CamphorCAS# 76-22-2 |
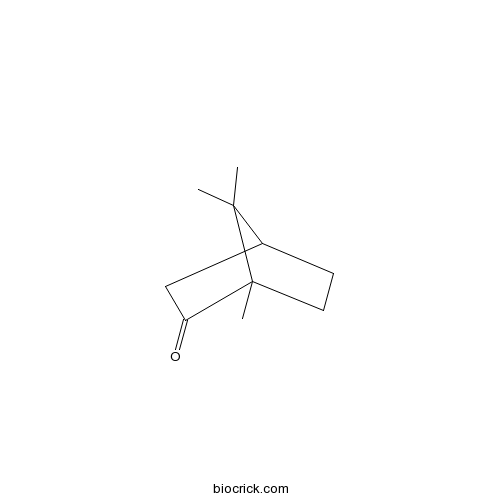
- (-)-Camphor
Catalog No.:BCN7160
CAS No.:464-48-2
- (+)-Camphor
Catalog No.:BCN7161
CAS No.:464-49-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 76-22-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2537 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C10H16O | M.Wt | 152.23 |
| Type of Compound | Isoprenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Freely soluble in chloroform and ethanol; slightly soluble in water | ||
| Chemical Name | 4,7,7-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-3-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1(C2CCC1(C(=O)C2)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DSSYKIVIOFKYAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H16O/c1-9(2)7-4-5-10(9,3)8(11)6-7/h7H,4-6H2,1-3H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Camphor Dilution Calculator

Camphor Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.569 mL | 32.845 mL | 65.6901 mL | 131.3801 mL | 164.2252 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.3138 mL | 6.569 mL | 13.138 mL | 26.276 mL | 32.845 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6569 mL | 3.2845 mL | 6.569 mL | 13.138 mL | 16.4225 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1314 mL | 0.6569 mL | 1.3138 mL | 2.6276 mL | 3.2845 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0657 mL | 0.3285 mL | 0.6569 mL | 1.3138 mL | 1.6423 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Pancreatic Polypeptide (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5711
CAS No.:75976-10-2
- 11-Hydroxycanthin-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN3104
CAS No.:75969-83-4
- [Nle4,D-Phe7]-α-MSH
Catalog No.:BCC5963
CAS No.:75921-69-6
- Bay 65-1942 R form
Catalog No.:BCC1410
CAS No.:758683-21-5
- 1-(3,5-Di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(2-(3-hydroxypropylamino)-5,6-dimethyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)ethanone
Catalog No.:BCC1481
CAS No.:758679-97-9
- Rimcazole dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7090
CAS No.:75859-03-9
- Dehydroevodiamine Chloride
Catalog No.:BCN6651
CAS No.:75853-60-0
- Momordicoside A
Catalog No.:BCC8340
CAS No.:75801-95-5
- Prosapogenin CP4
Catalog No.:BCN2534
CAS No.:75799-18-7
- ADX 10059 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6171
CAS No.:757949-98-7
- 3-Acetoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCC9200
CAS No.:7578-68-9
- Cedrusin
Catalog No.:BCN4307
CAS No.:75775-36-9
- Triamcinolone Acetonide
Catalog No.:BCC3871
CAS No.:76-25-5
- Oxymorphone
Catalog No.:BCC5255
CAS No.:76-41-5
- Bornyl isobutyrate
Catalog No.:BCC8134
CAS No.:50277-27-5
- Rhynchophylline
Catalog No.:BCN4979
CAS No.:76-66-4
- Neoquassine
Catalog No.:BCN3120
CAS No.:76-77-7
- Quassin
Catalog No.:BCN4315
CAS No.:76-78-8
- Tephrosin
Catalog No.:BCN4742
CAS No.:76-80-2
- Trityl Chloride
Catalog No.:BCC2805
CAS No.:76-83-5
- Mepenzolate Bromide
Catalog No.:BCC3809
CAS No.:76-90-4
- Conopharyngine
Catalog No.:BCN3975
CAS No.:76-98-2
- H-DL-Nva-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3303
CAS No.:760-78-1
- Lanatin
Catalog No.:BCC8194
CAS No.:76026-24-9
Regulation of Camphor Metabolism: Induction and Repression of Relevant Monooxygenases in Pseudomonas putida NCIMB 10007.[Pubmed:29735926]
Microorganisms. 2018 May 7;6(2). pii: microorganisms6020041.
For the first time, the differential rates of synthesis of all the key monooxygenases involved in the catabolism by Pseudomonas putida NCIMB 10007 of bicyclic (rac)-Camphor to (2,5)-3,4,4-trimethylpimelyl-CoA, the first aliphatic pathway intermediate, have been determined to help establish the relevant induction profile of each of the oxygen-dependent enzymes. The efficacy of both relevant substrates and pathway metabolites as inducers has been established. Further, inhibitors with characterised functionality have been used to indicate that the pertinent regulatory controls operate at the level of transcription of the corresponding genes.
Organic UV filters exposure induces the production of inflammatory cytokines in human macrophages.[Pubmed:29710614]
Sci Total Environ. 2018 Sep 1;635:926-935.
Organic ultraviolet (UV) filters, found in many personal care products, are considered emerging contaminants due to growing concerns about potential long-term deleterious effects. We investigated the immunomodulatory effects of four commonly used organic UV filters (2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzophenone, BP-3; 4-methylbenzylidene Camphor, 4-MBC; 2-ethylhexyl 4-methoxycinnamate, EHMC; and butyl-methoxydibenzoylmethane, BDM) on human macrophages. Our results indicated that exposure to these four UV filters significantly increased the production of various inflammatory cytokines in macrophages, particular tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). After exposure to the UV filters, a significant 1.1-1.5 fold increase were found in TNF-alpha and IL-6 mRNA expression. In addition, both the p38 MAPK and the NF-kappaB signaling pathways were enhanced 2 to 10 times in terms of phosphorylation after exposure to the UV filters, suggesting that these pathways are involved in the release of TNF-alpha and IL-6. Molecular docking analysis predicted that all four UV filter molecules would efficiently bind transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1), which is responsible for the activation of the p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways. Our results therefore demonstrate that exposure to the four organic UV filters investigated may alter human immune system function. It provides new clue for the development of asthma or allergic diseases in terms of the environmental pollutants.
Identification, contribution, and estrogenic activity of potential EDCs in a river receiving concentrated livestock effluent in Southern Taiwan.[Pubmed:29709864]
Sci Total Environ. 2018 Sep 15;636:464-476.
We assessed 22 selected endocrine-disrupting compounds (EDCs) and other emerging, potentially endocrine-active compounds with estrogenic activity from the waters of the Wuluo River, southern Taiwan. This watershed receives high amounts of livestock and untreated household wastewaters. The river is surrounded by concentrated animal feedlot operations (CAFOs). River water samples were analyzed for selected compounds by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), T47D-KBluc reporter gene assay, and E-screen cell proliferation in vitro bioassay. Total concentrations of summation operatoralkylphenolic compounds (bisphenol A, 4-nonylphenol, t-nonylphenol, octylphenol, nonylphenol mono-ethoxylate, nonylphenol di-ethoxylate) were much higher than summation operatorestrogens (estrone, 17 beta-estradiol, estriol, 17ss-ethynylestradiol, diethylstilbestrol), summation operatorpreservatives (methyl paraben, ethyl paraben, propyl paraben, butyl paraben), summation operatorUV-filters (benzophenone, methyl benzylidene Camphor, benzophenone-3), summation operatorantimicrobials (triclocarben, triclosan, chloroxylenol), and an insect repellent (diethyltoluamide) over four seasonal sampling periods. The highest concentration was found for bisphenol A with a mean of 302ng/L. However, its contribution to estrogenic activity was not significant due to its relatively low estrogenic potency. Lower detection rates were found for BP, EE2, TCS, and PCMX, while DES and EP were not detected. E1 and E2 levels in raw water samples were 50% higher than the predicted no-effect concentrations (PNEC) for aquatic organisms of 6 and 2ng/L, respectively. The potency of estrogenic activity ranged from 11.7 to 190.1ng/L E2T47D-Kbluc and 6.63 to 84.5ng/L E2E-Screen for extracted samples. Importantly, estrone contributed 50% of the overall activity in 60% and 44% of the samples based on T47D-KBluc and MCF-7 bioassays, followed by 17 ss-estradiol, highlighting the importance of total steroid estrogen loading. This study demonstrates that the estrogenic activity of target chemicals was comparable to levels found in different countries worldwide. More intense wastewater treatment is required in areas of intensive agriculture in order to prevent adverse impacts on the ambient environment and aquatic ecosystems.
Chemical diversity of the essential oils of twenty populations of Tanacetum polycephalum Sch. Bip. from Iran.[Pubmed:29768020]
Nat Prod Res. 2018 May 16:1-4.
Chemical diversity of the essential oils of twenty wild populations of Tanacetum polycephalum Sch. Bip., was investigated. The aerial parts of T. polycephalum were collected at full flowering stage from West Azerbaijan Province of Iran, air-dried; hydrodistilled to produce essential oils. The essential oils were analyzed by GC-FID and GC-MS. A total of forty compounds were identified accounting for 96.4-99.9% of the total oils. The most principal compounds were cis-thujone (0-82.3%), trans-thujone (0-79.8%), Camphor (1.3-75.0%), 1,8-cineole (4.5-43.3%), borneol (1.0-36.2%) and bornyl acetate (0-26.8%). Hierarchical cluster analysis based on the percentages (>0.5%) of the essential oils components was carried out to determine the chemical diversity among the populations studied. The cluster analysis resulted in the identification of four main chemotypes namely: 'Camphor + 1,8-cineole', 'mixed', 'cis-thujone' and 'trans-thujone'.
Survey of selected personal care products in surface water of coral reefs in Kenting National Park, Taiwan.[Pubmed:29710583]
Sci Total Environ. 2018 Sep 1;635:1302-1307.
Kenting National Park (KNP) located in the Hengchun Peninsula in southern Taiwan is a popular tourist spot, annually attracting millions of visitors, who engage in water sport and amusement activities. In this region, sewage is directly discharged into the marine environment. In this study, the concentrations of five organic UV filters [benzophenone (BP), 2,4-dihydroxy benzophenone (BP-1), 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy benzophenone (BP-3), 2,2'-dihydroxy-4-methoxy benzophenone (BP-8), and 4-methylbenzylidene Camphor], five preservatives [methylparaben (MeP), ethylparaben, propylparaben (PrP), butylparaben, and benzylparaben], one disinfectant [triclosan (TCS)], and twenty-four detergent derivatives [nonylphenol (NP), nonylphenol ethoxylates (NP2EO-NP12EO), octylphenol (OP) and octylphenol ethoxylates OP2EO-OP12EO] were detected in seawater and river water samples collected from eight beaches in KNP and two major river estuaries in the Hengchun Peninsula. BP-3 was detected at all sampling sites and was higher in concentration than the other organic UV filters. The highest concentration of BP-3 was 1233ng/L collected from Wanlitong Beach. MeP and PrP were the main preservative components in seawater. The highest total content of preservative agents was 164ng/L collected from Houwan Beach. Moreover, NP was detected at all sampling sites, with the highest concentration found at Sail Rock Beach (26.5ng/L). The highest concentration of OP was 113ng/L in the Boli River estuary. The widespread use of personal care products (PCPs) has resulted in the release of their major ingredients into natural ecosystems. Therefore, the potential long-term effects of multi-PCPs at low concentration exposure to on the coral reef ecosystem in KNP must be considered and monitored.
Effect of Lavender (Lavandula angustifolia) Essential Oil on Acute Inflammatory Response.[Pubmed:29743918]
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Mar 18;2018:1413940.
Lavandula angustifolia is a plant of Lamiaceae family, with many therapeutic properties and biological activities, such as anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial activities. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of Lavandula angustifolia Mill. essential oil (LEO) on acute inflammatory response. LEO was analyzed using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) methods and showed predominance of 1,8-cineole (39.83%), borneol (22.63%), and Camphor (22.12%). LEO at concentrations of 0.5, 1, 3, and 10 mug/ml did not present in vitro cytotoxicity. Additionally, LEO did not stimulate the leukocyte chemotaxis in vitro. The LEO topical application at concentrations of 0.25, 0.5, and 1 mg/ear reduced edema formation, myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity, and nitric oxide (NO) production in croton oil-induced ear edema model. In carrageenan-induced paw edema model, LEO treatment at doses of 75, 100, and 250 mg/kg reduced edema formation, MPO activity, and NO production. In dextran-induced paw edema model, LEO at doses of 75 and 100 mg/kg reduced paw edema and MPO activity. In conclusion, LEO presented anti-inflammatory activity, and the mechanism proposed of LEO seems to be, at least in part, involving the participation of prostanoids, NO, proinflammatory cytokines, and histamine.


