN4154
4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol623-05-2
Instructions

-
BCN4327
Ursolic acid77-52-1
Instructions

Rapid authentication and identification of different types of A. roxburghii by Tri-step FT-IR spectroscopy.[Pubmed: 29626818]
Anoectochilus roxburghii (Wall.) Lindl. (Orchidaceae) is a precious traditional Chinese medicinal herb and has been perennially used to treat various illness. However, there were unethical sellers who adulterated wild A. roxburghii with tissue cultured and cultivated ones. Therefore, there is an urgent need for an effective authentication method to differentiate between these different types of A. roxburghii. In this research, the infrared spectroscopic tri-step identification approach including Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), Second derivative infrared spectra (SD-IR) and two-dimensional correlation infrared spectra (2D-IR) was used to develop a simple and rapid method to discriminate between wild, cultivated and tissue cultivated A. roxburghii plant. Through this study, all three types of A. roxburghii plant were successfully identified and discriminated through the infrared spectroscopic tri-step identification method. Besides that, all the samples of wild, cultivated and tissue cultivated A. roxburghii plant were analysed with the Soft Independent Modelling of Class Analogy (SIMCA) pattern recognition technique to test and verify the experimental results. The results showed that the three types of A. roxburghii can be discriminated clearly as the recognition rate was 100% for all three types and the rejection rate was more than 60%. 70% of the validated samples were also identified correctly by the SIMCA model. The SIMCA model was also validated by comparing 70 standard herbs to the model. As a result, it was demonstrated that the macroscopic IR fingerprint method and the classification analysis could discriminate not only between the A. roxburghi samples and the standard herbs, it could also distinguish between the three different types of A. roxburghi plant in a direct, rapid and holistic manner.
Antidiabetic activities of polysaccharides from Anoectochilus roxburghii and Anoectochilus formosanus in STZ-induced diabetic mice.[Pubmed: 29438753]
Six polysaccharides were extracted from different parts (whole plants, roots and leaves) of Anoectochilus roxburghii and Anoectochilus formosanus (ARPs, ARPs-1, ARPs-2, AFPs, AFPs-1 and AFPs-2). Their primary characteristics were identified and their antidiabetic activities were evaluated in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Root polysaccharides (ARPs-1and AFPs-1) and leaf polysaccharides (ARPs-2 and AFPs-2) were distinct from each other in terms of the Mws, monosaccharide compositions and functional groups. Notably, the primary structures of ARPs and AFPs were similar to those of ARPs-1and AFPs-1, respectively. In animal experiment, after feeding with polysaccharides samples, the body weight, blood glucose, glycogen, insulin, total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), malondiadehyde (MDA) and antioxidant enzyme activities in liver and kidney of mice were tested to investigate the antidiabetic activities. All polysaccharides exhibited varying antidiabetic activities (antihyperglycemic, antioxidant and antihyperlipidemic activities), which were closely related to their primary characteristics. Furthermore, root polysaccharides with higher Mws and glucose content in both A. roxburghii and A. formosanus, exhibited better antidiabetic activities than leaf polysaccharides, and ARPs which showed the best antidiabetic activities had the potential to be used as functional food or medicine for diabetes treatment.
[Nontargeted metabolomic analysis of Anoectochilus roxburghii at different cultivation stages].[Pubmed: 29376262]
Anoectochilus roxburghii is a traditional Chinese medicine and natural health products. In the modern cultivation system, A. roxburghii is micropropagated in tissue culture, and the plants are transferred to soil cultivation for months. However, it remains unclear about the necessity of soil cultivation for the accumulation of health beneficial compounds. In this paper, we performed nontargeted metabolomic analysis using GC-TOF-MS and UPLC-Q-TOF-MS, on A. roxburghii plants at tissue culture stage or after 3 months of soil cultivation. The results showed that the primary metabolites such as alcohols and organic acids are abundant in the tissue culture plants. In contrast, polysaccharide, nucleoside, esters and secondary metabolites such as flavonoids, terpenoids were significantly accumulated in cultivated seedlings. Flavonoids and polysaccharides are considered as the principle effective components in A. roxburghii. Soil cultivation period is therefore essential for the accumulation of these metabolites.
[New records of medicinal plants in Hubei].[Pubmed: 29318848]
In this paper, we make a report on new records of medicinal plants in Hubei, which include one newly recorded genera and seven newly recorded species and a newly recorded variety. The newly recorded genera is Anoectochilus and its corresponding species is Anoectochilus roxburghii; These newly recorded species are Euphorbia micractina, Astragalus wulingensis, Blumea megacephala, Potentilla saundersiana, Blumea formosana, Lycoris houdyshelii and Colocasia gigantea ; The newly recorded variety is Neottia puberula var. maculata. Among these species, Anoectochilus roxburghii and N. puberula var. maculata are considered as the second-class protection in our country, A. roxburghii is regarded as Endangered(EN)and Astragalus wulingensis is regarded as Critically Endangered (CN) by IUCN. The report of these newly recorded plants borden the distribution and enrich the plant diversity of Hubei.
The active component screening of Anoectochilus roxburghii and the functional study on inhibition of melanogenesis in zebrafish.[Pubmed: 29258988]
The aim of this study is to explore the active components of Anoectochilus roxburghii capable of inhibiting melanin formation using chemical separation and extraction and functional analysis. Anoectochilus roxburghii were extracted with alcohol and separated into three groups: the total extraction group, alcohol extracted group and alcohol precipitated group. Zebrafish embryos at 0.75 h post-fertilization were exposed to various concentrations of the three groups of extracts, and analyzed at 72 h, using semi-quantitative RT-PCR and in situ hybridization. The results showed that the alcohol extracts inhibit melanogenesis most significantly in the zebrafish embryos. The mRNAs of melanin-related genes, such as silv, tyr, tyrp1a, were down-regulated by the alcohol extracts spatially and temporally. The alcohol extracts also inhibited the activity of tyrosinase, a key enzyme in melanogenesis, in a dosage dependent manner. In addition, the alcohol extracts also display a remarkable inhibitory effect on melanin synthesis through down-regulation of mRNAs of melanin-related genes and tyrosinase activity in zebrafish embryos, in which a large amount of melanin has already been synthesized. Such inhibitory effect could be reversed after the withdrawal of the alcohol extracts. Our results showed that the alcohol extracts of Anoectochilus roxburghii can significantly inhibit zebrafish melanogenesis, supporting the notion that Anoectochilus roxburghii could potentially be used in the development and production of natural whitening products.
Purification of polysaccharide from artificially cultivated Anoectochilus roxburghii (wall.) Lindl. by high-speed counter current chromatography and its antitumor activity.[Pubmed: 28892307]
None


