Capsicum annuum
Capsicum annuum
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Capsicum annuum
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
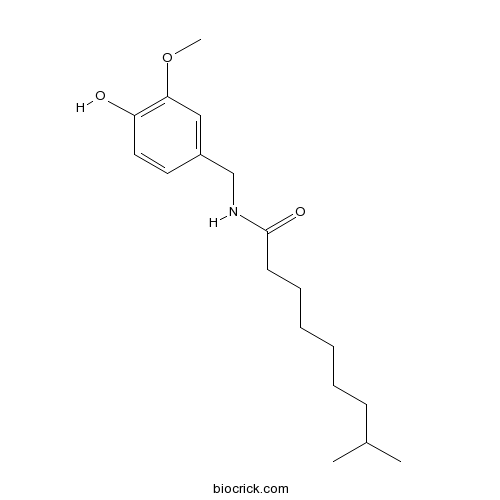
BCN1017
Dihydrocapsaicin19408-84-5
Instructions
-
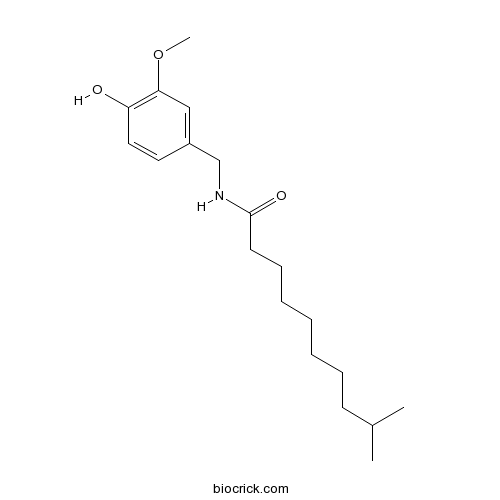
BCN7844
Homodihydrocapsaicin I20279-06-5
Instructions
-
BCN2387
Nordihydrocapsaicin28789-35-7
Instructions

-
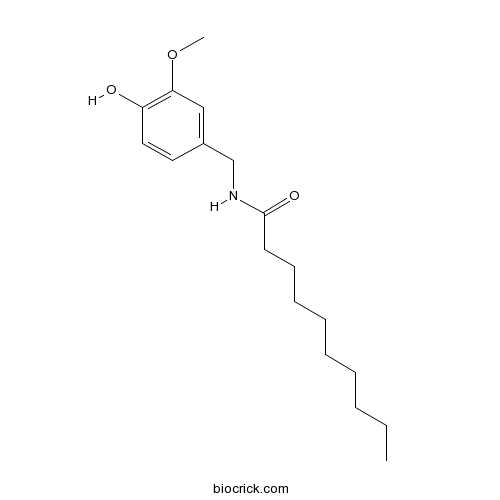
BCN7836
Decylic acid vanillylamide31078-36-1
Instructions
-
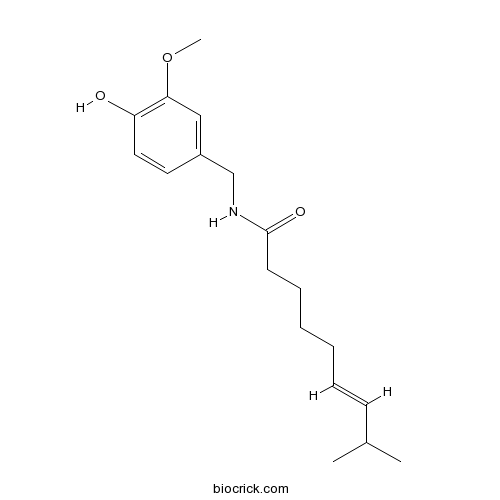
BCN1016
Capsaicin404-86-4
Instructions
Vanadium stimulates pepper plant growth and flowering, increases concentrations of amino acids, sugars and chlorophylls, and modifies nutrient concentrations.[Pubmed: 30092079]
Vanadium (V) can be absorbed by plants and regulate their growth and development, although contrasting effects have been reported among species and handling conditions. The objective of this work was to evaluate the beneficial effect of V on pepper plants (Capsicum annuum L.). The plants were grown in a hydroponic system with the application of four V concentrations (0, 5, 10, and 15 μM NH₄VO₃). Four weeks after the beginning of the treatments, growth, flowering, biomass, chlorophyll concentration, total amino acids, total soluble sugars, and nutrients were determined in leaves, stems, and roots. The application of 5 μM V increased plant growth, induced floral bud development, and accelerated flowering. The chlorophyll concentration varied according to the type of plant part analyzed. The concentrations of amino acids and sugars in leaves and roots were higher with 5 μM. With 10 and 15 μM V, the plants were smaller and showed toxicity symptoms. The K concentration in leaves decreased as the V dose increased (0 to 15 μM). However, 5 μM V increased the concentrations of N, P, K, Ca, Mg, Cu, Mn, and B, exclusively in stems. The application of 15 μM V decreased the concentrations of Mg and Mn in leaves, but increased those of P, Ca, Mg, Cu, and B in roots. We conclude that V has positive effects on pepper growth and development, as well as on the concentrations of amino acids and total sugars. V was antagonistic with K, Mg, and Mn in leaves, while in stems and roots, there was synergism with macro and micronutrients. Vanadium is a beneficial element with the potential to be used in biostimulation approaches of crops like pepper.
Characterization and classification of Spanish paprika (Capsicum annuum L.) by liquid chromatography coupled to electrochemical detection with screen-printed carbon-based nanomaterials electrodes.[Pubmed: 30086921]
Screen-printed electrodes based on graphite, carbon nanotubes, carbon nanofibers, and graphene were tested as amperometric detectors for the determination of phenolic compounds by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The chromatographic performance as well as the obtained sensitivity, detection and quantification limits suggest that carbon nanofibers modified screen-printed electrode (SPCE-CNF) is the amperometric sensor that provides the best analytical performance. Upon this confirmation, chromatographic data obtained using SPCE-CNF were exploited by means of linear discriminant analysis (LDA) to successfully characterize and classify 96 Spanish paprika (Capsicum annuum L.) samples with different origin and type: from La Vera (including sweet, bittersweet and spicy types) and from Murcia (including sweet and spicy types).


