Cinnamomum camphora
Cinnamomum camphora
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Cinnamomum camphora
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
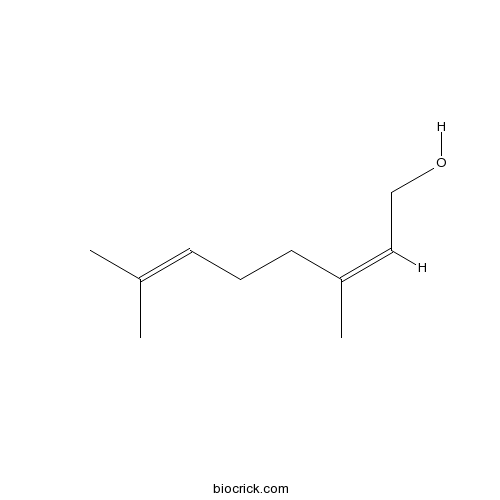
BCN8517
Nerol106-25-2
Instructions
-
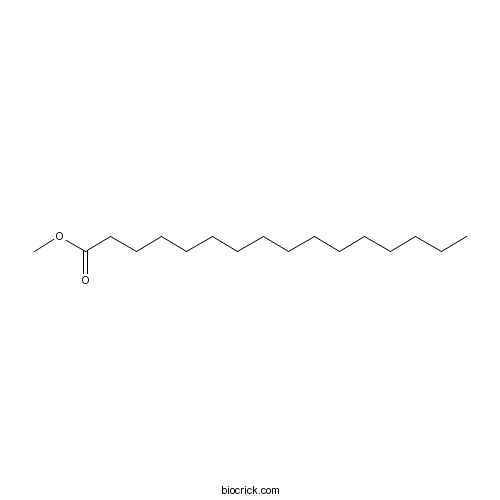
BCN8290
Methyl hexadecanoate112-39-0
Instructions
-
BCN1247
Isorhamnetin-3-O-beta-D-Glucoside5041-82-7
Instructions

-
BCN5616
Oleanolic acid508-02-1
Instructions

-
BCN2594
Sesamol533-31-3
Instructions

-
BCN6527
Perillen539-52-6
Instructions

-
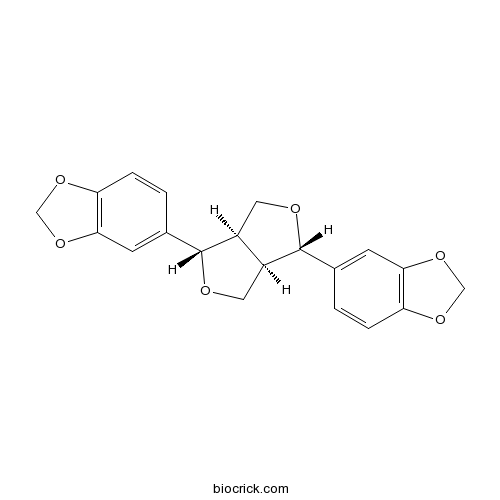
BCN4123
Sesamin607-80-7
Instructions
-
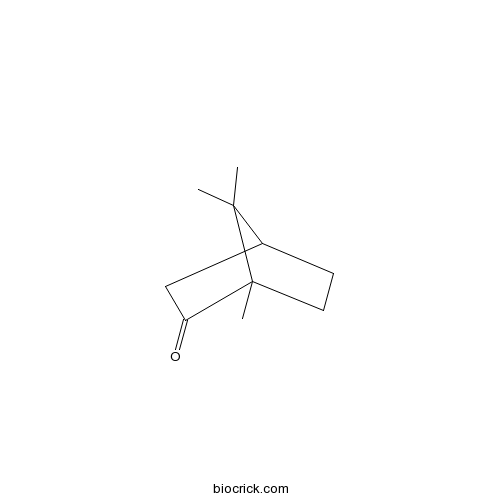
BCN8297
Camphor76-22-2
Instructions
Identification and Field Evaluation of the Sex Pheromone of Orthaga achatina (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae).[Pubmed: 30094705]
Orthaga achatina (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) is the most serious pest in south China of camphor trees, Cinnamomum camphora (L.) Presl, an important urban tree species. Gas chromatography-electroantennographic detection (GC-EAD) of the sex pheromone of O. achatina showed three EAD-active components. Coupled gas chromatography/mass spectrometry analyses identified these as (Z)-11-hexadecenol (Z11-16:OH), (Z)-11-hexadecenyl acetate (Z11-16:OAc), and (3Z,6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)-tricosapentaene (Z3,Z6,Z9,Z12,Z15-23:H). In field tests using different combinations of the three compounds, male moths were attracted to a mixture of Z11-16:OAc and Z3,Z6,Z9,Z12,Z15-23:H, but less attracted to other blends. Further field tests with different ratios of the two compounds determined the optimal ratio of the binary blend as 500:250. The addition of Z11-16:OH to Z11-16:OAc, or to the binary mixture of Z11-16: OAc and the pentaene did not yield higher catches. This shows that O. achatina uses a mixture of Type I and Type II sex pheromone components. Orthaga achatina is the third Pyraloidea species found to utilize Z3,Z6,Z9,Z12,Z15-23:H as a sex pheromone component.
Algicidal properties of extracts from Cinnamomum camphora fresh leaves and their main compounds.[Pubmed: 30077157]
Plant allelochemicals are considered as the source of effective, economic and friendly-environmental algaecides. To uncover the anti-algal activities of Cinnamomum camphora fresh leaves and their main algicidal agents, we investigated the inhibitory effects of water and methanol extracts from C. camphora fresh leaves on Microcystis aeruginosa and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cell growth, analyzed the composition of the water and methanol extracts, and determined the main compounds in extracts on the growth of the two algae and their anti-algal mechanism from photosynthetic abilities. Water and methanol extracts from C. camphora fresh leaves can inhibit M. aeruginosa and C. reinhardtii cell growth, and methanol extracts showed stronger inhibitory effects, due to their more compounds and higher molar concentration. There were 23 compounds in the water extracts, mainly including terpenoids, esters, alcohols, and ketones. Compared to the water extracts, 9 new compounds were detected in the methanol extracts, and the molar concentration of total compounds in methanol extracts increased by 1.3 folds. Camphor, α-terpineol and linalool were 3 main compounds in the water and methanol extracts. Their mixture (1: 3: 6) and individual compound showed remarkable inhibition on M. aeruginosa and C. reinhardtii cell growth. The degradation of photosynthetic pigments and the reduction of maximum quantum yield of photosystem II (PSII) photochemistry, coefficient of photochemical quenching as well as apparent electron transport rate in C. reinhardtii cells aggravated gradually with increasing the concentration of the mixture and individual compound, while the non-photochemical dissipation of absorbed light energy increased gradually, which led to the decline of photosynthetic abilities. This indicated that camphor, α-terpineol and linalool were 3 main algicidal agents in C. camphora fresh leaf extracts, and they inhibited algal growth by inducing photosynthetic pigment degradation and declining PSII efficiency. Therefore, C. camphora fresh leaf extracts and their main components have potential utilization values as algaecides.
Transcriptome analysis and identification of genes related to terpenoid biosynthesis in Cinnamomum camphora.[Pubmed: 30041601]
Cinnamomum camphora has been cultivated as an economically important tree for its medicinal and aromatic properties. Selective breeding has produced Cinnamomum plants for special uses, including spice strains with characteristic flavors and aromas and high-potency medicinal cultivars. The molecular biology underlying terpenoid biosynthesis is still unexplored.
Changes in soil microbial community structure and function after afforestation depend on species and age: Case study in a subtropical alluvial island.[Pubmed: 29996439]
It is well established that land use change can have a profound impact on soil physicochemical properties but the associated changes in soil microbial communities are poorly understood. We used long-term research sites in a subtropical alluvial island of eastern China to measure changes in soil physicochemical properties and microbial community abundance and composition (via phospholipid fatty acid (PLFA) analysis) and function (via extracellular enzyme activity) across different land use types developed on the same soil matrix, including a camphor (Cinnamomum camphora) plantation, a chronosequence of differently aged dawn redwood (Metasequoia glyptostroboides) plantings, a deforested land and a rice paddy. We hypothesized that afforestation could improve soil quality by enhancing carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) contents, microbial biomass and enzyme activities, but that this effect would vary depending on forest age and tree species. Soil C and N concentrations, PLFA abundances and activities of decomposition enzymes (β-glucosidase, urease, alkaline phosphatase and catalase) in older plantations all increased significantly compared to cropland. These variables changed little or decreased in deforested land compared to cropland. These variables also increased with planting age in the dawn redwood plantings. Soils under camphor plantations had higher soil nutrient contents, microbial biomass and lower enzyme activities than dawn redwood soils with similar age. We also found some significant relationships between soil chemical and biological properties: PLFA abundances were positively related to soil organic matter (SOM) contents; the fungal-to-bacterial ratio and fungal relative abundance were correlated positively with SOM contents and negatively with C/N ratio; both soil PLFA abundances and enzyme activities were positively linked with soil inorganic N content and potential net N mineralization rate; ratio of specific C, N and P (phosphorus) acquisition activities was limited to 10: 1: 10 across land use types. Our study underscores the fact that land use type can have a profound impact on soil microbial communities; in addition, tree species and planting age also play significant roles in afforestation.
Inhibitory effects of extracts from Cinnamomum camphora fallen leaves on algae.[Pubmed: 29944120]
None
Investigation of constituents from Cinnamomum camphora (L.) J. Presl and evaluation of their anti-inflammatory properties in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages.[Pubmed: 29660467]
Cinnamomum camphora (L.) J. Presl has been used for the traditional medicine as a therapeutic agent of inflammation-related diseases, including sprains, rheumatic arthritis, abdominal pain, cough and bronchitis, for a long history. The aim of the present study was to illustrate anti-inflammatory substances of C. camphora and their mechanism of action, and to establish the correlations between chemical constituents and traditional uses of this plant.
Temporal changes of fine root overyielding and foraging strategies in planted monoculture and mixed forests.[Pubmed: 29454355]
Mixed forests are believed to enhance ecosystem functioning and sustainability due to complementary resource use, environmental benefits and improved soil properties. The facilitation between different species may induce overyielding. Meanwhile, the species-specific fine root foraging strategies and tradeoffs would determine the structure and dynamics of plant communities. Here the aim was to investigate the admixing effects of fine-root biomass, vertical distribution and morphology in Pinus massoniana-Cinnamomum camphora mixed plantations and corresponding monocultures at 10-, 24- and 45-year old stands.


