Cimicifuga foetida
Cimicifuga foetida
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.

Natural products/compounds from Cimicifuga foetida
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN8709
Asiaticoside B125265-68-1
Instructions

-
BCN6528
Cimicidanol 3-O-alpha-L-arabinoside161207-05-2
Instructions

-
BCN7853
Cimifugin 4'-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside1632110-81-6
Instructions

-
BCN1159
Actein18642-44-9
Instructions

-
BCN2906
26-Deoxycimicifugoside214146-75-5
Instructions

-
BCN5174
Cimigenoside27994-11-2
Instructions

-
BCN5979
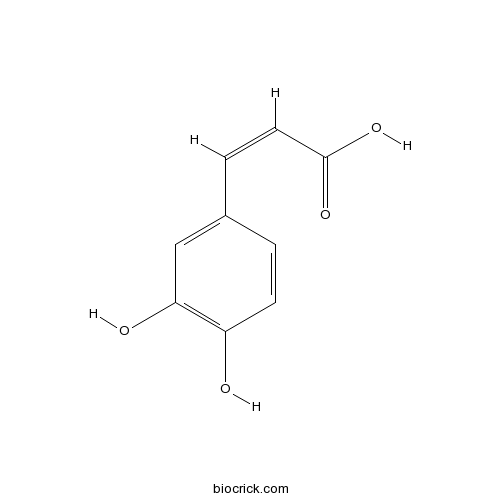
Caffeic acid331-39-5
Instructions
-
BCN5433
Cimifugin37921-38-3
Instructions

-
BCN1447
Acetylcimigenol 3-O-alpha-L-arabinopyranside402513-88-6
Instructions

-
BCN5540
Bergenin477-90-7
Instructions

-
BCN5897
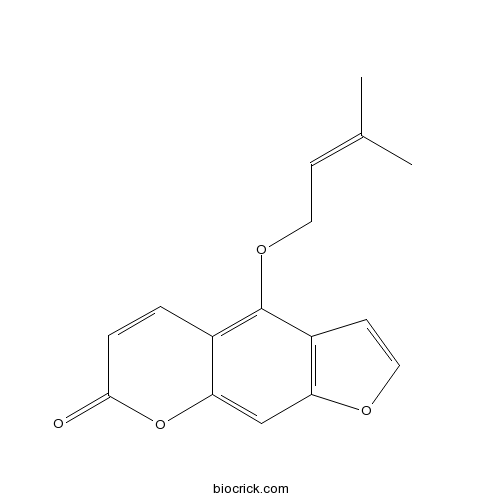
Isoimperatorin482-45-1
Instructions
-
BCX1035
Isoferulic Acid537-73-5
Instructions

Cimitriteromone A-G, Macromolecular Triterpenoid-Chromone Hybrids from the Rhizomes of Cimicifuga foetida.[Pubmed: 30044102]
None
Influence of hormone therapy or C. foetida extract on breast tenderness in postmenopausal women.[Pubmed: 29542344]
To evaluate the prevalence of breast tenderness in a population treated with menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) or Cimicifuga foetida extract.
Efficacy and safety evaluation of Cimicifuga foetida extract in menopausal women.[Pubmed: 29198157]
The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of long-term treatment with Cimicifuga foetida extract in menopausal women.
Actein ameliorates hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in high fat diet-induced NAFLD by regulation of insulin and leptin resistant.[Pubmed: 29156528]
Insulin and leptin resistance are highly involved in metabolic syndrome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Presently, no approved treatment is available. Actein is isolated from the rthizomes of Cimicifuga foetida, a triterpene glycoside, exhibiting important biological properties, such as anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and anti-oxidant activity. However, its effects on metabolic syndrome are poorly understood. The aims of the study were mainly to investigate the molecular mechanisms regulating insulin and leptin resistance, and lipogenic action of actein in high fat diet-fed mice. Our data indicated that actein-treated mice displayed lower body weight, epididymal and subcutaneous fat mass, as well as serum lipid levels. Also, improved insulin and leptin resistance were observed in actein-treated groups. Liver inflammation and fibrosis triggered by high fat diet were decreased for actein administration. Moreover, hepatic lipid accumulation was also reduced by actein along with reductions of hepatic de novo lipogenesis-linked signals in actein-treated rodents with high fat diet. High fat diet-induced activation of insulin receptor substrate 1/Forkhead box protein O1 (IRS1/FOXO1), Janus kinase 2 gene/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK2/STAT3) and Protein Kinase B/Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (AKT/GSK3β) pathways in liver was inhibited by actein, a potential mechanism by which hyperinsulinemia, hyperleptindemia and dyslipidemia were attenuated. Thus, the findings above might be of nutritional and therapeutic importance for the treatment of NAFLD.
Actein induces apoptosis in leukemia cells through suppressing RhoA/ROCK1 signaling pathway.[Pubmed: 29039493]
Actein is a tetracyclic triterpenoid compound, extracted from the rhizome of Cimicifuga foetida, exhibiting anticancer activities as previously reported. However, the effects of actein on human leukemia have not been explored before. In this study, the role of actein in regulating apoptosis induction in human leukemia cells was investigated. Actein administration significantly enhanced apoptosis, especially in human leukemia cell line of U937 and the primary human leukemia cells. The promotion was accompanied by caspase-9, caspase-3 and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage, and cytochrome c (Cyto-c) release. Additionally, translocation of Bax into mitochondria was increased by actein, while anti-apoptotic signals of myeloid cell leukemia-1 (Mcl-1) and B cell CLL/lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) were decreased, accompanied by reduced phosphorylated Bcl-2-associated death promoter (Bad). Furthermore, protein kinase B (AKT) activation was downregulated by actein treatment in U937 cells. RhoA, but not caspase-3, regulated Rho kinase 1 (ROCK1) expression induced by actein. Suppression of RhoA and ROCK1 reduced ROCK1 expression, caspase-9, caspase-3 and PARP cleavage. In contrast, AKT inactivity enhanced apoptosis levels, as well as caspase signaling pathway expression. The anticancer role of actein was potentiated by inactivating AKT. In vivo, U937-bearing tumor growth was suppressed by actein, which was related to ROCK1 suppression, AKT dephosphorylation and apoptosis induction. These results indicated that actein has a suppressive role in human leukemia progression through inactivating RhoA/ROCK1 and inducing caspases.
Cimicifoetones A and B, Dimeric Prenylindole Alkaloids as Black Pigments of Cimicifuga foetida.[Pubmed: 28393490]
None


