Cedrus deodara
Cedrus deodara
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Cedrus deodara
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
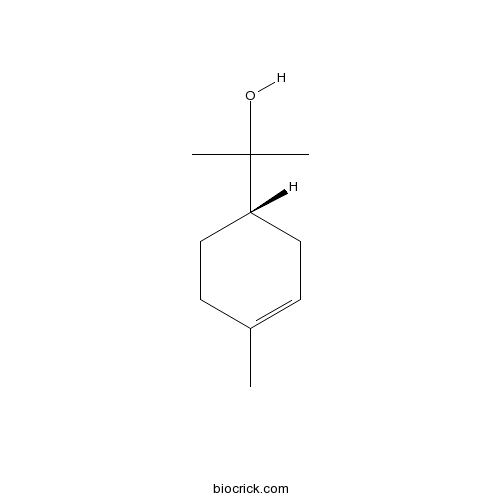
BCN8136
Alpha-Terpineol10482-56-1
Instructions
-
BCN1247
Isorhamnetin-3-O-beta-D-Glucoside5041-82-7
Instructions

-
BCN5687
Magnolol528-43-8
Instructions

-
BCN5692
Myricetin529-44-2
Instructions

Antioxidant Effects of Four Heartwood Extractives on Midgut Enzyme Activity in Heterotermes indicola (Blattodea: Rhinotermitidae).[Pubmed: 29528387]
Heterotermes indicola (Wasmann) (Blattodea: Rhinotermitidae) is a species of subterranean termite that is a destructive pest of wood and wood products in Pakistan. This study evaluated the antioxidant and antienzyme potential of heartwood extractives against H. indicola. Heartwood extractives of four durable wood species, Tectona grandis (L.f), Dalbergia sissoo (Roxb.), Cedrus deodara (Roxb.), and Pinus roxburghii (Sarg.) were removed from wood shavings via soxhlet extraction with an ethanol:toluene solvent system. The antioxidant potential of the extractive compounds was determined using the DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) radical scavenging test. Results showed maximum antioxidant activity for extractives of D. sissoo. D. sissoo had the lowest IC50 (the concentration where 50% inhibition of the DPPH radical is obtained) at 28.83 µg/ml among the heartwood extractives evaluated. This antioxidant activity, however, was not concentration dependent as was observed in the other heartwood extractives tested. At the maximum test concentration, T. grandis showed the highest percent inhibition at 89.7%, but this inhibition was lower compared to the positive control antioxidant compounds butylated hydroxytoluene and quercetin. When termites were fed filter paper treated with IC50s of the extractives and control compounds, glutathione S-transferase activity in the guts of H. indicola workers was significantly reduced by T. grandis and D. sissoo extractives. Similarly, esterase activity was reduced more by P. roxburghii extractives compared to control antioxidant treatments and other tested extractives. However, none of the extractives examined significantly reduced the activity of catalase enzymes in H. indicola compared to treatments with the antioxidant control compounds.
Impact and ecosystem service of forest and sacred grove as saviour of water quantity and quality in Garhwal Himalaya, India.[Pubmed: 28852894]
The present study was conducted in environs of the sacred grove of Garhwal Himalaya, India, with a view to assess the impacts of sacred groves and forests on the quality and quantity of water and also to assess the effect of seasonality on perennial stream quality. Water samples were collected from three randomly selected stream spots of both the sacred grove dominated by deodar (Cedrus deodara) and the non-sacred patch dominated by oak (Quercus leucotrichophora). Water samples from both patches were within the World Health Organization (WHO) standard limits. Based on an already established water quality index, water quality of both patches was safe for domestic and irrigation purposes but needs treatment for drinking purposes. Results of the present study also showed a very prominent impact of forest type as well as management condition on water quality and quantity. The water discharge from an oak forest shows more consistency than the discharge from a deodar forest. Due to the presence of the sacred grove, the area has become the source of good quality water supply during lean season for the surrounding villages. Water quality and quantity differed along with the change in season. The sacred grove and the existing forest leave a great impression on local dwellers, as due to its presence, local dwellers never run out of water supply during the dry season. As a result, the villagers sincerely want to protect the area for the sake of their own well-being.
Classification and ordination of understory vegetation using multivariate techniques in the Pinus wallichiana forests of Swat Valley, northern Pakistan.[Pubmed: 28271176]
An understory vegetation survey of the Pinus wallichiana-dominated temperate forests of Swat District was carried out to inspect the structure, composition and ecological associations of the forest vegetation. A quadrat method of sampling was used to record the floristic and phytosociological data necessary for the analysis using 300 quadrats of 10 × 10 m each. Some vegetation parameters viz. frequency and density for trees (overstory vegetation) as well as for the understory vegetation were recorded. The results revealed that in total, 92 species belonging to 77 different genera and 45 families existed in the area. The largest families were Asteraceae, Rosaceae and Lamiaceae with 12, ten and nine species, respectively. Ward's agglomerative cluster analysis for tree species resulted in three floristically and ecologically distinct community types along different topographic and soil variables. Importance value indices (IVI) were also calculated for understory vegetation and were subjected to ordination techniques, i.e. canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) and detrended correspondence analysis (DCA). DCA bi-plots for stands show that most of the stands were scattered around the centre of the DCA bi-plot, identified by two slightly scattered clusters. DCA for species bi-plot clearly identified three clusters of species revealing three types of understory communities in the study area. Results of the CCA were somewhat different from the DCA showing the impact of environmental variables on the understory species. CCA results reveal that three environmental variables, i.e. altitude, slope and P (mg/kg), have a strong influence on distribution of stands and species. Impact of tree species on the understory vegetation was also tested by CCA which showed that four tree species, i.e. P. wallichiana A.B. Jackson, Juglans regia Linn., Quercus dilatata Lindl. ex Royle and Cedrus deodara (Roxb. ex Lamb.) G. Don, have strong influences on associated understory vegetation. It is therefore concluded that Swat District has various microclimatic zones with suitable environmental variables to support distinct flora.
Locational comparison of essential oils from selected conifers of Himachal Pradesh.[Pubmed: 28095708]
Nine samples of essential oil from needles of three conifers of Pinacea family namely Abies pindrow, Picea smithiana and Cedrus deodara collected from three different locations of Himachal Pradesh (India) were evaluated using gas chromatography and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. A total of 31, 17 and 13 compounds were identified from essential oil of A. pindrow, P. smithiana and C. deodara, respectively. Among the characterised components, monoterpenoid hydrocarbons were predominated. α-Pinene, β-pinene, β-merycene, limonene and camphene were characterised as major components. Oil of C. deodara has significant effect of location on its oil composition. Principle component analysis on gas chromatographic data reveals variation in chemical composition which may be attributed to altitude and environmental conditions.
An antidiabetic polyherbal phytomedicine confers stress resistance and extends lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans.[Pubmed: 27853905]
An Ayurvedic polyherbal extract (PHE) comprising six herbs viz. Berberis aristata, Cyperus rotundus, Cedrus deodara, Emblica officinalis, Terminalia chebula and Terminalia bellirica is mentioned as an effective anti-hyperglycemic agent in 'Charaka Samhita', the classical text of Ayurveda. Previously, antidiabetic drug metformin was found to elicit antiaging effects and PHE was also found to exhibit antidiabetic effects in humans. Therefore, we screened it for its in vivo antioxidant antiaging effect on stress and lifespan using human homologous Caenorhabditis elegans model system. The effect on aging is evaluated by studying effect of PHE on mean survival in worms. The stress modulatory potential was assessed by quantification of intracellular ROS level, autofluorescent age pigment lipofuscin, oxidative and thermal stress assays. Additionally, stress response was quantified using gene reporter assays. The 0.01 µg/ml dose of PHE was able to enhance mean lifespan by 16.09% (P < 0.0001) in C. elegans. Furthermore, PHE treated worms demonstrated oxidative stress resistance in both wild type and stress hypersensitive mev-1 mutant along with upregulation of stress response genes sod-3 and gst-4. The delayed aging under stress can be attributed to its direct reactive oxygen species-scavenging activity and regulation of some age associated genes like daf-2, daf-16, skn-1, sod-3 and gst-4 in wild-type worms. Additonally, PHE delayed age related paralysis phenotype in CL4176 transgenic worms. Altogether, our results suggest PHE significantly improves the oxidative stress and life span in C. elegans. Overall the present study suggests this polyherbal formulation might play important role in regultaing aging and related complications like diabetes.
A dual antibacterial mechanism involved in membrane disruption and DNA binding of 2R,3R-dihydromyricetin from pine needles of Cedrus deodara against Staphylococcus aureus.[Pubmed: 27719936]
The antibacterial activity and mechanism of 2R,3R-dihydromyricetin (DMY) against Staphylococcus aureus were investigated. The minimum inhibitory concentration of DMY against S. aureus was 0.125mg/ml, and the growth inhibitory assay also revealed that DMY showed a potent antibacterial activity against S. aureus. Massive nucleotide leakage and flow cytometric analysis demonstrated that DMY disrupted the membrane integrity of S. aureus. Morphological changes and membrane hyperpolarization of S. aureus cells treated with DMY further suggested that DMY destroyed cell membrane. Meanwhile, DMY probably interacted with membrane lipids and proteins, causing a significant reduction in membrane fluidity and changes in conformation of membrane protein. Moreover, DMY could interact with S. aureus DNA through the groove binding mode. Overall, the results suggested that DMY could be applied as a candidate for the development of new food preservatives as it achieved bactericidal activity by damaging cell membrane and binding to intracellular DNA.
Antibacterial Activity and Membrane-Disruptive Mechanism of 3-p-trans-Coumaroyl-2-hydroxyquinic Acid, a Novel Phenolic Compound from Pine Needles of Cedrus deodara, against Staphylococcus aureus.[Pubmed: 27548123]
Recently, we reported that a novel phenolic compound isolated from Cedrus deodara, 3-p-trans-coumaroyl-2-hydroxyquinic acid (CHQA), exhibits a potent antioxidant activity. The present study aimed to evaluate the antibacterial activity of CHQA against eleven food-borne pathogens and to elucidate its mechanism of action against Staphylococcus aureus. The results from minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) determinations showed that CHQA exhibited moderate inhibitory effects on all of the tested pathogens with MIC values ranging from 2.5-10 mg/mL. Membrane potential measurements and flow cytometric analysis demonstrated that CHQA damaged the cytoplasmic membrane of S. aureus, causing a significant membrane hyperpolarization with a loss of membrane integrity. Moreover, CHQA induced an increase in membrane fluidity and conformational changes in membrane protein of S. aureus, suggesting that CHQA probably acts on the cell membrane by interactions with membrane lipid and protein. Transmission electron microscopic observations further confirmed that CHQA disrupted the cell membrane of S. aureus and caused severe morphological changes, which even led to leakage of intracellular constituents. These findings indicated that CHQA could have the potential to serve as a natural antibacterial agent to control and prevent the growth of pathogens in food and in food-processing environments.


