Callicarpa nudiflora
Callicarpa nudiflora
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Callicarpa nudiflora
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
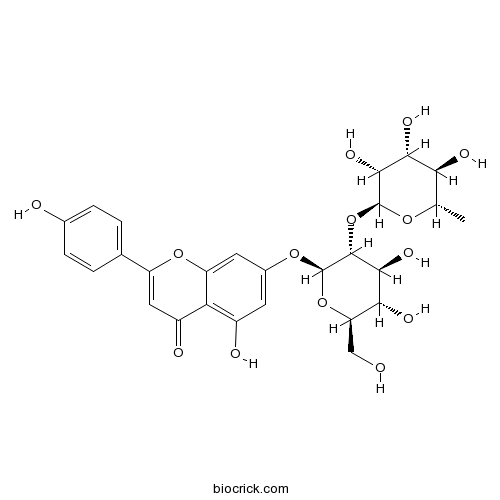
BCN1112
Rhoifolin17306-46-6
Instructions
-
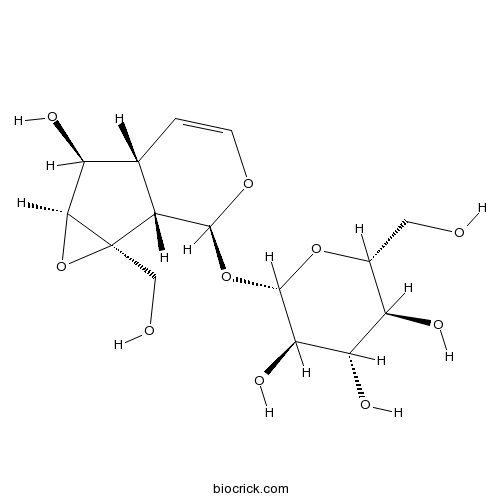
BCN5094
Catalpol2415-24-9
Instructions
-
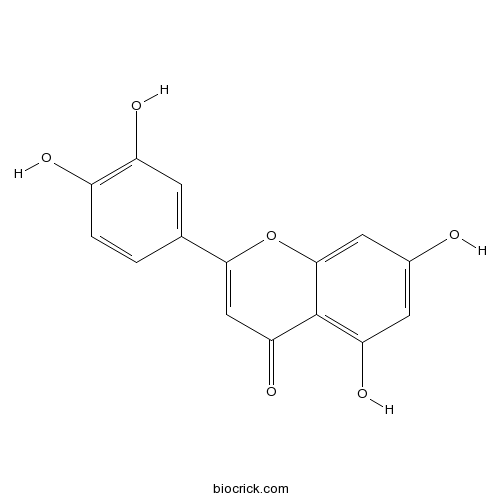
BCN5600
Luteolin491-70-3
Instructions
-
BCN5616
Oleanolic acid508-02-1
Instructions

-
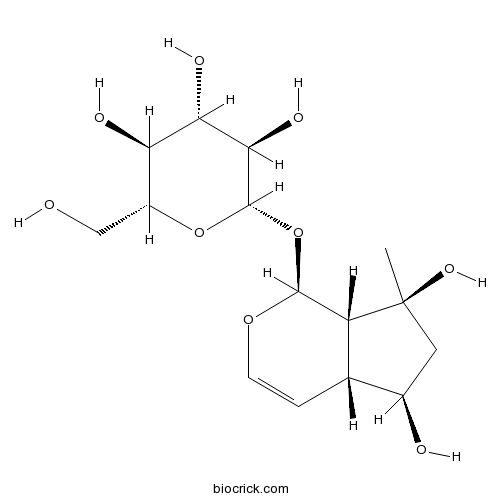
BCN2883
Ajugol52949-83-4
Instructions
-
BCN5388
Luteolin-7-O-glucoside5373-11-5
Instructions

-
BCN4136
Acteoside61276-17-3
Instructions

-
BCN3877
Alpha-caryophyllene6753-98-6
Instructions

-
BCN1205
Forsythoside B81525-13-5
Instructions
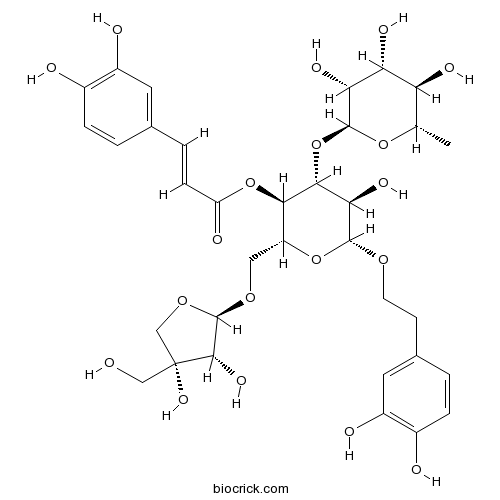
Seco-labdane diterpenoids from the leaves of Callicarpa nudiflora showing nitric oxide inhibitory activity.[Pubmed: 29455054]
Nine previously undescribed seco-labdane diterpenoids, nudiflopenes A-I, were isolated from the leaves of Callicarpa nudiflora. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of extensive 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopic data analysis, and the absolute configurations of these compounds were established by the modified Mosher's method and experimental and calculated electronic circular dichroism spectra. Nudiflopenes A-I belong to the class of seco-labdane diterpenoids. All of the isolates showed inhibitory activities on lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide (NO) production in murine microglial BV-2 cells. The possible mechanism of NO inhibition of some bioactive compounds was also investigated using molecular docking, which revealed interactions of bioactive compounds with the inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) protein.
Two new iridoid glycosides from the leaves of Callicarpa nudiflora.[Pubmed: 28537085]
Two new iridoid glycosides, callicoside C (1) and callicoside D (2), together with three known compounds (3-5), were isolated from the leaves of Callicarpa nudiflora. Their structures were established by 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. In an in vitro bioassay, compound 1 showed pronounced hepatoprotective activity against d-galactosamine-induced toxicity in WB-F344 rat hepatic epithelial stem-like cells.
[Chemical Constituents from Callicarpa nudiflora].[Pubmed: 27356380]
To study the chemical constituents of Callicarpa nudiflora.
Rapid analysis of Callicarpa L. using direct spray ionization mass spectrometry.[Pubmed: 26938160]
Direct spray such as leaf spray and paper spray ionization mass spectrometry (MS) is a powerful type of ambient MS for phytochemical analysis. In this paper, direct spray MS methods to rapidly distinguish and analyze five species of Callicarpa L. have been developed. To distinguish species, leaf spray MS was employed to directly analyze leaves. A small triangular leaf sample was wetted with 15 μL of spray solvent and a high DC voltage was then simply applied to the wet leaf sample, which was positioned in front of the inlet of a mass spectrometer to produce electrospray ionization. The MS signals of phenylpropanoid glycosides, i.e. forsythiaside B, poliumoside, verbascoside in leaves could be sensitively detected. The content characteristics of the phenylpropanoid glycosides in five species including Callicarpae kwangtungensis Folium, Callicarpae macrophyllae Folium, Callicarpa nudiflora Folium, Callicarpae formosanae Folium, Callicarpa longissima Folium could be used to distinguish them, then the mass spectra of the Callicarpa L. samples were analyzed using principal component analysis(PCA) or partial least squares-discriminant analysis(PLS-DA). For the rapid semi-quantitative analysis, of phenylpropanoid glycosides in leaves, paper spray MS was employed to determine phenylpropanoid glycosides in the extracts of Callicarpa L. leaves. Ginsenoside Rg1 was selected as an internal standard (I.S.). The calibration curves were constructed through ratios of target ion abundance to I.S. ion abundance vs. concentration of targets. The linearity range was 8-250 μg/mL (R(2)=0.9947) for forsythiaside B, 9-280 μg/mL (R(2)=0.9939) for verbascoside, and 9-260 μg/mL (R(2)=0.9917) for poliumoside, respectively. The limit of detection (LOD) was 1 μg/mL, 0.5 μg/mL and 1 μg/mL for forsythiaside B, verbascoside, and poliumoside, respectively.
Hepatoprotective iridoid glucosides from Callicarpa nudiflora.[Pubmed: 26507813]
Two new iridoid glucosides, callicoside A (1) and callicoside B (2), were isolated from the leaves of Callicarpa nudiflora. Their structures were elucidated by means of spectroscopic methods and chemical evidences. In an in vitro bioassay, compound 1 showed pronounced hepatoprotective activity against D-galactosamine-induced toxicity in WB-F344 rat hepatic epithelial stem-like cells.
[Study on HPLC fingerprint of Callicarpa nudiflora and determination of ten components].[Pubmed: 26323147]
This study is to establish the HPLC fingerprint and determine eight components of Callicarpa nudiflora, and provide a scientific basis for the identification and quality control. The Waters sunfire C18 column (4.6 mm x 250 mm, 5 µm) was used and the detection wavelength was 330 nm . The column temperature was 30 °C. The mobile phases were acetonitrile (A) and 0.1% formic acid (B) eluting in a gradient program at a flow rate of 1.0 mL · min(-1). The chromatographic fingerprint similarity evaluation system for tradition Chinese medicine(2012) was used for analysis. C. nudiflora from different samples were of high similarity in fingerprint and the separation of ten components was good. There was an obvious difference between other samples and C. nudiflora leaves. In quantitative analysis, the ten components showed good regression(R2 > 0 999 0) with linear ranges, and their recoveries were in the range of 96.0%-105.0%. The established qualitative and quantitative methods are highly specific, simple and accurate, which can be used for the identification and quality control of C. nudiflora.
Simultaneous determination of four active components in rat plasma by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry and its application to a pharmacokinetic study after oral administration of Callicarpa nudiflora extract.[Pubmed: 26246725]
Callicarpa nudiflora has been commonly used as a Chinese folk medicine for resolving toxin, dispersing edema and hemostasis; however, its pharmacokinetic (PK) behavior remains unknown. In our present study, a simple and sensitive ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method was firstly developed on simultaneous determination and PK study of four active components (luteoloside, dracocephaloside, juncein and nudifloside) following the oral administration of C. nudiflora extract to investigate their PK profiles.


