4'-HydroxyacetophenoneCAS# 99-93-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 99-93-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 7469 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C8H8O2 | M.Wt | 136.2 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | p-Acetophenol; 4-Hydroxyphenylethanone; p-Hydroxyphenyl methyl ketone; Piceol | ||
| Solubility | Freely soluble in methan | ||
| Chemical Name | 1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethanone | ||
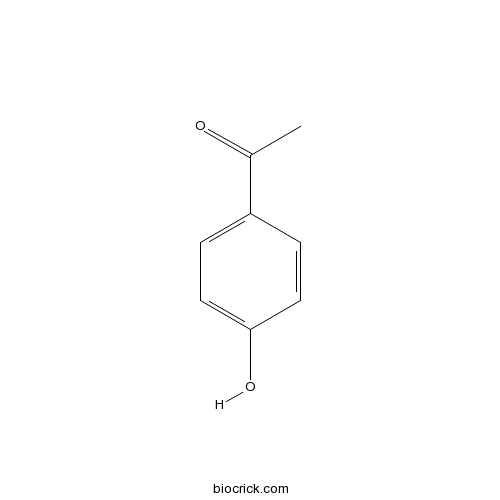
| SMILES | CC(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | TXFPEBPIARQUIG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 4'-Hydroxyacetophenone is a potent xanthine oxidase inhibitor, three 4′-hydroxyacetophenone-related phytoalexins from Polymnia sonchifolia have antifungal activity. |
| Targets | Antifection | Xanthine oxidase |
| In vitro | Inhibition of xanthine oxidase by Rhodiola crenulata extracts and their phytochemicals.[Pubmed: 24712453]J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Apr 30;62(17):3742-9.Using a fractionation technique, four phytochemicals were isolated from Rhodiola crenulata extracts. These compounds were identified as 4'-Hydroxyacetophenone (4-HAP), epicatechin-(4β,8)-epicatechin gallate (B2-3'-O-gallate), salidroside, and p-tyrosol using mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
|
| Structure Identification | J Phys Chem A. 2014 Sep 18;118(37):8170-6.Controlling dissociation of alkyl phenyl ketone radical cations in the strong-field regime through hydroxyl substitution position.[Pubmed: 24576102 ]
Phytochemistry, 1996, 43(5):1019-21.Three 4′-hydroxyacetophenone-related phytoalexins from Polymnia sonchifolia.[Reference: WebLink]Inoculation of sliced yacon tubers with Pseudomonas cichorii resulted in the formation of antifungal compounds. Three major phytoalexins were isolated and identified by spectroscopic methods as 4′-hydroxy-3′-(3-methylbutanoyl)acetophenone, 4′-hydroxy-3′-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)acetophenone and 5-acetyl-2-(1-hydroxy-1-methylethyl)benzofuran. |

4'-Hydroxyacetophenone Dilution Calculator

4'-Hydroxyacetophenone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 7.3421 mL | 36.7107 mL | 73.4214 mL | 146.8429 mL | 183.5536 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.4684 mL | 7.3421 mL | 14.6843 mL | 29.3686 mL | 36.7107 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.7342 mL | 3.6711 mL | 7.3421 mL | 14.6843 mL | 18.3554 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1468 mL | 0.7342 mL | 1.4684 mL | 2.9369 mL | 3.6711 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0734 mL | 0.3671 mL | 0.7342 mL | 1.4684 mL | 1.8355 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 4-Isopropyltoluene
Catalog No.:BCC8282
CAS No.:99-87-6
- Methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate
Catalog No.:BCN4540
CAS No.:99-76-3
- Valproic acid
Catalog No.:BCC4260
CAS No.:99-66-1
- 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4537
CAS No.:99-50-3
- 2-Methyl-5-Isopropenyl-2-Cyclohexenone
Catalog No.:BCC8279
CAS No.:99-49-0
- Chelidonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6547
CAS No.:99-32-1
- Methyl gallate
Catalog No.:BCN3823
CAS No.:99-24-1
- Trehalose
Catalog No.:BCC9182
CAS No.:99-20-7
- Prunasin
Catalog No.:BCN4535
CAS No.:99-18-3
- Ac-DL-Leu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2977
CAS No.:99-15-0
- 3,5-DHBA
Catalog No.:BCC7951
CAS No.:99-10-5
- Fmoc-Arg(Mtr)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3074
CAS No.:98930-01-9
- 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4546
CAS No.:99-96-7
- Fentanyl citrate
Catalog No.:BCC6000
CAS No.:990-73-8
- Imiquimod
Catalog No.:BCC2492
CAS No.:99011-02-6
- Imiquimod hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4196
CAS No.:99011-78-6
- [Ala107]-MBP (104-118)
Catalog No.:BCC5835
CAS No.:99026-77-4
- [Ala113]-MBP (104-118)
Catalog No.:BCC5836
CAS No.:99026-78-5
- Limonexic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4534
CAS No.:99026-99-0
- Kushenol I
Catalog No.:BCN2983
CAS No.:99119-69-4
- Kushenol E
Catalog No.:BCN3348
CAS No.:99119-72-9
- Kushenol C
Catalog No.:BCN3351
CAS No.:99119-73-0
- Yadanzioside I
Catalog No.:BCN6715
CAS No.:99132-95-3
- Yadanzioside L
Catalog No.:BCN6713
CAS No.:99132-97-5
Controlling dissociation of alkyl phenyl ketone radical cations in the strong-field regime through hydroxyl substitution position.[Pubmed:24576102]
J Phys Chem A. 2014 Sep 18;118(37):8170-6.
The hydroxy-substituted alkyl phenyl ketones 2'-, 3'- and 4'- (ortho, meta, and para) hydroxyacetophenone were excited in the strong-field regime with wavelengths ranging from 1200-1500 nm to produce the respective radical cations. For 2'- and 3'-hydroxyacetophenone, the parent molecular ion dominated the mass spectrum, and the intensity of the fragment ions remained unchanged as a function of excitation wavelength. In contrast, 4'-hydroxyacetophenone exhibited depletion of the parent molecular ion with corresponding enhanced formation of the benzoyl fragment ion upon excitation with 1370 nm as compared with other excitation wavelengths. Density functional (DFT) calculations suggest that dissociation occurs when the acetyl group in 4'-hydroxyacetophenone radical cation twists out-of-plane with respect to the phenyl ring, enabling a one-photon transition between the ground cation state D0 and the excited cation state D2 to occur. The DFT calculations also suggest that the lack of dissociation in the wavelength-resolved strong-field excitation measurements for 2'- and 3'-hydroxyacetophenone arises because both isomers have a barrier to rotation about the carbon-carbon bond connecting the phenyl and acetyl groups. These results help elucidate the effects of substituents on the torsional motion of radical cations and illustrate the potential for controlling molecular dissociation through the addition of substituents.
Inhibition of xanthine oxidase by Rhodiola crenulata extracts and their phytochemicals.[Pubmed:24712453]
J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Apr 30;62(17):3742-9.
Using a fractionation technique, four phytochemicals were isolated from Rhodiola crenulata extracts. These compounds were identified as 4'-hydroxyacetophenone (4-HAP), epicatechin-(4beta,8)-epicatechin gallate (B2-3'-O-gallate), salidroside, and p-tyrosol using mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The inhibition of xanthine oxidase (XO) activity by these purified compounds was then evaluated and compared to that of a known XO inhibitor (allopurinol; IC50 = 12.21 +/- 0.27 muM). Both 4-HAP and B2-3'-O-gallate showed an XO inhibitory effect, for which the half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values were 15.62 +/- 1.19 and 24.24 +/- 1.80 muM, respectively. However, salidroside and p-tyrosol did not show significant inhibitory effects on XO at 30 muM. Furthermore, an inhibition kinetics study indicated that 4-HAP and B2-3'-O-gallate are mixed competitive inhibitors. The inhibition constants (Ki) of 4-HAP and B2-3'-O-gallate were 8.41 +/- 1.03 and 6.16 +/- 1.56 muM, respectively. These results suggest that 4-HAP and B2-3'-O-gallate are potent XO inhibitors.


