Aster tataricus
Aster tataricus
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Aster tataricus
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
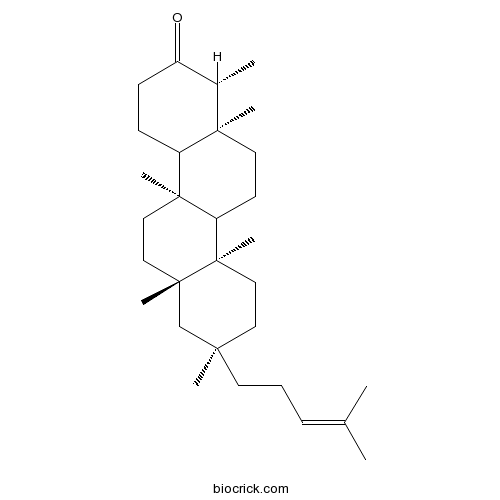
BCN1274
Shionone10376-48-4
Instructions
-
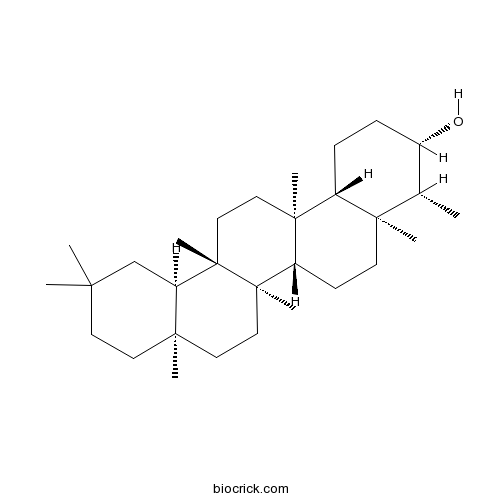
BCN1104
Epifriedelanol16844-71-6
Instructions
-
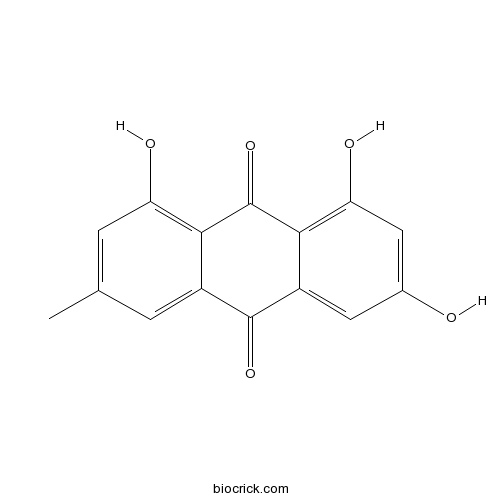
BCN5649
Emodin518-82-1
Instructions
-
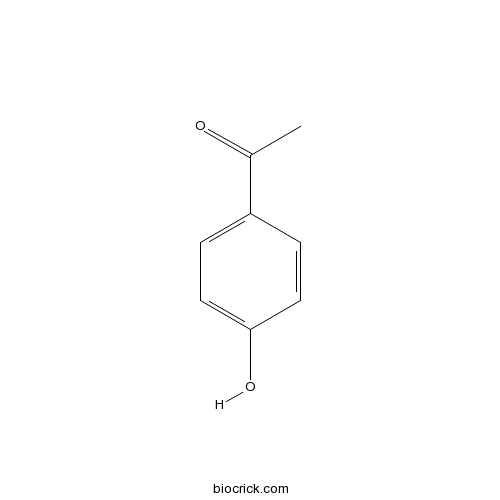
BCN4544
4'-Hydroxyacetophenone99-93-4
Instructions
A systematic data acquisition and mining strategy for chemical profiling of Aster tataricus rhizoma (Ziwan) by UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS and the corresponding anti-depressive activity screening.[Pubmed: 29573734]
In this study, a systematic data acquisition and mining strategy aimed at the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) complex system based on ultra high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS) was reported. The workflow of this strategy is as follows: First, the high resolution mass data are acquired by both data-dependent acquisition mode (DDA) and data-independent acquisition mode (DIA). Then a global data mining that combined targeted and non-targeted compound finding is applied to analyze mass spectral data. Furthermore, some assistant tools, such as key product ions (KPIs), are employed for compound hunting and identification. The TCM Ziwan (ZW, Aster tataricus rhizoma) was used to illustrate this strategy for the first time. In this research, total 131 compounds including organic acids, peptides, terpenes, steroids, flavonoids, coumarins, anthraquinones and aldehydes were identified or tentatively characterized in ZW based on accurate mass measurements within ±5 ppm error, and 50 of them were unambiguously confirmed by comparing standard compounds. Afterwards, based on the traditional Chinese medical theory and the key determinants of firing patterns of ventral tegmental area (VTA) dopamine (DA) neurons in the development of depression, the confirmed compounds were subsequently evaluated the pharmacological effect of activity of VTA DA neurons and anti-depressive efficacy. This research provided not only a chemical profiling for further in vivo study of ZW, but also an efficient data acquisition and mining strategy to profile the chemical constituents and find new bioactive substances for other TCM complex system.
[Oligopeptides in plant medicines cited in Chinese Pharmacopoeia].[Pubmed: 28920330]
In total, 23 plant plant medicined containing oligopeptides were cited in Chinese Pharmacopoeia (1 part) of 2015 version including Rubia cordifolia, Linum usitatissimum, Aster tataricus, Psammosilene tunicoides, Pseudostellaria heterophylla, Stellaria dichotoma, Vaccaria segetalis, Dianthus superbus, Celosia argentea, Lycii Cortex, Citrus medica, C. aurantium, Panax ginseng, Parmx notoginseng, Schisandra chinensis, Sparganium stoloniferum, Euryale ferox, Ophiopogon japonicas, Pinellia ternate, Achyranthes bidentata, Physalis alkekengi, Polygonatum odoratum, and Leonuri Fructus. There were 187 oligopeptides in plant medicines above as reported. Oligopeptides consisted mainly of linear peptides and cyclic peptides. The linear peptides included dipeptides, tripeptides and pentapeptides, and cyclic peptides included cyclic, bicyclic and tricyclic peptides. The number of residues of single cyclic peptides ranged from two to twelve. Bicyclic peptides were isolated mainly from R. cordifolia and C. argentea. Modern pharmacological study showed that oligopeptides had many pharmacological effects, including antitumor, anticoagulant, antibacterial, immune suppression and so on.
Protective effect of Aster tataricus extract on retinal damage on the virtue of its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effect in diabetic rat.[Pubmed: 28262614]
Effect of Aster tataricus (AT) was estimated on the retinal injury in diabetic rats by its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity. Streptozotocin (STZ) was used to induce diabetes at a dose of 60mg/kg, i.p. and blood glucose was estimated to confirm the diabetic rats. All the animals were separated in to 5 different groups (n=10) such as control, diabetic retinopathy (DR) receives saline solution, and AT treated group receives AT (100, 200 and 400mg/kg) for the duration of 8 week. After treatment protocol period blood glucose and HbA1c% was estimated in the blood sample of diabetic rats. Retinal tissue was isolated for the fundus photography and retinal vessel diameter, retinal vascular permeability and leukocytosis were estimated. Moreover in the retinal tissue homogenate oxidative stress parameters such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH) and catalase (CAT) and concentration of cytokines (TNFα, IL10) was estimated. Result of the study suggested that root extract of AT contain rich amount of polyphenol in it which significantly reduces the body weight and concentration of glucose in blood in diabetic rats. Fundus photography suggested that AT extract attenuates the structure and functional abnormalities that develops due to diabetes. Retinal leukocytosis and vascular permeability was significantly decreases in AT treated group than DR group. There was significant increase in the activity of GSH, CAT and SOD in AT treated group than DR group. Moreover AT also attenuates the altered concentration of TNFα, IL10 and NF-κB in the retina of STZ induced diabetic rat. Thus present study concludes that root extract of AT effectively manages the diabetic retinopathy by controlling the blood glucose and also by attenuating the altered oxidative stresss and inflammatory mediators such as TNFα, IL10 and NF-κB in the retina of STZ induced diabetic rat.
Simultaneous Determination of Five Components in Aster tataricus by Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry.[Pubmed: 26620425]
A novel quantitative method using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry was developed for simultaneous determination of the important active constituents including shionone, luteolin, quercetin, kaempferol and ferulic acid in Aster tataricus from different habitats. The separation was performed on a C18 column with acidified aqueous acetonitrile gradients. Quantification of the analytes was achieved by the use of a hybrid quadrupole spectrometer. Multiple reaction monitoring scanning was employed with positive and negative modes at the same time in a single run. The validated results of the method indicated that the method was simple, rapid, specific and reliable. The results demonstrated that the quantitative difference in content of five active compounds was useful not only for chemotaxonomy of numerous samples from different sources but also for the standardization and differentiation of several similar samples. It was the first time to report a UPLC-ESI-MS-MS method for determination of five components in A. tataricus extract. Simultaneous quantification of bioactive components by UPLC-ESI-MS could be a well-acceptable strategy to control the quality of A. tataricus extract comprehensively.
Development and validation of an LC/MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of shionone and epi-friedelinol in rat plasma for pharmacokinetic study after oral administration of Aster tataricus extract.[Pubmed: 26581126]
A rapid and sensitive liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) method was developed and validated using spinasterol as the internal standard (IS) for the simultaneous determination of shionone and epi-friedelinol in rat plasma. Plasma samples were pretreated using liquid-liquid extraction with ethyl ether. Chromatographic separation was achieved on a C18 column (100 × 2.1 mm, 5 μm) with an isocratic elution consisting of acetonitrile-0.1% formic acid water (75:25, v/v) at a flow rate of 0.30 mL/min. Detection was performed under the selected reaction monitoring scan using an electrospray ionization in the positive ion mode. The mass transitions were as follows: m/z 427.4 → 95.1 for shionone, m/z 411.4 → 205.2 for epi-friedelinol and m/z 395.3 → 105.2 for IS. All calibration curves exhibited good linearity (r > 0.995) over the concentration range for both components. The intra- and inter-day precisions at three QC and lower limit of quantitation levels were both <10.21% in terms of relative standard deviation, and the accuracy ranged from -7.13 to 8.02% in terms of relative error. The extraction recoveries of the compounds ranged from 82.07 to 89.81%. The developed method was successfully applied to the pharmacokinetic study of shionone and epi-friedelinol after oral administration of Aster tataricus extract to rats.
Expectorant, antitussive, anti-inflammatory activities and compositional analysis of Aster tataricus.[Pubmed: 25701752]
The root of Aster tataricus L. f., recorded in all versions of Chinese Pharmacopoeia, is a traditional Chinese medicine with the function of dispelling phlegm and relieving cough for more than 2000 years. This study was designed to evaluate the expectorant, antitussive, and anti-inflammatory activities of the root of A. tataricus and to explore the chemical substances responsible for these activities.


